Is it possible to treat teeth during pregnancy?
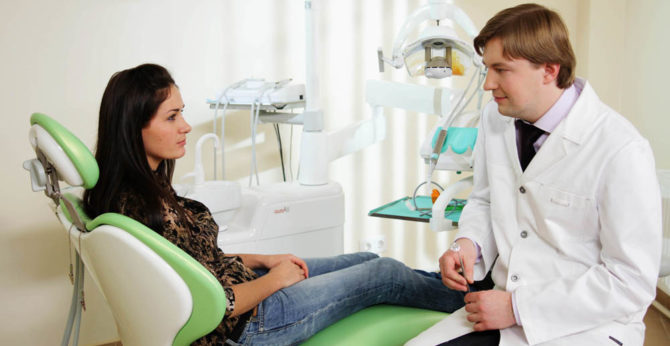
When carrying a child, many prohibitions arise, which in many respects change the lifestyle and attitude to one's own health. In this period You can not carry out many medical procedures and take drugs that are difficult for the body. But the answer to the question of whether it is possible to treat or remove teeth during pregnancy is not so straightforward, because it depends on many factors. In this case, the woman needs to listen to the recommendations of the dentist, and to the opinion of the gynecologist who leads her pregnancy.
Content
Risk factors
Dental procedures are different. Some of them are really urgent, among them - treatment or removal with infectious inflammation of the dental tissues. Those activities that are aimed at improving the appearance, for example, enamel bleaching, are not vital - their implementation can be postponed.
Almost any intervention in the state of the oral cavity carries risks: sometimes it is not possible to correctly perform the manipulations, and then additional therapy is required. Some people are allergic to anesthesia. That is why dental treatment during pregnancy has its own characteristics:
- Many drugs, especially antibiotics and anesthetics can cause harm to the fetus, penetrating his body through the placenta.
- Painkillers can narrow the lumen of the vessels, which affects the nutrition, respiration and development of the child.
- The expectant mother is experiencing stress, which in extreme cases can provoke spontaneous abortion or childbirth.
- Complications associated with the development of infection at the site of the treatment procedures adversely affect the well-being of the woman and her child.
These factors cause fear in expectant mothers, and they often refuse to visit the dentistry department, even if they suffer from severe toothache. And when carrying a baby, such problems arise extremely often. There are objective reasons for this:
- calcium and other vital elements go to the construction of the skeleton of the fetus;
- hormonal background is unstable, especially in the first and last weeks, and provokes inhibition of local and general immunity;
- toxicosis can lead to a lack of nutrients.
Indications and contraindications
In order to find out whether it is worthwhile to treat teeth during pregnancy and what week to start the procedure, in each individual case, an individual approach and specialist advice is needed. There are situations when it is impossible to refuse dental services even during the period of bearing the baby:
- Dental diseases, accompanied by the formation in the enamel, dentin and pulp of holes in which the infection can develop. Such are caries, pulpitis, periodontitis.
- Inflammatory diseases of the gums and oral mucosa, which also create a source of pathogenic microflora in the body. For example, gingivitis, periodontitis or infectious stomatitis.
- An abundance of tartar, under which the remains of food and bacteria accumulate. The procedure for their removal is painless and does not require the introduction of anesthetics.
The following dental services are contraindicated during pregnancy:
- Installation of implants. This process is very unpleasant, it requires anesthesia with an injection, the use of antibacterial drugs.
- Enamel whitening. The components of bleaching agents easily penetrate through the placental vessels into the fetal tissue.
- Removing wisdom teeth if their condition is not critical. This operation is more difficult to tolerate than the removal of other molars, anterior incisors or fangs, due to the special anatomical location and shape of the roots.
- General anesthesia. In fact, this is a state of artificial coma that can lead to the most tragic consequences.
The best time for treatment
The best option is pregnancy planning, in which the future mother and father undergo examinations in advance and perform the necessary procedures. But more often the opposite happens: health problems are detected after conception. Therefore, you have to decide at what time you can treat your teeth so that the harm to the fetus is the least.
 Given the stages of development of the child in the womb of the expectant mother, we can conclude that the most adverse effects occur in the early stages. In the first trimester, the baby's organs are laid, during the formation period they are most vulnerable. The use of toxic drugs can provoke congenital abnormalities of any organ.
Given the stages of development of the child in the womb of the expectant mother, we can conclude that the most adverse effects occur in the early stages. In the first trimester, the baby's organs are laid, during the formation period they are most vulnerable. The use of toxic drugs can provoke congenital abnormalities of any organ.
Going to the dentistry in the first three months is possible only for the purpose of prevention or performing simple manipulations without anesthesia: stones are allowed to be removed. If the woman is not very suspicious, you can treat your teeth during pregnancy from the early stages of caries, in which they do not use a painkiller injection.
In the second trimester, there are more favorable circumstances for visiting a dentist. The baby’s organs are formed, and the mother’s body does not experience such overloads as in the later stages. It is only necessary to decide how to treat teeth during pregnancy with the least risk.
In the third trimester, treatment of any diseases in the oral cavity is prohibited if there is no urgent need. For a woman, this is a lot of stress, which complements the excitement before childbirth. Stress can stimulate uterine contractions and the development of preterm labor.
The main nuances
Pregnant teeth are not treated as normal patients, since all risk factors must be considered. The approach to the procedures during this period is built on the basis of such nuances:
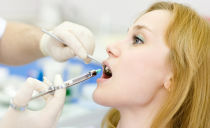
 First you need to solve the question of whether it is possible to do anesthesia during pregnancy. Anesthesia is better not to use, but only if the negative effect of stress does not exceed the harm from the drug. If you can not do without an anesthetic, you should choose one that does not contain adrenaline. It is this component that can negatively affect the placenta, because of which the baby will not receive a sufficient amount of nutrients. Anesthesia for dental treatment during pregnancy is possible with the use of Ultracain, Septanest or Primacain.
First you need to solve the question of whether it is possible to do anesthesia during pregnancy. Anesthesia is better not to use, but only if the negative effect of stress does not exceed the harm from the drug. If you can not do without an anesthetic, you should choose one that does not contain adrenaline. It is this component that can negatively affect the placenta, because of which the baby will not receive a sufficient amount of nutrients. Anesthesia for dental treatment during pregnancy is possible with the use of Ultracain, Septanest or Primacain.- If a woman is too sensitive and experiences stress even from almost painless manipulations, a slight dental anesthesia is provided, which is not prohibited during pregnancy and is characterized by the use of gels or sprays for the oral cavity.
- During pregnancy, the dentist should not use arsenic-containing medicines to remove the nerve.
- X-ray is a mandatory procedure in many situations, but x-ray irradiation harms the body, especially children. That is why on all patients, and especially pregnant women, they put on an apron in the X-ray room, which can delay the rays.
A woman must tell the dentist about her situation so that he can navigate the situation and choose the safest methods.
Choosing a clinic and doctor
The choice of a doctor and the dentistry department should be taken seriously. A good clinic is not available in every city, and in the countryside it is almost impossible to use high-quality dental services. But for the sake of the health of the unborn child, it is worth choosing more modern clinics that are in Moscow, St. Petersburg or other large cities where new equipment is used and safer anesthesia for pregnant women in need of dental treatment.
The doctor must be a qualified specialist. It is better to use the recommendations of friends or close relatives who have successfully received treatment with this doctor. A good dentist is able not only to inject qualitatively, anesthetize, remove and fill a tooth, he can find an individual approach to any patient.
You should definitely go to your doctor to carry out preventive examinations, carry out control of your cured teeth, and determine when to treat your teeth during pregnancy. Before carrying out the procedures, it is necessary to discuss with him the main points: whether the patient is able to endure discomfort or whether it is necessary to anesthetize with an injection, using Ultracain, Primacain or another relatively safe means.
The health of the oral cavity is very important for the whole organism, since this part of the body is associated with the respiratory and digestive organs, and indirectly with all other physiological systems. Should pregnant women treat their teeth, perform the procedure with or without anesthesia - the final decision must be made by the doctor, who can assess the condition of the tooth of the future mother and identify symptoms of diseases of the oral cavity.
In the presence of dental defects in the second trimester, a woman will have to be treated so that there is no foci of infection in her body. The procedures must be completed as early as possible so that they do not have to be postponed until the last weeks before the birth and urgently perform complex manipulations. Ignoring toothache during pregnancy can lead to serious consequences.