Maxillary sinus cyst: causes, symptoms, treatment and removal
The maxillary sinus cyst is a neoplasm that can occur due to a violation of the glands that produce nasal mucus. Treatment of cysts of the right and left maxillary sinus should preferably be started at an early stage, otherwise the development of serious complications cannot be avoided.
Content
Features of the course of the disease
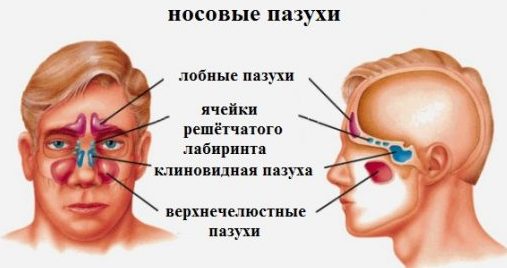
The maxillary (maxillary) sinuses are covered with a membrane containing a large number of excretory glands. These glands produce mucus that performs a protective function. If the duct of the gland closes, it will begin to fill with its own product, as a result of which it will stretch and take on the shape of a ball - this is a cyst.
The danger of this condition is that, significantly increasing in size, the neoplasm can provoke a violation of the respiratory function and the development of severe complications affecting the brain.
Most often, a cyst occurs in the left maxillary sinus. However, pathology can develop even in two sinuses at the same time.
The disease can manifest itself with a number of symptoms or may be asymptomatic. A person may not even be aware of what is happening in his body. Gradually, the condition worsens, which negatively affects health. Pathology can provoke the development of diseases of vital organs, including the brain.
Reasons for the development of maxillary sinus cyst
Blockage of the gland, leading to the accumulation of mucus in the maxillary sinus, can occur if there are the following predisposing factors:
- chronic diseases of the ENT organs;
- congenital or acquired anatomical features in the structure of the nasal septum, in which the normal air flow is disturbed, or the lining of the sinuses is poorly supplied with blood;
- allergic reactions;
- weakened immunity;
- diseases of the oral cavity;
- respiratory infections leading to the accumulation of lymphatic fluid in the vessels;
- hereditary predisposition.
Varieties of cysts
In medical science, the cyst of the maxillary sinus is classified according to several criteria: according to the secreted content, origin (development mechanism), place of formation. When prescribing a course of treatment, the doctor takes into account these characteristics.
| Cyst classification criteria | Types of Cysts |
|---|---|
| By content |
|
| At the place of education |
|
| By origin |
|
In addition, the neoplasm can be true and false, innate and acquired, single and plural.
Retention cyst
Retention cysts form when the patency of the ducts of the glands that cover the lining of the sinuses is impaired. When cysts form, the glands do not stop working and continue to produce mucus. Gradually, the formation increases, and its walls become thinner.Over time, it expands so much that it fills the entire space of the sinus, injuring its walls and closing the lumen.
If a neoplasm is detected, surgery is performed, during which it is removed.
To prevent the formation of a maxillary sinus retention cyst, it is necessary to monitor the condition of the nose and treat rhinitis in time. In addition, edema, scars on the mucous membranes of the upper respiratory tract and blockage of the ducts of the glands can lead to the development of pathology.
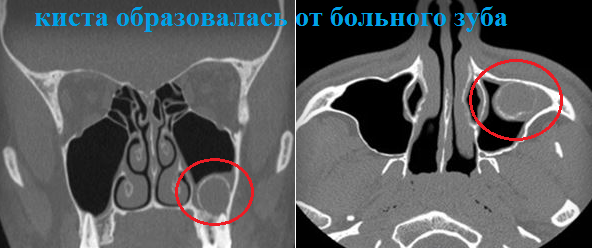
Odontogenic maxillary sinus cyst
Odontogenic cyst occurs when purulent contents accumulate in the root zone of an inflamed tooth. Over time, pus penetrates through the jaw bone into the lower part of the sinus.
The formation of odontogenic neoplasm can be caused by such types of tooth inflammation:
- near-root - occurs due to the development of pulpitis, as well as in situations where the entire root canal is involved in the inflammatory process of a bacterial nature;
- radicular - formed at the root of a tooth affected by caries;
- follicular - more often diagnosed in childhood and adolescence, when not yet cut tooth inflames.
To reduce the risk of the formation of an odontogenic maxillary sinus cyst, carefully monitor the condition of the oral cavity and treat diseased teeth.
Symptoms of maxillary sinus cyst formation
Symptoms characteristic of a maxillary sinus cyst do not always occur. Usually, a pathological neoplasm has formed in the nasal cavity that requires immediate treatment, the following symptoms indicate:
- difficulty breathing
- headaches, aggravated by a sharp change in weather and giving away to any part of the head: nape, forehead, temple;
- dizziness, fatigue, a feeling of irritability;
- insomnia, lack of appetite;
- pain in the nose, aggravated by jumps in atmospheric pressure;
- the allocation of a non-standard amount of fluid from one nostril.
The size of the neoplasm does not affect the intensity of the symptoms. Symptoms depend on the nature of the course and neglect of the disease, the individual characteristics of the human body.
Diagnostic Methods
In the presence of symptoms that directly or indirectly indicate congestion of the maxillary sinuses, a comprehensive examination of the ENT organs is carried out. During the examination of the oral cavity, the doctor draws attention to the condition of the teeth, especially the incisors and premolars of the upper jaw on the left and right sides.
The following diagnostic methods are used to make an accurate diagnosis for suspected cysts:
| Diagnostic method | Short description |
|---|---|
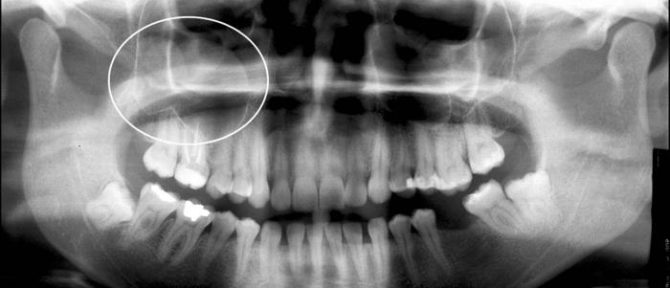
| Roentgenography | A contrast agent is introduced into the right and left RFPs. Using the image in the image, it is possible to diagnose a neoplasm of even the smallest size. |
| Orthopantomogram | Using a high-quality image made on digital equipment, it is possible to reliably determine the size and place of formation of the cystic sac (right or left, bottom or top). |
| Maxillary sinus puncture | Puncture is a puncture of the RF by means of a special needle. By the nature of the content, an accurate diagnosis is made, and further measures are planned to eliminate the symptoms of pathology. |
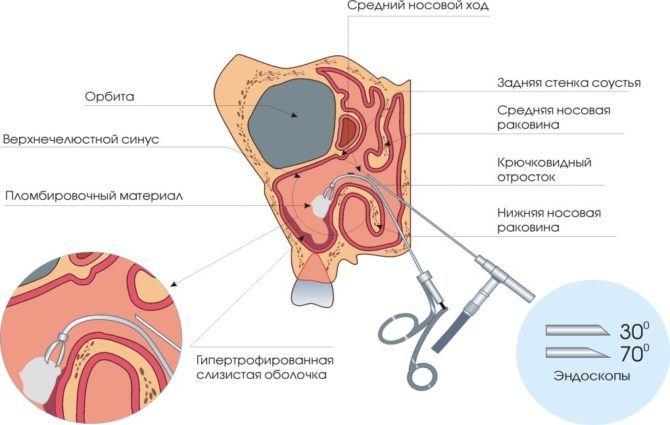
| Endoscopic examination | One of the most informative methods for the diagnosis of cystic formations. The affected sinus is examined in detail through an endoscope. Features in its structure and functioning are revealed, the complexity of the pathology is diagnosed. |
| Cone Beam Tomography | Allows you to detect any pathological process localized in the upper region of the face. |
Treatment and removal of maxillary sinus cyst
Treatment of a cyst of the left maxillary sinus consists in surgical intervention and the elimination of factors that led to the formation of the neoplasm. The treatment of cysts in the right sinus of the nose is based on the same principle.
Neither medication, nor physiotherapy, nor warming up will help get rid of cystic formation. Such methods of therapy can only worsen the condition, as they increase the risk of developing pathological nasal congestion.
The tactics of therapy and surgery to remove the maxillary sinus cyst depends only on the cause of the formation of the neoplasm, its size does not affect the course of treatment. The indication for surgical intervention is not the size of the neoplasm, but the patient’s presence of complications or complaints of poor health.
Almost all clinics in Moscow and other large cities of the Russian Federation are equipped with the equipment necessary for the painless treatment of cysts of the right and left maxillary sinuses. The average cost of an operation in private clinics varies from 35 to 50 thousand rubles.
Cyst Removal Methods
There are several methods for performing an operation to remove a cyst from the maxillary sinus:
- Endoscopic method. A tumor can be removed with an endoscope. Incisions are not made during surgery.
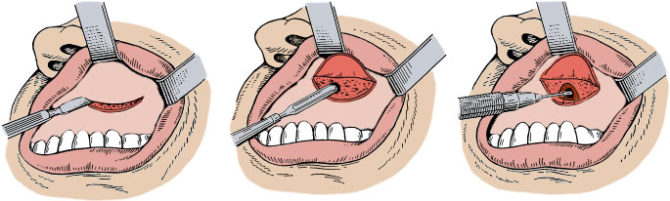
- Caldwell-Luc Technique. The neoplasm is removed by cutting. During the procedure, an oblique incision of the soft tissues from the gingival side is made, and trepanation of the jaw is performed. The method is rarely used.
- Denker's method. It is used in rare cases and consists in trepanation of the jaw. The procedure is performed under general anesthesia, is painful and has many shortcomings, the main one is a long recovery period after surgery.
Preventive actions
The formation of cysts in both maxillary sinuses can be avoided if you monitor your health and treat diseases of ENT organs in time. You need to carefully care for your teeth and regularly visit the dentist, even if there is no serious cause for concern. Dental diseases such as periodontal disease and caries are especially dangerous.
It is necessary to monitor the state of the ENT organs. In the presence of sinusitis, rhinitis and other inflammatory processes in the paranasal or nasal cavities, systematic observation by a specialist is necessary.
The risk of cysts in the cfp is increased in the presence of complications that developed after viral respiratory diseases.
When the first symptoms appear, indicating the formation of a cystic formation, it is urgent to consult a doctor to prescribe a therapeutic course and conduct surgery. Folk remedies can only be used for therapeutic purposes and are not able to cope with the disease.