Who is a dentist, periodontist, what does he do, features of treatment by a periodontist
Dentists are different, as are the problems that they fix. The therapist can save the patient from tooth decay, but if it is a deeper lesion of the teeth or gum disease, he will be referred to doctors with a narrow profile. One of those is a periodontist who treats diseases of the soft and hard tissues surrounding the tooth.
Content
What is periodontology
The oral cavity is in contact with a variety of substances, among which many are not the most useful, and microorganisms that like to settle in a warm and humid environment. Without proper hygiene, with a general weakening of the body and associated internal diseases, the teeth, gums and the mucous membranes surrounding them become easily vulnerable to infections and inflammation. Periodontology is just that branch of dentistry that studies the periodontal gingival tissue (periodontium), the bone tissue surrounding the tooth (periodontium) and their pathology.
Dentist-periodontist: what he does and in what cases
When destructive processes in the mouth go beyond caries and capture the surrounding space, patients are referred to a periodontist who treats these pathologies. The most common diseases that lead people to the periodontist's office are gingivitis, periodontitis, and periodontal disease.
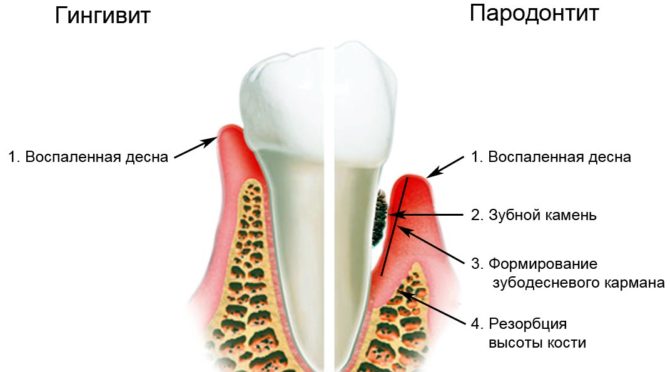
Gingivitis is an inflammation of the soft periodontal tissues. Such a diagnosis is made with bleeding, redness and soreness of the gums. The sooner periodontal treatment is started, the faster and more stable the result will be. Therefore, it is so important to consult a periodontist at the initial stage of gingivitis as soon as the gums begin to bleed while brushing your teeth. The doctor will make a debridement of the oral cavity and tell you how to quickly restore the normal state of the mucous membranes of the gums.
Periodontitis replaces untreated gingivitis and represents a lesion of deeper tissues, at which their modification begins under the influence of impaired blood flow. The main symptoms of the disease are exposure of the necks of the teeth and the appearance of periodontal pockets with purulent contents next to them. The person is haunted by bad breath, the inability to thoroughly chew food due to painful sensations and possible easy loosening of the teeth.
Periodontitis can also occur as a result of a number of diseases of the internal organs and systems, hormonal or immune failure. In any of these cases, simultaneously with the treatment of the underlying disease, the patient needs the help of a periodontist who can prevent further destruction of the gums.
Periodontal disease affects all tissues called periodontal disease, including bone, leading to gum deformity, exposure of tooth necks, loosening and loss of teeth. Few bring their jaws to such a deplorable state, but sometimes this happens, especially in the presence of internal diseases that directly affect the state of the oral cavity.
A specialist periodontist does everything to maximize the preservation of native teeth with the help of special designs. If the process of destruction of the dentition has already passed into the irreversible stage, this doctor will help prepare the gum for prosthetics.
Periodontist treating and brushing teeth
The dentist-periodontist begins to tidy the oral cavity with the procedure for removing plaque and tartar, since these deposits are the location of pathogenic microbes. For this, both mechanical and ultrasonic and other modern methods of cleaning are used in dentistry. If inflammation of the gum site is in the initial stage, professional brushing is enough to stop the pathological process. But only on condition that the patient will conscientiously carry out at home all the recommendations received at the doctor’s appointment.
With the development of the following stages of gingivitis after removal of deposits and dead tooth tissue, the doctor administers injectable anti-inflammatory drugs and, if necessary, prescribes a home course of antibiotics.
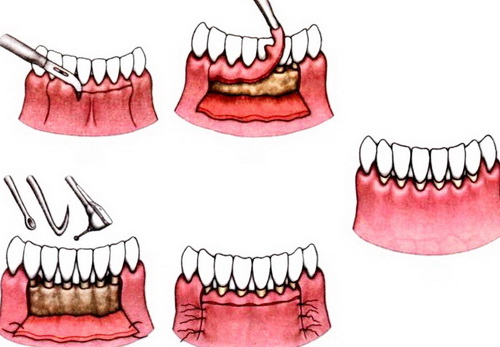
With the development of periodontitis in a patient, a periodontist flushes the formed periodontal pockets with antiseptic solutions, and then eliminates tooth mobility using methods such as patchwork, splinting and open curettage. These serious interventions require local anesthesia and subsequent restoration of the periodontium using physiotherapy or antibiotic therapy with the formation of abscesses and other suppurations.
With periodontal disease, tooth rescue tactics are developed based on x-ray examination and laboratory tests. In addition to the treatment methods that are used for periodontitis, at this severe, often irreversible stage of gum disease, treatment methods are used to stop the atrophy of the teeth. To activate their blood supply, patients are prescribed physiotherapy, a laser, ultrasound, and medications. If the dystrophic process is in an advanced stage, the tissues are enlarged surgically for subsequent prosthetics.
The result achieved after the clinical manipulations of the periodontist is fixed at home with the help of medications for oral administration, herbal rinses, therapeutic ointments and gels. In each case, the doctor periodontist develops an individual treatment course, taking into account the characteristics of the patient and the picture of the development of the disease.
Preventive recommendations
In addition to the diagnosis and treatment of diseases that have already arisen, the periodontist is engaged in routine examinations aimed at preventing them. If you regularly visit the dental clinic, you can prevent pathologies that require a long, painful and expensive treatment or prosthetics. And timely professional toothbrushing by a periodontist, according to the doctors themselves, would significantly reduce the flow of patients with severe periodontal inflammation.
Specialists in the field of periodontics advise the prevention of periodontal diseases not only in the clinic, but also at home. Such preventive measures include:
- regular and proper brushing of teeth and tongue;
- timely - every three months - replacement of the toothbrush and its correct selection, which is based on the stiffness of the bristles (it is undesirable to use a very stiff brush without a dentist)
- the use of dental floss, which cleans the spaces between the teeth;
- periodic rinsing of the mouth with decoctions of herbs with anti-inflammatory and firming effects: chamomile, yarrow, oak bark, sage;
- periodic gum massage.
And, most importantly, no self-medication. At the first suspicions of bleeding, swelling, itching in the gums, do not delay going to the doctor. Consultation of an experienced periodontist at this stage of the development of the disease will help to avoid serious complications and frequent visits to the clinic in the future.