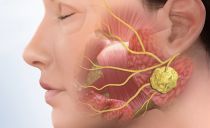
Facial neuritis: causes, symptoms and treatment
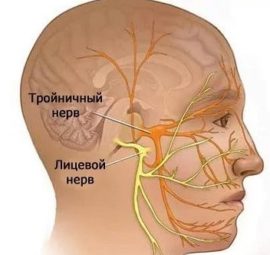
The facial nerve is responsible for the facial, motor and sensory functions of the face. With inflammation muscle paralysis occurs, and symmetry is broken. In the high-risk zone are primary schoolchildren and people of retirement age. Symptoms and treatment of facial neuritis depend on the stage of development of the pathology.
Content
Features of the disease
Neuritis is an inflammation of one of the seven pairs of cranial nerves. With a disease, a person loses the ability to fully show emotions, chew food and talk normally. The violation has noticeable visual manifestations: half of the face twists, the symmetry is distorted.
The facial nerve passes through the narrow channels of the bones, which makes it very vulnerable. Even mild inflammation is fraught with constriction, followed by severe oxygen starvation. Most often, facial muscles are damaged on one side, and only 2% of patients experience bilateral neuritis.
Neuritis can be divided into two categories:
- primary;
- secondary.
The primary inflammatory process occurs against the background of hypothermia, the secondary is a complication with existing diseases of tonsilogenic or otogenic origin.
Causes of facial neuritis
All possible causes of inflammation of the facial nerve lead to narrowing and spasms of the arteries. The blood in the capillaries stagnates, causing them to expand. The liquid part of the blood accumulates in the intercellular spaces, the outflow of lymph is disturbed due to swelling of the tissues and compression of the lymphatic vessels and nerves.
Violation of blood circulation of the nerve is fraught with a lack of nutrition. The nerve trunk is getting bigger numerous hemorrhages occurinterfering with impulses transmitted from the brain to the muscles.
The facial nerve becomes inflamed due to several reasons:
- local hypothermia;
- herpes;
- multiple sclerosis;
- depression and frequent stress;
- hypertension;
- alcoholism;
- sinusitis;
- otitis media;
- endocrine system diseases;
- atherosclerosis.
Also inflammation is possible in the first trimester of pregnancy: at this time, women are faced with serious hormonal changes and inhibition of immunity, which negatively affects the state of the nervous system. During this period, the disease is treated more difficult, since many drugs are dangerous to the fetus and are prohibited for use.
Symptoms of facial neuritis
Symptoms of facial inflammation on the face depend on the form of pathology. It can be subacute or acute. First there is aching or sharp pain in the ear area. An obvious sign of the disease is facial muscle paralysis. - It will appear 1-2 days after the onset of the disease.
Additionally, the following symptoms may occur:
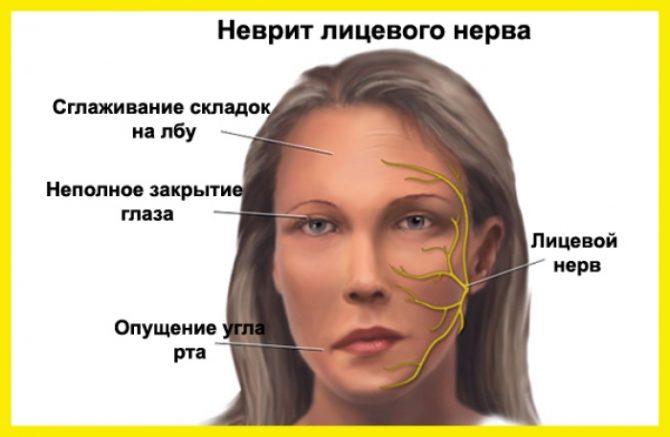
- noticeable smoothness of the nasolabial fold;
- Bell symptom;
- omission of the corner of the lips;
- masked face;
- skewed to the healthy side;
- violation of salivation;
- hearing impairment.
During an illness, a person becomes irritable and nervous, migraine attacks, insomnia and aching pains throughout the body are possible. Body temperature rises to 38 ° C.
Pain in the affected area is atypical or typical. In the first case, the discomfort is constant, undulating: attacks occur suddenly, subside and repeat.Typical pain is sharp, shooting, similar to electric shocks in the area of nerve fibers.
A symptom of Bell is characterized by a violation of visual functions. When you try to squint, the eyeballs are taken up. It is impossible to completely close the eyelids on the sore side of the face; a white sclera is visible in the ajar gap.
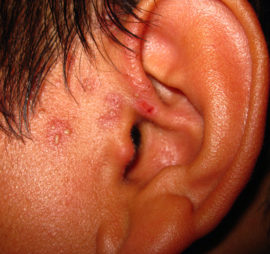
After the onset of the disease, the muscles of the affected side weaken, which makes the simplest facial expressions impossible: smiles, eyebrow movements, winks. With herpes virus, signs of Hunt syndrome are added. - in the area of the ear there is an acute, constant pain that radiates to the cervical-occipital region. In the area of the nasopharynx and the external auditory canal, rashes appear.
Signs of inflammation of the facial nerve will help a specialist determine the affected area. If the pyramid of the temporal bone or the cranial cavity is affected, salivation will decrease, the front of the tongue will lose its ability to determine taste, and your hearing may become sharp or abyss.
When inflammation occurs in the nuclei of the facial nerve, nystagmus appears (rapid involuntary movements of the eyeballs), half of the face goes numb. Signs of damage to the cerebral cortex leads to paralysis of the facial muscles on the lower face. With laughter, the asymmetry is not visible, but the patient is constantly pursued by a nervous tic.
Necessary diagnostics
If there are alarming symptoms or suspected neuritis, should be contacted by a neurologist. Treatment of inflammation of the facial nerve is carried out only after confirmation of the diagnosis and under the supervision of a specialist, which will avoid possible complications.
Despite the obvious visual symptoms, a single examination and collection of complaints is not enough. Additionally, the following diagnostic measures may be recommended:
- general blood analysis;
- MRI
- CT scan of the brain;
- electromyography;
- electroneurography.
A blood test is necessary to confirm the presence of an active inflammatory process in the body. The doctor will pay attention to the erythrocyte sedimentation rate, the content of lymphocytes and white blood cells. MRI excludes other pathologies in which similar symptoms occur: inflammation of the meninges, heart attacks, or tumors.
Computed tomography may indicate the causes of neuropathy. Therapeutic tactics are selected based on the results of this study.
Possible complications
With timely and proper treatment of facial inflammation, the prognosis is quite favorable. Poor therapy increases the risk of the following complications:
- face synhesia;
- muscle atrophy;
- keratitis;
- chronic conjunctivitis;
- involuntary spasms of the face;
- facial muscle contractures.
Nerve cells recover for a long time, and all the doctor's recommendations must be followed: to undergo a full course of treatment, do massage on time and take all prescribed medications. You also need to find out the causes of neuritis of the facial nerve in order to protect yourself from a relapse of the disease.
Treatment of facial neuritis
In order for the treatment of inflammation of the facial nerve to be effective, the elimination of symptoms can not be undone - we need complex therapy. From the first days of the disease, medical treatment is necessary, physiotherapy with the use of non-contact heat is allowed. From the second week, physiotherapy exercises and massages are connected. Noticeable improvements should appear within the first 2-3 months.
Medications
If the nerve is inflamed, the main “bet” is on glucocorticoids - steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: Prednisolone or Dexamethasone. They relieve inflammation, eliminate pain and reduce swelling. There is an activation of the release of a neurotransmitter - a substance that improves the conductivity of impulses along the nerve fiber.
Additionally, can be assigned:
- Diuretics: Furon, Furosemide.Free tissues from the fluid that causes swelling, reduce the risk of blood vessels being squeezed.
- Anticholinesterase: Galantamine, Proserin. They increase muscle tone, normalize the work of the excretory glands (salivary and lacrimal).
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory: Nurofen, Nise. They remove inflammation along the nerve fibers, remove pain in the ear and eye.
- Vitamins: group B. Necessary for the proper functioning of the nervous system and its protection from exposure to toxins.
 Antiviral: Acyclovir, Zovirax. Are prescribed for the herpes virus, block the division of its cells.
Antiviral: Acyclovir, Zovirax. Are prescribed for the herpes virus, block the division of its cells.- Antispasmodics: Antispasmodic, No-spa. Expand arteries, relieve spasms of smooth muscles. Improve blood circulation on the affected side of the face.
- Neurotropic: Phenytoin, Levomepromazine, Carbamazepine. Normalize the mineral metabolism of nerve cells, reduce the frequency of involuntary muscle contraction and improve the functioning of the entire nervous system.
Before using any drug, it is necessary to read the instructions for use and a list of contraindications. Any medication can provoke an allergic reaction or cause side effects. If undesirable consequences occur, you should inform your doctor.
Massage
It is recommended to start massage on the 5-7th day after the facial nerve is inflamed. If possible, it is better to contact a specialist: improper self-exposure can adversely affect the course of the disease.
Immediately before the procedure, a warm-up is performed: head tilts back and forth, rotation and turns are performed. Each exercise is done slowly, 7-10 times. The massage itself begins with the neck and neck to prepare the lymph vessels.
The impact is on both sides of the face and head: the one with which the nerve was inflamed, and on the healthy one. Be sure to stretch the collar zone and the mastoid process.
In the first 2-3 days, all actions should be soft and smooth, superficial: too intense contact is dangerous painful muscle contraction.
The average duration of the session is no more than 15 minutes. Massage is advised before the onset of recovery and the disappearance of all symptoms of neuritis.
ethnoscience
Folk remedies are often used as an auxiliary effect in the treatment of an inflamed nerve. They can not fully replace drug treatment, but they improve overall well-being and speed up the healing process.
With the approval of a doctor, the following apply:
- Rubbing: Ready 10% mummy solution is applied to a cotton swab, which is used to massage the face for 3-5 minutes. Movement should be light and move from the center to the ear area. Course duration - 14 days.
 Warming up: clean sand or salt (200–250 grams) is calcined in a pan. The mixture is placed in dense tissue and applied to the area of the inflamed nerve for 20-30 minutes. You can start the procedure on the seventh day after the start of the main treatment.
Warming up: clean sand or salt (200–250 grams) is calcined in a pan. The mixture is placed in dense tissue and applied to the area of the inflamed nerve for 20-30 minutes. You can start the procedure on the seventh day after the start of the main treatment.- Compresses: 3 bags of pharmacy chamomile are brewed in a glass of boiling water, infused for 15 minutes. The liquid drains, and moist sachets are applied to the face, covered with cling film and a warm cloth. You can do the procedure once a day while the main drug treatment is carried out.
- Ointment: two tablespoons of dry or fresh poplar buds are crushed in a blender, the same amount of soft butter is added. Apply to the problem area of the face after warming up. It is possible to treat inflammation in this way for 14 days.
To strengthen the immune system, herbal teas and infusions with natural liquid honey are additionally recommended.
Any component of a folk remedy can be an allergen, so when the first side effects appear, the recipe is prohibited.
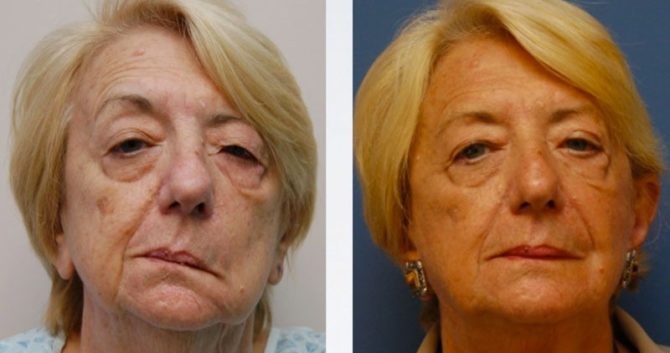
Surgery
If it is necessary to treat inflammation of the facial nerve for longer than 6-8 months, and there is no obvious improvement, doctors recommend surgical intervention.
This method should be used during the first year of the disease: neuritis provokes changes in the facial muscles, and over time they become irreversible.
In most cases, surgery is required for an ischemic form of the disease, when the nerve compresses the narrow fallopian canal. Provoke a similar violation of trauma to the bones of the skull or chronic inflammation of the middle ear.
During the procedure, an incision is made behind the auricle to find the area in which the nerve exits from the awl-mastoid opening. The outer wall of the canal is removed to stop the process of compression of the nerve by the temporal bone. The operation is performed under general anesthesia and has a high percentage of effectiveness.
Prevention
Primary neuritis is much easier to treat. If inflammation of the facial nerve reappears on the same side of the face, the prognosis is less favorable, the chances of a full recovery are reduced. To avoid relapse it is recommended:
- avoid stress and prolonged depression;
- temper;
- provide yourself with good nutrition;
- avoid hypothermia of the body;
- self-massage throughout the year;
- timely get rid of viral and infectious diseases.
Immediately after treatment, it is important to choose the appropriate vitamin and mineral complex and include as many vegetables and fruits as possible in order to support the immune system.
The final decision on how to treat facial neuritis is made by the doctor. Trying to choose therapy yourself is dangerous worsening the course of the disease and the rapid onset of complications. After this, the only way to get rid of the disease will remain surgical intervention.