Causes, Symptoms and Treatment of Trigeminal Neuralgia
Scientists call this disease a pain tic of Trousseau and Fosergil's disease, it is known to patients as trigeminal neuralgia. You can independently determine the pathology by paroxysmal, extremely intense pain in the eyes, forehead, and jaw. If this distinguishing feature is found, you should immediately contact a medical institution, even a single symptom that arises - an occasion to begin treatment of trigeminal neuralgia as soon as possible.
Content
- Anatomical structure
- Causes of trigeminal neuralgia
- Risk group and features of the course of the disease
- Symptoms of trigeminal neuralgia of the face
- Symptoms of an advanced case of neuralgia
- Diagnostics
- Methods of treating Fosergil's disease
- Drug treatment
- Surgery
- Physiotherapeutic treatment
- Preventative measures
- Possible complications
Anatomical structure
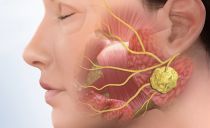
The fifth pair of cranial nerves is called trigeminal, they are located symmetrically: on the right and left sides of the face. The function of the trigeminal nerve is the innervation of a number of facial muscles. It consists of three main branches, including many smaller branches. The path of the branches to the innervated areas passes through channels in the bones of the skull, where nerve fibers can undergo compression.
Causes of trigeminal neuralgia
Identifying the origin of neuralgia allows you to objectively evaluate the clinical picture and cure the patient quickly and with minimal strain on the body. The most common causes of trigeminal neuralgia are considered by doctors:
- vascular pathologies, among which are changes and anomalies in the development of blood vessels or their location;
- deterioration of blood flow due to hypothermia of the face;
- inflammatory processes in the branching zone, which can be caused by otorhinolaryngological, ocular and dental problems;
- injuries to the face and skull;
- violation of metabolic processes in the body;
- chronic viral diseases;
- congenital narrowness of the channels along the branches;
- any tumors whose localization occurs in the trigeminal zone;
- multiple sclerosis;
- inflammation of an allergic nature;
- stem stroke;
- psychogenic factors.
Risk group and features of the course of the disease
Trigeminal neuralgia is a very common cause of contacting a neurologist. The reason for this is a large number of factors that provoke the development of the disease, pain attacks of extremely high intensity and long-term therapy of advanced cases. The number of people at risk for trigeminal neuralgia is quite large.
Middle-aged people are more often affected by neuritis, mainly the disease manifests itself at the age of 40 to 50 years. The percentage of patients suffering from trigeminal neuralgia among women is significantly higher than among the male part. An important determining factor is the presence of chronic diseases that contribute to the development of neuralgia in the patient's history.
In seventy percent of cases, the right side is affected, both sides are extremely rarely affected by the disease. The course of the pathology is cyclical: the acute period is replaced by remission. Peaks of exacerbations occur in autumn and spring.
Symptoms of trigeminal neuralgia of the face
Fosergil's disease has obvious symptoms, obvious even to a lay person.However, how to effectively treat trigeminal neuralgia can only be determined by a doctor that takes into account the entire clinical picture.
Symptoms of a pain tic of Trousseau are divided into three groups that manifest themselves in stages: at first, only pain, then motor and reflex disturbances, and then vegetative-trophic disturbances. In the third stage, not only the symptoms undergo changes, but also the medical prognosis of complete healing worsens significantly.
Nature of pain
The first sign of a pain tic of Trousseau is intense pain attacks in the innervation zone of the affected branch. The pain is burning and excruciating, characterized by extreme intensity, it is paroxysmal, it occurs very sharply.
Patients compare a pain attack with neuralgia with a backache and the passage of electric current. Paroxysm lasts from a few seconds to several minutes. At the time of exacerbation, the frequency of seizures is very high.
According to a scientific article on the study of the disease, a pain attack with neuralgia can occur up to three hundred times a day.
Pain localization
The pain can be localized both in the zone of innervation of the whole nerve, and in one of its branches. A characteristic feature is that the pain spreads from one branch to another, and over time, the entire affected half of the face is involved. The longer the disease lasts without medical intervention, the more likely it becomes to damage the whole nerve and the spread of the pathological process to other branches.
With lesions of the ocular branch, the pain concentrates in the forehead and eye. With a disease of the maxillary branch, the pain spreads along the upper and middle parts of the face. Lesions of the mandibular nerve can cause pain in the masticatory muscles, lower jaw and wings of the nose. Sometimes echoes of pain are felt in the neck, temple and neck.
It happens that the pain is clearly concentrated in the area of a particular tooth, which is why the dentist often becomes the first specialist to make an appointment with a patient with neuralgia. When examining a tooth, the cause of pain is not revealed, if treatment is nevertheless carried out, it does not bring any effect or relief. The main task of the dentist in this situation is to send the patient for a consultation with a neurologist.
Provocation of pain
Pain paroxysm can be triggered by touching or clicking on the exit points of the nerve branches in the face and trigger zones. Everyday activities, such as chewing and brushing teeth, washing, shaving, even blowing in the wind, speech and laughter, can also cause an attack of pain. At the moment when an attack occurs, the patient often freezes, fearing to make the slightest movement, and slightly rubs the pain zone.
Movement and reflex disorders
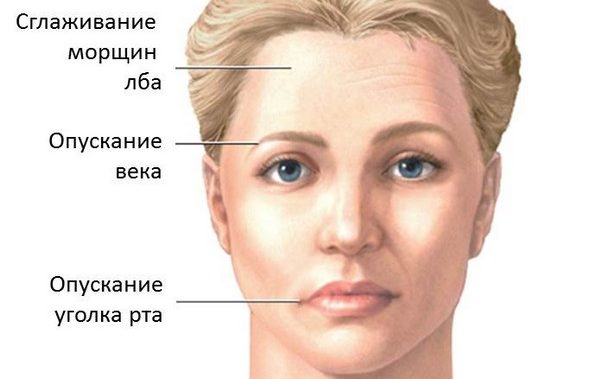
- Spasm of the facial muscles. At the time of paroxysm, the muscles of the face involuntarily contract. Reflex disorders begin with blepharospasm or trismus, with the course of the disease spasms can be transmitted to the entire half of the face.
- Degradation of the superciliary, corneal and mandibular reflexes. A disorder is detected during examination by a neurologist.
Vegetative-trophic symptoms
At the initial stage of the disease, vegetative-trophic symptoms are practically absent, or the signs appear exclusively during the attack. Only the occurrence of painful paroxysm, local redness or pallor of the skin is characteristic. The secretion of the glands changes, a runny nose, lacrimation and salivation may appear.
With the progression of the disease, the vegetative-trophic symptoms of trigeminal neuralgia also intensify, and therefore a longer and more extensive treatment is required.
Symptoms of an advanced case of neuralgia
In advanced cases, a number of symptoms are added.Eliminating the cause of the disease no longer leads to recovery in one hundred percent of cases; complex treatment methods are required.
Signs of advanced trigeminal neuralgia are:
- Swelling of the face, loss of eyelashes, a change in the secretion of skin glands.
- The spread of pain to other parts of the face.
- The appearance of pain from the slightest pressing on any part of the face from the affected side.
- The occurrence of pain on any stimuli, up to a loud sound or bright light, even a reminder of a previous attack can be a contributing factor.
- The permanent nature of the pain.
- Change in localization and duration of pain attacks.
- Strengthening of vegetative-trophic symptoms.
Diagnostics
Correct treatment of trigeminal neuralgia requires the identification of all symptoms, they will help determine the stage and specificity of the course of the disease. Of paramount importance in the diagnosis is the history and questioning of the patient. The examination helps to determine the localization of the decrease and increase in skin sensitivity on the face, to identify possible degradation of muscle reflexes.
During the period of remission of the disease, if it is at an early stage, the pathology is not always noticeable during examination. To detect the cause of neuritis, MRI can be recommended to the patient, however, even the most modern tomography performed in Moscow does not always show pathology. Patients with symptoms of neuralgia are advised to immediately visit a neurologist.
Methods of treating Fosergil's disease
The treatment of trigeminal neuralgia is performed by the following methods, mainly used in complex:
- physiotherapy;
- prescribing drugs;
- surgical intervention.
Attempts to be cured by all kinds of folk remedies are not only ineffective for neuralgia, but also very dangerous. The main risk is that time will be lost and skilled assistance will not be provided on time.
Drug treatment
The prescription of drug treatment is justified when the cause of trigeminal neuralgia is vascular pathology or a tumor. Therapy involves:
- Antiepileptic drugs.
- Painkillers or injections.
- Muscle relaxants.
- Antiviral agents.
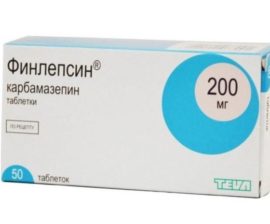 The main drug in most cases becomes an anticonvulsant drug based on carbamazepine. Vitamin-based adjunctive therapy has proven itself well. In addition, they are used for treatment.
The main drug in most cases becomes an anticonvulsant drug based on carbamazepine. Vitamin-based adjunctive therapy has proven itself well. In addition, they are used for treatment.
- Valproic acid.
- Pregabalin.
- Baclofen.
- Gabapentin.
- Lamotrigine.
The doctor selects the optimal medications and dosages individually. The main objectives of therapy are to relieve pain attacks, eliminate the causes of the disease, and prevent complications. Treatment of trigeminal neuralgia with medications takes about six months with a gradual decrease in dosage.
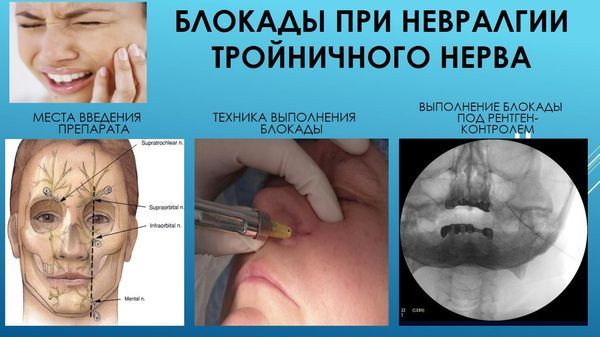
Surgery
It is better to perform surgery in the early stages of the disease, this increases the likelihood of complete healing. To date, two main groups of operations are used to treat neuralgia. One is effective in cases where it is necessary to correct the position of the artery, or if neuralgia is provoked by compression of the nerve branch by any anatomical formation. The second is used if neuralgia was treated with conservative methods, and therapy did not give positive results.
The type of surgical intervention varies depending on the pathology that caused the neuralgia:
- If the cause of the compression is vascular pathology, the microvascular decompression method is used. This is a microsurgical operation in which the nerve and vessel are separated. The effectiveness of the method is very high, but it must be taken into account that the operation is traumatic.
- If the cause is the development of the tumor process, the tumor is first removed, and after that treatment is prescribed.
- If it is necessary to remove pain impulse along the nerve fiber, percutaneous balloon compression is performed.
In some cases, destruction of the nerve is necessary. The following methods are used for this:
- Non-invasive ionizing radiation. Used only in the early stages of the disease.
- Stereotactic percutaneous rhizotomy. The root of the nerve is destroyed under the influence of an electric current, which is supplied to the damaged area using the thinnest electrode.
- Radiofrequency ablation, in which nerve fibers are destroyed by high temperature.
- Glycerin injections in the branching nerve.
Physiotherapeutic treatment
Physiotherapeutic procedures are prescribed to speedy relieve pain symptoms and complete healing in tandem with drug therapy. After the start of treatment, surgical or physiotherapeutic, the pain does not recede instantly. The period of complete disappearance of paroxysm is individual and due to the vastness of the process, the duration of the disease, therefore, the doctor additionally prescribes painkillers.
The most effective in the treatment of pain tic of Trousseau show the procedure:
- laser therapy;
- diadynamic currents;
- electrophoresis using novocaine;
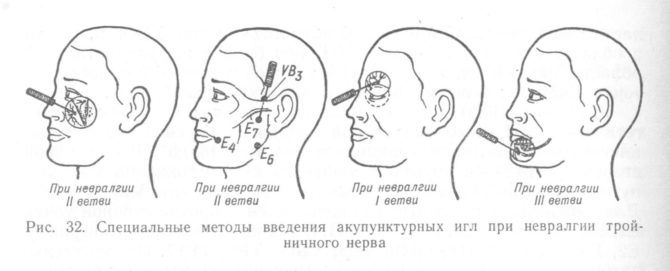
- acupuncture;
- phonophoresis using hydrocortisone.
Preventative measures
It is impossible to avoid all potentially dangerous factors, especially considering that some of the causes are congenital: narrow channels, pathologies in the structure and arrangement of blood vessels. However, you can reduce the risk of a disease by eliminating several provoking factors. As a primary prevention should:
- avoid hypothermia of the face and head;
- timely treat diseases that can give rise to trigeminal neuralgia;
- avoid head injuries.
Doctors consider the timely treatment of trigeminal diseases to be a complete secondary prevention, therefore, with the first symptoms of pathology, you should immediately contact the clinic.
Possible complications
Trigeminal neuralgia cannot be triggered, Fosergil disease causes complications:
- paresis of the facial muscles;
- hearing loss;
- irreversible damage to the nervous system, up to inflammation in the brain.
It is impossible to categorically relieve pain with analgesics and hopes that neuralgia will pass by itself. This is a serious neuralgic disease that should only be treated by a doctor. The sooner the patient seeks help, the more successful and less prolonged the therapy will be.