What are tooth alveoli and where are they
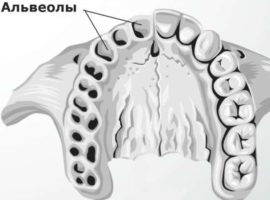
Alveoli in the mouth are called recesses in the jaw plates, which are located on the alveolar tooth processes. Normally, their number corresponds to the number of teeth - 16 on each jaw. In the process of human life, the structure and structure of the alveoli undergo individual changes associated with the natural processes of aging.
Content
The structure of the alveoli in the mouth
Alveola translates to cell. The term is used in pulmonology, dentistry and other medical industries. Alveoli have a spongy structure pierced by:
- a network of nerve endings providing their sensitivity;
- a network of blood vessels supplying the alveolar processes with nutrients.
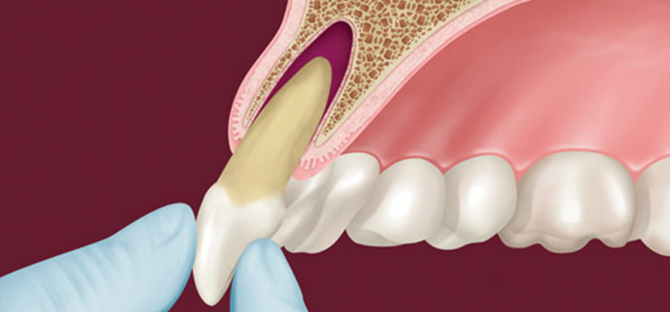
The walls of the dental alveoli are divided into internal, located closer to the throat, external, located on the side of the lips, and interdental. From the inside, the holes are divided by thin bone partitions, the location of which depends on the structure of the roots of the teeth. Their inner part is covered with a spongy plate, the size of which exactly corresponds to the size of the tooth located in the hole. The outer edge is closed by a cortical jaw plate.
The alveolar tissue is dominated by elastic fibers. The main function of the remaining cells is the constant restoration and renewal of bone tissue. The balance between the processes of its destruction and growth depends on them.
Bone tissue contains both organic and inorganic particles. Its main components are:
- proteoglycans;
- osteoclasts;
- collagen;
- osteocytes;
- osteoblasts.
In the event of tooth loss or extraction, the well overgrows quite quickly. A few weeks after extraction, the gums heal, and after a few months a new gingival cover is completely formed.
Alveolar Cell Functions
Alveoli are designed for reliable attachment of teeth to the jaw. Their structure provides a stable position of the teeth, eliminates their displacement and loss.
Thanks to dental alveoli, people can chew food without the risk that incisors, fangs and molars will loosen or fall out, unable to withstand the load.
Between the holes and the teeth are the connecting fibers of the periodontal tissue. Penetrating into the upper layers of the bone tissue of the tooth and the cell walls, periodontal tissues tightly bind them, which contributes to the correct position of the tooth in the hole. Additionally, periodontium acts as a shock absorber, which reduces the load on the dentition and slows down its destruction.
The formation of dental cells
The formation of alveoli begins in the perinatal period. When separating the tooth primordia from the jaw plate, bone bars are formed around them - the future walls of the alveoli. Fully cells form during teething.
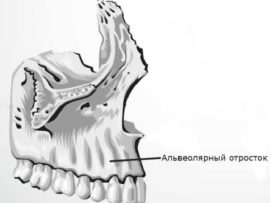
The formation of the alveolar process occurs in infancy under the influence of alveolar bone remodeling caused by tissue changes that accompany the eruption of milk incisors, canines and molars. Subsequently, the bone outgrowths fuse together and form the dimples surrounding each tooth.
In adulthood, the structure of the alveoli of the teeth undergoes reverse changes: atrophic processes are activated in the bone tissue and pulp, as a result, the elasticity of collagen fibers in the hole decreases. As the condition of the alveolar tissues worsens, the risk of loosening and displacement of incisors, canines and molars increases.
The rate of development of atrophic processes depends on the state of the body and bone tissue, the quality of adherence to oral hygiene and nutrition. The solution to the problem should be approached comprehensively: attention should be paid to all factors that may affect the state of the cells.
Dentists evaluate the condition of the alveolar holes based on the clarity of diction and how firmly the teeth are in the dentition.
What is the feature of the upper alveoli of teeth
Regardless of which jaw the alveoli are on, there are no significant differences in their structure. The peculiarity of the upper alveoli of the teeth lies only in the fact that their structure affects diction and speech intelligibility, which is due to the proximity of the alveolar ridge and palate.
Alveoli are susceptible to a number of dental diseases, the most dangerous of which is alveolitis. The disease can cause relaxation of the alveolar tissue, as a result of which the tooth can move, loose, or even fall out. If there is a suspicion that the teeth began to move, you should immediately contact dentistry.