Wisdom teeth: structure, growth features, indications for removal
The so-called wisdom tooth is the eighth tooth in the lower and in the opposite jaw. It owes its beautiful name to teething periods: in some cases the first third molar begins to grow older than 20 years, which, according to popular opinion, coincides with the advent of life experience and wisdom.
Content
Location and structure
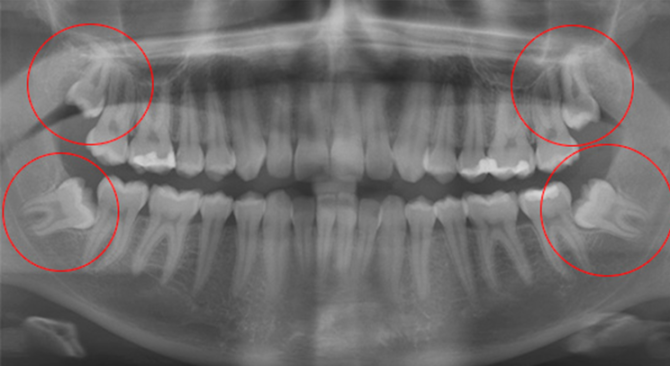
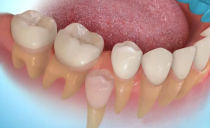
 In the dentition, the third molars occupy the most extreme position and close the dental arch. The absence of a visual examination does not yet say that a person does not have them: sometimes eights are in the thickness of the gums. This pathology is called retention, as it looks, look at the photos.
In the dentition, the third molars occupy the most extreme position and close the dental arch. The absence of a visual examination does not yet say that a person does not have them: sometimes eights are in the thickness of the gums. This pathology is called retention, as it looks, look at the photos.
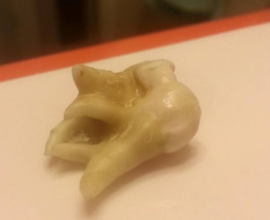
The structure of the wisdom tooth is no different from the structure of other molars: the neck, the root system (4-5 pieces), the crown. In case of impaired development, the roots can form a single conglomerate - a single-root tooth grows.
Features of the wisdom tooth
The main difference between the “extreme” tooth and the rest is the fact that in the light of recent studies it is considered not as a full-fledged organ, but as a rudiment. That is, during evolution, the function of the third molar was lost, and it gradually becomes unnecessary, so it does not grow at all in a certain percentage of people.
There are several important parameters that distinguish eighth teeth from others:
- They have no milk predecessors, which makes growth and teething difficult: there simply is no space left on the dental arch, which leads to various pathologies.
- Larger, in comparison with other molars, the number of roots: up to 5 pieces. The problem of its treatment or removal often depends on how many roots a wisdom tooth has.
- The roots of the eights are significantly curved, which creates difficulties in cleaning, treating canals.
- Relatively poor blood supply leads to early aging of wisdom teeth, which is accompanied by an increase in their brittleness, a greater tendency to caries. And this is despite the fact that the wisdom teeth are located eighth in a row on the upper and opposite jaws, due to which the load on them is minimal.
- A large number of pathological conditions are associated with eights: pericoronaritis, malocclusion, pathology of the masticatory muscles, and others.
All these facts indicate that there are much more negative consequences from the presence of third molars than positive effects. Many people learn what a wisdom tooth is only when it appears, and a person has to immediately contact a dentist for his treatment.
How to cut a wisdom tooth
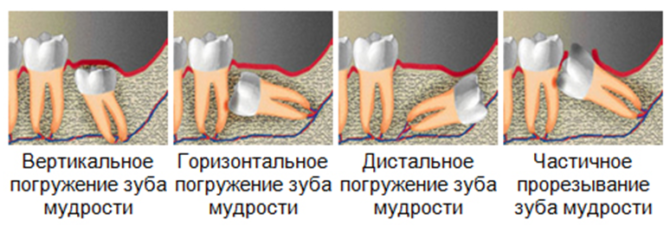
Problems with the Eights begin even when they did not have time to grow: at the stage of their eruption. Any deviation of the tooth from the vertical axis is a pathology called dystopia. Depending on the direction in which the wisdom tooth deviates, several of its types are distinguished:
- Medial tilt. The molar with its apex is directed towards the forward seven. The constant pressure of the teeth on each other leads to damage to the enamel, which increases the likelihood of tooth decay with subsequent destruction of the crowns.
- Distal tilt. With this pathology, a wise tooth is located with an inclination back, which is often accompanied by malocclusion - it becomes difficult to close the mouth, chronic pain syndrome is noted.
- Buccal tilt. The figure eight tilts or completely shifts toward the cheek.
- The language inclination. Incorrect tooth positioning is shifting towards the tongue.
In the last two cases, the danger lies in the chronic traumatic effect on the mucous membrane of the cheek or tongue. This can lead to the development of infectious and inflammatory diseases, and with a very long exposure, to cancer of the tongue.
In addition to deviations in growth, there are others. For example, a wise tooth may not cut through the gum at all or partially cut through, in which case it is called retinirovanny or poluretinirovanny. Sometimes the molar takes a normal position (vertical immersion) or lies on its side (horizontal position).
Teething wisdom is often accompanied by rather unpleasant symptoms from the jaw apparatus:
- a pulling pain appears due to the fact that the tooth has to grow through the already formed gum;
- sore throat, which occurs due to the irradiation of pain from the area of eruption;
- swelling and redness of the gums over the cutting tooth;
- local lymphadenitis - inflammation of the cervical and submandibular lymph nodes.
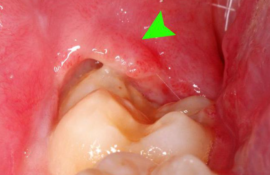
As eighth teething sometimes lasts for several years, symptoms can bother a person for quite some time. Incomplete eruption leads to the formation of a gingival hood - folds of the gums above the tooth. A feature of this formation is that it is often stuffed with food, which is very difficult to clean with a toothbrush. When seeds of food are seeded with microorganisms, a very unpleasant disease develops - pericoronaritis.
Reasons to Remove Wisdom Teeth
Specific indications for the removal of eights are determined by the dental surgeon. The following conditions require surgery:
- incorrect position of the tooth in the gum, accompanied by trauma to the cheek or tongue;
- damage to adjacent teeth - second premolars;
- the impossibility of a full treatment of eights, for example, with pulpitis;
- granulomas, cysts, pericoronitis;
- purulent diseases, which include osteomyelitis, abscess, phlegmon.
Timely removal of wisdom teeth avoids most of the problems associated with them. It is recommended to pull out the third molars in the so-called cold period, that is, when a person is not bothered by a toothache. During this period, without much discomfort, you can go through all the necessary examinations and remove the eights, while with inflammation, anesthesia does not work so well.
There are no absolute contraindications to the removal of wisdom teeth. There are only conditions in which it is recommended to carry out specific treatment and consult a doctor later. These include:
- inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity: gingivitis and stomatitis;
- a number of systemic infectious diseases: HIV infection, viral hepatitis;
- diseases of the heart and blood vessels in the stage of decompensation;
- mental disorders.
Pregnant women are not recommended to pull their teeth in the first and last trimesters. Since this procedure is recommended to be carried out under anesthesia, and in the first months the fetus should not be exposed to drugs - it is possible to provoke a miscarriage. In the later stages, pain during removal can provoke a premature birth.
How to remove a wisdom tooth
Like any medical intervention, removal begins with a visit to the doctor in dentistry. At the first contact with the patient, the doctor must evaluate his general condition and decide whether it is possible to pull out the tooth now or whether it is worth preparing a little.
An anamnesis is necessarily collected: the presence of chronic diseases that can complicate the course of the postoperative period is clarified. Such pathologies are diabetes mellitus, bronchial asthma, arterial hypertension.The doctor is simply obliged to ask the patient if he has allergic reactions.
At the next stage, you need to do an orthopantomogram. Panoramic x-ray gives the most clear picture, which shows how the eights are in relation to other teeth. The picture allows you to more accurately determine the treatment regimen.
The tooth removal procedure itself begins with anesthesia: the doctor injects a local anesthetic into the gum with a thin needle syringe. Then the patient waits 10-15 minutes until the medicine works. Further events develop in two ways:
1. Easy removal
Despite the fact that a person’s wisdom tooth is located in a relatively inaccessible place, the doctor grabs it with special forceps and removes it from the bone tissue by swinging and rotating it. An antiseptic is placed in the empty hole. A competent dentist will definitely stitch the hole.
Removing a simple category is often used when extracting teeth from the upper jaw.
2. Removing a complex category
This option is used in case of a refined or semi-reinforced tooth, as well as in case of severe destruction of the molar, when there is simply nothing to grab with forceps, and with a horizontal arrangement of eights. Difficulty may depend on how many roots a tooth has and how bent they are. The frequency of application of this method is higher when removing teeth from the lower jaw.
Extraction in this case may be accompanied by a cut of the gum, drilling a tooth with its roots or sawing. The operation can take up to 1.5–2 hours. After such an operation, an antiseptic is necessarily laid in the hole and sutures are applied.
What to do after removal
After a simple removal, you need to adhere to the general recommendations:
- remove the swab from the wound as soon as the root holes stop bleeding;
- try not to touch the hole with your tongue;
- apply cold to the cheek for 10-20 minutes;
- do not eat 3 hours after removal;
- abstain from smoking and drinking alcohol.
In complex cases, after an extensive operation to remove the tooth, it is recommended to take the following actions:
- Take pain medication. You can do this before the end of the local anesthesia, until there is pain in the gum bordering the torn tooth.
- Start taking antibiotics if the surrounding tissue has been inflamed. The specific drug and dosage is prescribed by the doctor.
After removing the wisdom tooth and any other you can not take aspirin, it can increase bleeding from the hole.