Types of correct and incorrect bite of teeth in humans
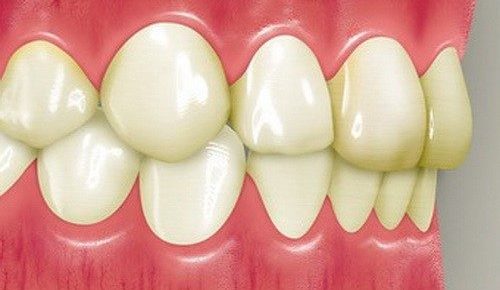
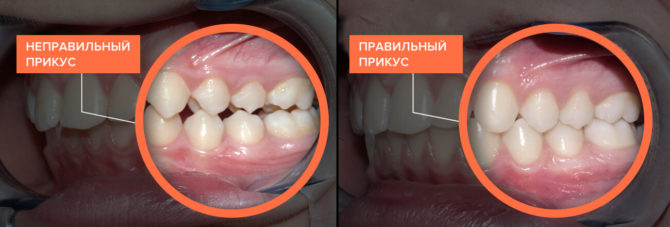
Bite affects the expression and symmetry of the oval of the face. It can cause both pride and the emergence of a mass of complexes. Non-specialists attribute bite problems to the category of aesthetic ones, in reality, beauty in this matter is secondary: health and psychological state come to the fore. The photo shows a bite of teeth that is close to ideal and rarely found in humans, but it is not the only correct one.
Content
What is a bite in dentistry and its types
Closing the jaws during chewing is called occlusion. In dentistry, the concept of central occlusion is distinguished - the position of the maximum compression of the upper and lower jaws. The way in which the dentition is located relative to each other is called a bite.
The inhabitants divide the bite into the correct and abnormal. Dentists believe that the correct bite of teeth in humans should meet only one requirement - to ensure the normal functioning of the dentition - therefore, even within the framework of the norm, bites are different.
Types of Right Bite
- Orthognathic bite. An ideal bite that provides aesthetic appeal, the most accurate diction and high-quality chewing of food. With such a bite, the upper row closes the lower one by 1/3 of the dental crown, there are not the slightest cracks and gaps when closing. The incisors are even, central located symmetrically.
- A direct bite in a person is characterized by closure along the cutting edges: the upper root elements do not completely overlap the lower ones. Externally, a direct bite is similar to orthognathic. but even a small defect in closure leads to an increase in the load on the cutting part of the teeth.
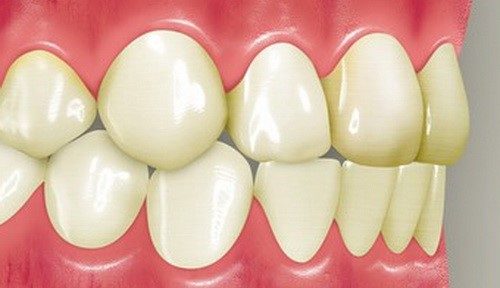
- Progenic. From an ideal orthognathic progenic bite can be distinguished by the characteristic, slightly forward position of the lower jaw.
- Bioprognatic. It is characterized by the regular shape of the jaw arches, symmetrical arrangement of teeth and good contact between the jaws. A distinctive feature is that the dentition is pathologically inclined outward to the lips, which is visually noticeable only when examining the jaw from the side.
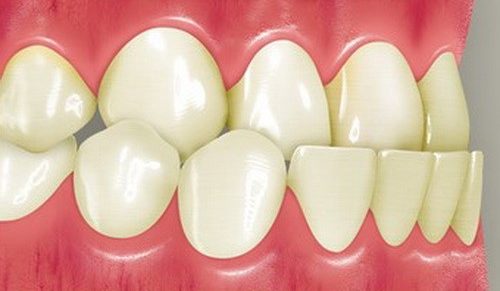
- Opistognathic. All teeth are tilted to the inside of the oral cavity. On visual examination of the opistognathic bite in front, the dentition looks too flat.
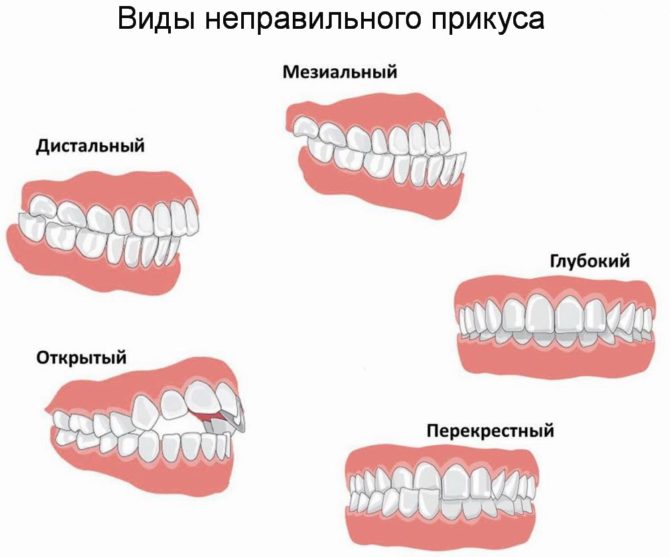
Types of malocclusion
- Prognathic (distal). Overdevelopment of the upper jaw is disproportionate to the development of the lower jaw arch. As a result, the upper jaw protrudes too far in relation to the lower jaw.
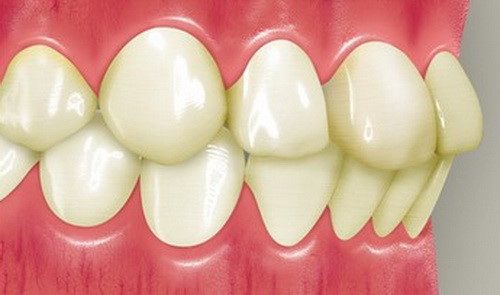
- Mesial (reverse bite). Deforms the oval of the face. Due to the fact that the lower jaw is significantly extended forward, the lower teeth overlap the upper.
- Open. Most of the teeth in both jaw rows do not close. Depending on the non-adjoining areas, frontal and lateral pathology is distinguished.
- Deep. The front teeth of the upper jaw row overlap the lower ones by more than half, which is fraught with constant trauma to the mucous membranes of the oral cavity.
- Cross (scissor bite).One arch of the dentition is severely underdeveloped, which provokes the intersection of the dentition diagonally. Usually accompanied by curvatures within the jaw arch itself, jagged teeth are often the result of premature extraction of milk teeth and improper eruption of molars. When chewing food, gums and palate are constantly injured.
- Reducing It is formed due to the friction of teeth against each other and their gradual abrasion (grinding of teeth) or after the loss of several teeth. The consequence is the rapid deterioration of the tissues of the teeth and the deterioration of their condition.
How to independently determine whether the bite is correct or not
To determine the closure parameters, dentists have established a number of characteristics. Evaluate the condition and correct closing of the jaws should be with a compressed static position of the teeth. If, after conducting a home examination, you consider the bite to be incorrect or doubt its specific characteristics, consult your dentist. The doctor will help to reliably find out if there is a maladjustment, establish all the characteristics of the bite and give appropriate recommendations.
Signs of proper closure
To find out whether the bite is correct or not, close the jaw and look at the location of the teeth. It should correspond to a number of parameters:
- The lower part of the face is symmetrical. The front teeth of the upper jaw overlap the lower by thirty percent of the entire height of the tooth.
- The upper and lower dentitions are in close contact, without forming gaps.
- The tooth elements of the same name (incisors of the upper and lower row, molars, premolars) are vertically symmetric to each other.
 The jaw arches differ in shape and size. The upper has a semi-oval shape and is slightly larger than the lower. The lower jaw arch is parabolic in shape and smaller. This structure provides a normal inclination of the dentition. The photo on the side shows that with a proper bite, the human tooth elements are located at an angle to the jaw: The upper ones are slightly inclined to the lip, and the lower ones inward. When the lower jaw moves back and forth, the premolars and molars of both jaws do not lose contact with each other.
The jaw arches differ in shape and size. The upper has a semi-oval shape and is slightly larger than the lower. The lower jaw arch is parabolic in shape and smaller. This structure provides a normal inclination of the dentition. The photo on the side shows that with a proper bite, the human tooth elements are located at an angle to the jaw: The upper ones are slightly inclined to the lip, and the lower ones inward. When the lower jaw moves back and forth, the premolars and molars of both jaws do not lose contact with each other.- In the rows there are no noticeable interdental spaces, or supercontact of the dentition.
Bite formation in children
Bite formation occurs from birth to adolescence. It is possible to identify the type of bite after changing all primary teeth to permanentHowever, the dentist may notice an incorrect bite at the stage of its formation.
The determining factors in the pathological development of the dentition are heredity and habits.
To form a normal bite in a child, the following conditions must be met:
- The development of tooth primordia begins even in the prenatal period, therefore, during pregnancy, a woman should monitor the metabolism and balance nutrition in such a way that a sufficient amount of micro and macro elements enter the body. If necessary, the doctor will prescribe the intake of synthesized vitamins.
- Artificial feeding from a bottle can cause the habit of tightening lips and lead to a violation of the natural swallowing reflex pattern. This may interfere with the correct closure of the tooth. Soothers and bottles should be used as little as possible. If this is not possible, you need to purchase an orthodontic dummy. Dentists consider breastfeeding the basis for the proper development and closure of teeth.
- A baby older than two years should be weaned as quickly as possible from sucking fingers and toys, as this also leads to malocclusion.
- It should develop a child’s habit of sleeping in a comfortable, but in the right position: without tipping the head. Breathing should be even, calm, through the nose, with a closed mouth. Timely treatment of inflammatory diseases of the respiratory system and their prevention is very important.
- Due attention should be paid to the quality of the child’s nutrition and the compliance of the diet with age norms.
Lack of minerals, prevalence of soft, homogenized food that is not appropriate for age, increases the risk of malocclusion.
- From the age of two, it is time to begin the formation of oral hygiene skills.
- The child should develop proper posture. Few parents pay attention to the spine in the context of occlusion, but each type of occlusion of a person’s teeth is directly related to the characteristic position of the spine and head.
A systematic visit to a pediatric orthodontist ensures timely identification of problems in the development of the dentition. The doctor will be able to explain which bite is considered correct for a specific age category, identify pathology at the initial stage, give preventive advice and prescribe the correct treatment. If the child has the first symptoms of malocclusion, the doctor will prescribe formative gymnastics and corrective massage or advise to establish trainers, a vestibular plate.
Preventing problems with occlusion is easier and faster than correcting the formed defects of the dentition. But in adults, the risk of abnormal bite formation remains. The reasons for this may be:
- maxillofacial injuries;
- gum disease;
- gross errors of the doctor during prosthetics;
- tooth loss.
What problems can cause malocclusion?
- Due to poor closing of the teeth, the quality of chewing food is impaired, which can provoke the development of gastrointestinal diseases.
- The load distribution on the teeth is incorrect, which leads to premature loss.
- Violations in the speech apparatus lead to problems with diction.
- There is a change in facial proportions, which is especially noticeable in the chin area. Perhaps the emergence of facial asymmetry, unaesthetic smile.
The back bite is visible on the overly protruding massive chin, the distal bite on the disproportionately small chin. Cross and lower bite provoke asymmetry, which is clearly visible from the side.
- Diseases of the teeth and gums due to deterioration of oral hygiene. It is difficult to properly clean all teeth from food, as a result of which pathogenic bacteria begin to accumulate on the enamel and in the interdental spaces. A frequent occurrence with an incorrect bite is involuntary gnashing of teeth, it can occur both in a dream and during wakefulness. The result of bruxism is loosening, premature grinding of teeth.
- Decreased quality of the respiratory system. Normally, breathing is carried out through the nose, with some types of anomalies, nasal breathing is difficult, and you have to breathe constantly through the mouth. Improper closure of teeth can increase the risk of night apnea.
Correction of malocclusion
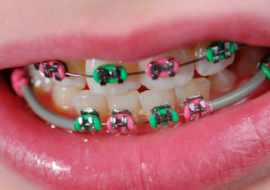 The determination of the correctness of the bite and its correction is carried out by the orthodontist dentist. Depending on the type of pathology, special plates, mouth guards or bracket systems can be assigned. The latter are preferable in the presence of additional problems: an uneven tooth, hypersensitivity of the mucous membranes.
The determination of the correctness of the bite and its correction is carried out by the orthodontist dentist. Depending on the type of pathology, special plates, mouth guards or bracket systems can be assigned. The latter are preferable in the presence of additional problems: an uneven tooth, hypersensitivity of the mucous membranes.
In most cases, you can do without surgical intervention. Even complex anomalies are successfully corrected; if necessary, dentists from regional clinics are referred for consultation with specialists in Moscow. Bite correction can take from one to three years, but on average it does not last longer than 18 months.