How many channels and nerves in the teeth, table
Dental canals are narrow cavities located inside the roots of teeth. Their number depends on the number of roots, but does not always equal it.
Content
Features of the structure of teeth, their roots and canals
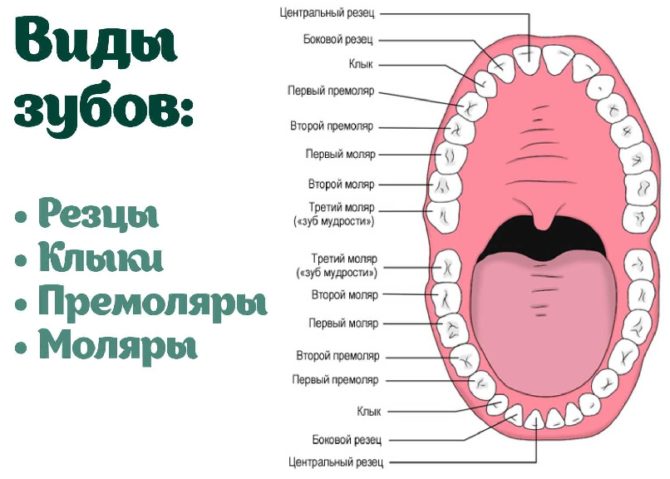
Two identical root dental systems do not exist, which is explained by the purely individual structure of human teeth. In addition, the root system of incisors, canines and molars is arranged in accordance with their purpose:
- Units and deuces (incisors) are needed to bite off food.
- Fours and fives (premolars) perform the initial chewing function.
- Sixes and sevens completely chop food.
Based on this, it becomes clear that the seventh tooth needs more nutrients than the fifth. It must be strong and hardy, therefore, it has a more developed channel system. Despite the fact that the 6th tooth on the lower jaw performs the same functions as the seventh, it usually has fewer canal passages. This is due to the fact that it is less chewing load.
For a detailed study of the structure of the dentition of a particular patient, an X-ray study is used.
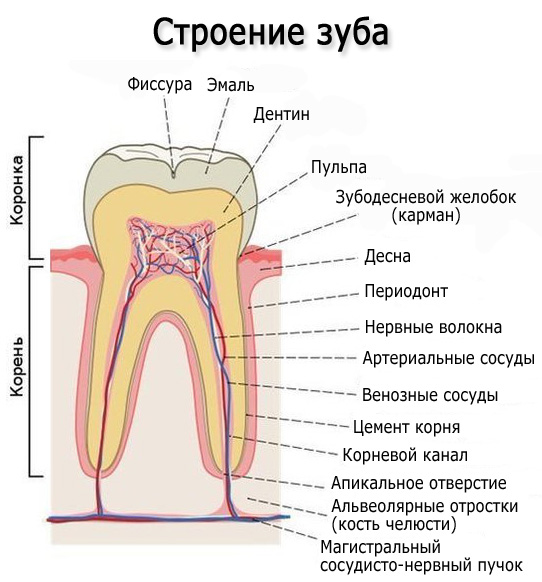
Tooth structure
Each dental unit consists of:
- crowns - a section above the gum;
- necks - the area between the crown and the root;
- root - the area under the gum.
Inside the crown is a pulp that passes into the root canals. At the end of the root there is a small apical opening through which the blood vessels and nerve endings pass, starting from the main neurovascular bundle and ending in the pulp.
When a pulp becomes inflamed in a person, it is necessary to clean not only the tissues affected by the infection, but also all the root canals, since they are “communicating vessels”. If at least one channel is left untreated, pathogenic microorganisms will continue to develop inside the dental unit, which will lead to its removal. That is why the doctor must know the exact number of channels in the tooth.
How many nerves in a person’s tooth
Thanks to the nerve, the tooth can respond to external stimuli. After removing the pulp and filling the canal, the dental unit loses its sensitivity, as it loses its nerve. But due to the removal of blood vessels, problems begin with its blood supply and mineralization. The crown becomes less durable and more prone to various chips and breaks. The enamel quickly darkens, and it cannot be whitened qualitatively even with strong chemical reagents.
Before removing the pulp, the patient is sent for x-ray to find out how many channels in the operated tooth: a person has one tooth nerve in a tooth, and there can be several channels. Such preparation allows for depulpation competently and quickly.
Types of Root Canals
There are several options for the structure of the dental canals:
- at the root there is one canal passage, which corresponds to one apical opening;
- in the root there are several channel branches that connect in the area of a single apical foramen;
- two different branched passages have one mouth and two apical openings;
- channel cavities in one root merge and diverge several times;
- three root canal passages leave one mouth, but have 3 different apical openings.
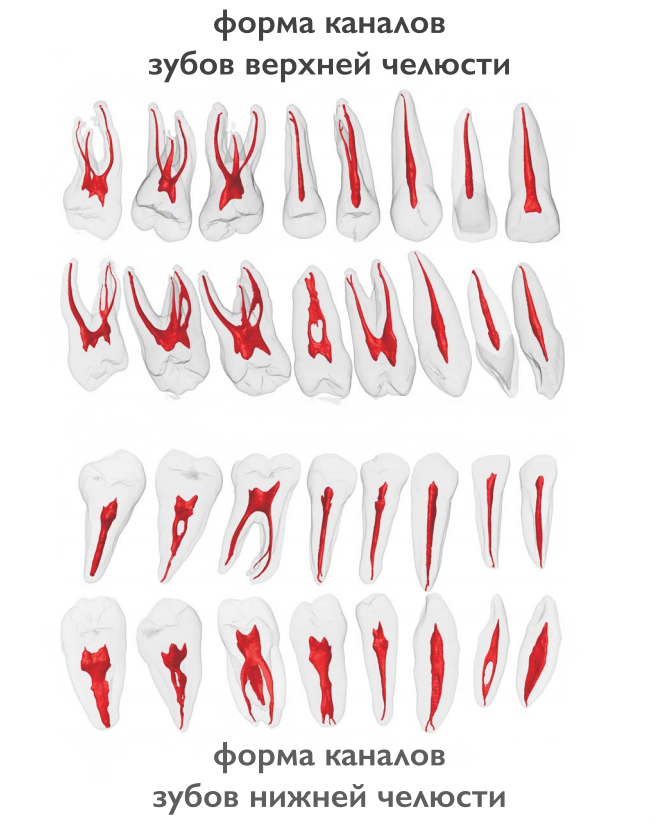
There can be as many channels as roots, but often their number is different.In one molar and premolar canals of several types can be present.
How many channels in a person’s teeth - table
According to statistics the number of channels depends on the depth of the tooth: the deeper it is located in the jaw, the more channels it has. This is due to the increased load on the molars located at the base of the dentition.
Typically, the teeth of the upper jaw have more channels. But such a pattern is not observed in all patients.
The table below presents the average statistical data on how many channels in the human teeth are above and below.
| Dental unit | The number of channel moves | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fangs | Top | 1 | ||
| Lower | 2 | |||
| Incisors | Top | 1 | ||
| Lower | Central | in most cases 1, less often 2 | ||
| Side | 1 or 2 (approximately the same probability) | |||
| Premolars | Top | First | most often 2, but sometimes the first premolars with 1 or 3 channels are found | |
| Second | in most cases 2, sometimes 1 or 3 | |||
| Lower | First | 1 or 2 | ||
| Second | 1 | |||
| Molars | Top | First | 3 or 4 with the same probability | |
| Second | in most cases 3, sometimes 4 | |||
| Third | around 5 | |||
| Lower | First | most often 3, sometimes 2 or 4 | ||
| Second | usually 3, but there are roots with 4 channels | |||
| Third | no more than 3 | |||
The number of channels in the teeth on the lower jaw
The teeth on the lower and upper jaw are significantly different from each other. This is partly due to the not quite uniform load and various functions. Usually in the teeth on the lower jaw there are fewer channels. But each case requires a detailed study. Therefore, at first the dentist sends the patient for an X-ray, and only then proceeds to open the crown and treat pulpitis.
It is impossible to start treatment of caries and pulpitis, based only on encyclopedic information, because:
- 6 the tooth of the lower jaw can have any number of channels - from 2 to 4;
- in the 5th tooth at the bottom there is usually only 1 canal, but in about 10% of patients there are fives with 2 canals;
- 4 teeth usually have only 1 canal, but in about a third of cases there are 2.
The eighth tooth on the lower jaw is the most “unpredictable”. How many channels in the wisdom tooth located below can be determined only with the help of radiography. Officially there are no more than 3, but during the treatment of caries, additional cavities usually open. It is because of the incomprehensible structure and inconvenient location that the eight is most often deleted.
It is impossible to treat a dental unit without studying the structure of its root and canal system. This can only aggravate the pathology and lead to complications.
The number of channels in the teeth on the upper jaw
The root system of the teeth of the upper jaw is more complex and branched. This explains the longer treatment of molars located at the top, and the frequency of repeated visits due to incompletely sanitized dental cavities.
Features in the structure of the canal tooth system in the upper jaw:
- 6 tooth of the upper jaw is most often three-channel. But sometimes there are four-channel first molars.
- The fourth and fifth teeth from above are most often two-channel, but sometimes single-channel and three-channel premolars are found.
- The 4 upper tooth usually has 2 channels, but sometimes premolars with 1 or 3 canal passages are found.
The “wise” eight on the upper jaw is a four-channel tooth. Extremely rare are the third molars with 5 channels. However, in dentistry, even cases of the presence of eight-channel wisdom teeth located above are recorded.
Canals in milk teeth
In milk teeth there are as many nerves as in molars - one. In addition, temporary units are similar to those that are constant in the structure of the root system. That is, such a milk tooth, like the upper six or the second molar, has a channel system similar to its molar counterpart - the second premolar.
Nerve endings perform standard functions:
- signal developing caries;
- responsible for the growth and development of the tooth;
- control the flow of water and nutrients to dentin and enamel.
The root canals of milk teeth are also treated and sealed, but the tactics of their treatment depend on how long they erupted. Permanent units are formed under temporary units, so treatment should be aimed at preserving them. Milk teeth can only be removed if the constants are ready for teething.
The roots of permanent incisors, fangs and molars do not form immediately, but within about 3 years. The treatment of permanent teeth with unformed roots is also different from the standard. The channels in the teeth of patients four, five, and six years old (depending on the rate of formation of the dentition) are filled with a special paste with calcium and fluorine, which helps close the roots.
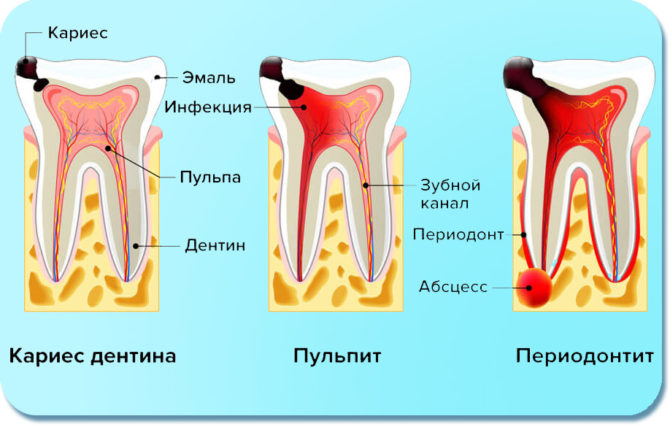
What diseases canals inflame
Root canals can become inflamed with the development of the following diseases:
- caries;
- pulpitis;
- periodontitis.
An accurate diagnosis of inflammation of the pulp and canals of the tooth can only be determined by the dentist after an X-ray diagnosis and visual examination of the oral cavity.
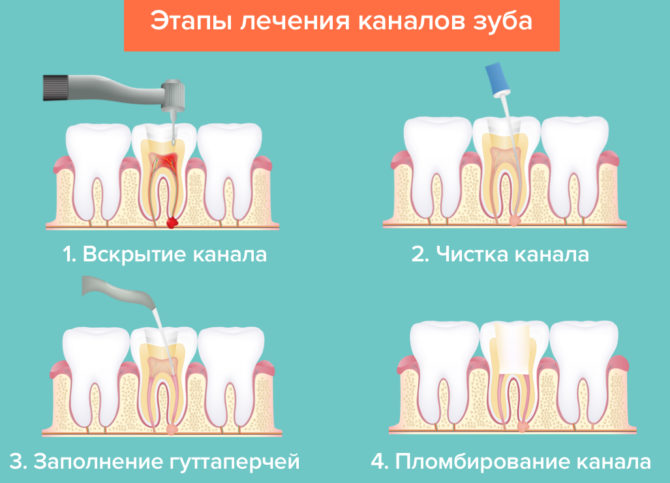
Canal treatment
The dental canal treatment regimen consists of several stages:
- First, access to the problem area is freed up: with the help of a special dental tool, the fillings or the part of the crown damaged by caries is removed.
- Then the contents of the pulp are extracted, and the channel passages are cleaned mechanically using antiseptic drugs.
- After that, the root is prepared for filling. At this point, the dentist can form the correct conical shape of the duct.
- Then the canals are carefully sealed. If milk teeth are treated, the dentist uses a special filling paste, which gradually dissolves as the root is resorbed.
- After that, a seal is installed on the crown.
The indicated treatment regimen is standard and does not depend on exactly how many channels in a diseased tooth. The main thing is that all dental canals are cleaned, treated with an antiseptic and carefully closed. With improper treatment, removal of the dental unit and a visit to the maxillary surgeon may be required.
The teeth are single-channel, two-channel, three-channel and even eight-channel. In case of inflammation of one of the passages, it is necessary to clean and fill not only it, but also all other channels, as the infection could penetrate into them.