Gum disease in adults: photos, symptoms and treatment
Gum disease has happened at least once in the life of every adult, and we are assured by medical statistics and life experience. The causes of this trouble are various, the manifestations are painful. Know what gum disease is, the symptoms and treatment of each, timely response to alarming calls - means to protect yourself from serious complicationscapable of undermining the health of the whole organism.
Content
Diseases of the teeth and gums: names and photos
In order to detect an infection in time, you need to know how healthy gums look. Their tissue - periodontal - is flat, dense, without swelling, redness and does not bleed when brushing your teeth. The slightest discomfort in the mouth should alert and force a closer look at everything that surrounds the teeth.
Pain is the main symptom of gum infection.but far from the first. It is noticeable when the process is in full swing, and pathogens have thoroughly settled in soft, and sometimes in bone tissues. The first alarm signals appear much earlier:
- teeth begin to react sensitively to cold and hot, sour and sweet foods;
- an unusual smell or taste appears in the mouth;
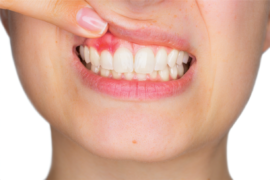
- the surface of the gums turns red or swells;
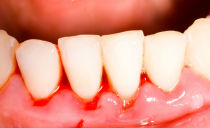
- bleeding occurs when brushing.
With these symptoms, the body signals that it already needs help. With such manifestations, the most common gum disease, gingivitis, can begin. If untreated, it can develop into more formidable diagnoses: periodontitis and periodontal disease.
Gingivitis: symptoms and course
Gingivitis is inflammation of the upper layer of the marginal part of the gums, that is, the area adjacent to one or more teeth. Interdental gingival papillae also get into the infection zone - as a result, their fibrous growth can begin.
According to dentists, the vast majority of cases of gingivitis could have been prevented by regularly getting rid of plaque, stone and food particles between the teeth. It is in these deposits that the infection causing the inflammatory process is based.
Other possible causes of gingivitis include:
- injuries to the jaw or individual teeth;
- hormonal disorders in the body;
- hereditary predisposition;
- viral and bacterial infections;
- vitamin deficiencies;
- autoimmune diseases;
- blood diseases;
- allergic reactions;
- taking certain medications;
- smoking and frequent drinking.
Four types of gingivitis are distinguished depending on the stage. The catarrhal form looks like mild irritation with a slight bleeding when cleaning and bad breath. It is at this stage that the easiest way to stop the infection from penetrating deep into the tissues.
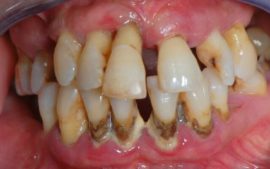
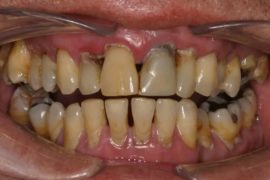
If treatment has not been started, the disease becomes hypertrophic with swelling and redness, compaction and contour of the gums, purulent discharge from the tooth pockets, and increased bleeding. Red gums in an adult are a typical pattern at this stage.
If you do not go to the doctor even at this stage, the disease becomes ulcerative-necrotic, which leads not only to painful destruction of the mucous membrane and gingival tissue, but also to general intoxication of the body, and may result in atrophy of the gum sections, which is noticeable by exposure of the teeth necks, and subsequently roots.This condition portends a deep and dangerous inflammation of the gums called periodontitis.
Periodontitis: symptoms and course
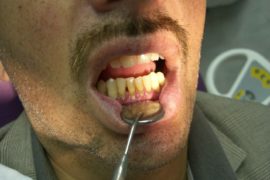
Unlike gingivitis, periodontitis affects not only the mucous membranes, but also the deeper layers - down to the bone tissue. A striking symptom of periodontitis is the formation of hard tartar and purulent discharge from under them.
Between the teeth and gums appear cavities, which are called periodontal pockets, further exposure of the necks occurs, tooth mobility and tooth displacement develop. These phenomena are accompanied by redness, a sharp putrid breath and severe pain, especially when biting solid food.
Periodontitis can be not only a complication of gingivitis. Various abnormalities in the structure of the jaw apparatus may contribute to its appearance: high density of teeth, hypertonicity of chewing muscles, irregular traumatic bite, high attachment of frenum.
Causes of the disease can also be serious malfunctions in the human body, which undermine the immune system:
- severe pathologies of internal organs;
- blood diseases;
- immunodeficiency conditions;
- infections
- diabetes.
In the initial stage of the disease, you can observe the red edges of the gums, soreness and bleeding. The exposed necks are initially white, but due to the loose structure of the dentin, they quickly stain and darken. An x-ray will show bone loss, and visually using a probe, the dentist will determine the depth of the bone pocket within 3.5 mm.
In the middle form of periodontitis, the pockets are increased to 5 mm, a person complains of spontaneous bleeding, displacement or loss of teeth, a sharp putrid odor from the mouth.
Open and inflamed dental pockets become the ideal habitat for pathogenic flora. Severe periodontitis can be one of the causes of periodontal disease, which destroys the mechanism created by nature to attach teeth to the jaws - the alveolar process.
Periodontal disease: symptoms and course
Due to its irreversibility and the severity of the consequences, a gum disease such as periodontal disease is called the most destructive. But at the same time, it is one of the rarest in dentistry. Despite the similarity of the name, this disease is very different from periodontitis: it is chronic, not inflammatory, and develops over many years.
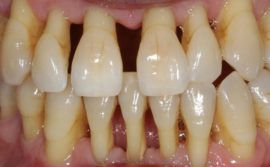
With periodontal disease, the gums do not look red, do not bleed and do not fester, there is no characteristic smell from the mouth and pain, the teeth can be white, without signs of caries. Destructive processes occur in the bone tissue, the rarefaction of which causes atrophy of the tooth holes. This leads to gum deformation and exposure of the roots of the teeth.
A person in this state reacts extremely painfully to any effects on the teeth, cannot chew food normally. At the final stage, the teeth become loose and may fall out. Until this moment, from the onset of gum disease, periodontal disease lasts an average of about 15 years.
Untreated gingivitis or periodontitis are not the only problems that can cause a gum disease such as periodontal disease. The causes may occur in a hereditary predisposition, as well as be a consequence of conditions and syndromes that cause metabolic disorders, hormonal and immune changes in the body:
- vegetovascular dystonia, atherosclerosis and other vascular diseases that violate the nutrition of tissues;
- hypertension;
- liver disease
- gastritis with high acidity;
- diabetes mellitus, hyperthyroidism and any other endocrine and metabolic disorders;
- immunodeficiencies and oncology;
- osteopenia.
Pregnancy is also a special condition in which hormonal failure, especially in the second and third trimesters, can cause serious problems with the gums.In turn, an infection in the oral cavity can complicate the course of pregnancy and harm the development of the child, therefore it must be eliminated.
The causes of gum inflammation can be anomalies in the development of wisdom teeth, as well as the consequences of errors in prosthetics and the installation of crowns.
Gum disease and treatment
In the treatment of periodontal diseases, a whole arsenal of potent medicines and folk remedies is used. Only a doctor can choose from them exactly what a specific patient needs, taking into account his individual characteristics.
Treatment with folk remedies
Instead of going to the doctor as soon as the gums reddened, many try to cope on their own at home and get serious complications. Folk remedies can indeed temporarily alleviate the symptoms, but do not eliminate the cause of the disease. It is progressing slowly at this time, and the patient sometimes comes to the doctor too late to preserve his or her native teeth.
For any gum disease in both adults and children treatment with folk remedies is permissible only as an auxiliary to professional. In periodontology, along with antibiotics and other medicines, rinses with decoctions of plants with anti-inflammatory properties are often prescribed. Their names are well known:
- chamomile;
- calendula;
- sage;
- Oak bark;
- lingonberry leaves;
- solutions of natural antiseptics: propolis, sea salt, tea tree oil.
Treatment at the dentist
Whatever the problems with the gums, treatment begins with the establishment and elimination of their causes. After a visual examination and x-ray examination, the doctor will determine the treatment regimen. It usually begins with the elimination of foci of infection, that is, removal of dental plaque, as well as soft plaque.
To treat gingivitis, after cleaning, the affected mucosa is treated with anti-inflammatory drugs and home rinses are prescribed with antiseptics. A ten-day treatment course is usually enough to stop the infection. The patient is also instructed on how to properly brush their teeth in the future in order to avoid relapse.
Periodontitis requires more serious treatment. After removing the deposits, the doctor cleans the gingival pockets and lays antiseptic preparations in the cavity. To restore the viability of the gums, they are massaged, lotions are made, rinses and physiotherapy are prescribed, if necessary, treated with a course of antibiotics.
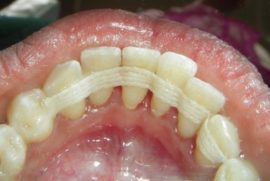 With pronounced tooth mobility, they are fixed with special tires (in the photo) for the period of bone tissue strengthening, in order to prevent its further injury.
With pronounced tooth mobility, they are fixed with special tires (in the photo) for the period of bone tissue strengthening, in order to prevent its further injury.
With periodontal disease, the treatment strategy depends on the degree of tissue damage, as well as on the underlying disease, which has become the trigger for degeneration. After rehabilitation of the oral cavity and removal of decayed teeth, antibacterial and anti-inflammatory therapy is carried out, the need for splinting, surgical intervention to restore the lost bone volume and further prosthetics is considered.
In addition to the traditional methods of treating gum disease in adults, modern periodontology also uses faster and less painful laser therapy and ultrasound.
Gum Disease Prevention
Any periodontist will confirm: The cause of most inflammations is a frivolous attitude towards oral hygiene. Diseases of the gums and teeth in adults are often interconnected, as in the photo, so treatment should be aimed at eliminating the symptoms and gingival inflammation, and dental disease. Although sometimes gingival pathology develops even without a hint of caries - as an independent phenomenon.
It is not too late to seek the help of a dentist even in the most deplorable situation.However, at advanced stages, treatment and especially prosthetics will be long, painful and costly. You can avoid this big problem by taking in the habit:
- regular and proper brushing with high-quality toothpaste;
- daily monitoring of the gums;
- timely treatment of caries, preventive examinations at the dentist every six months, professional cleaning if necessary;
- monitoring the condition of the whole organism, timely treatment of diseases of internal organs and infectious diseases;
- good nutrition with minimal consumption of tea, coffee, sweet soda and sugar in general;
- a healthy lifestyle without smoking and alcohol abuse, with reasonable physical exertion and hardening that strengthen the body.
For preventive purposes, folk remedies are just appropriate - rinsing with organic antiseptics, the use of herbal teas, which, by the way, can successfully replace black tea and coffee. Having become part of the lifestyle, these simple habits will help a person avoid many diseases of the teeth and gums.