Causes, symptoms and treatment of aphthous stomatitis
Stomatitis is an inflammation of the oral mucosa, which is accompanied by the formation on its surface of small aft like ulcers. The principle of treatment of aphthous stomatitis depends on the cause of its occurrence, the age of the patient, the severity of the course of the disease, and requires mandatory medical intervention.
Content
Causes of aphthous stomatitis
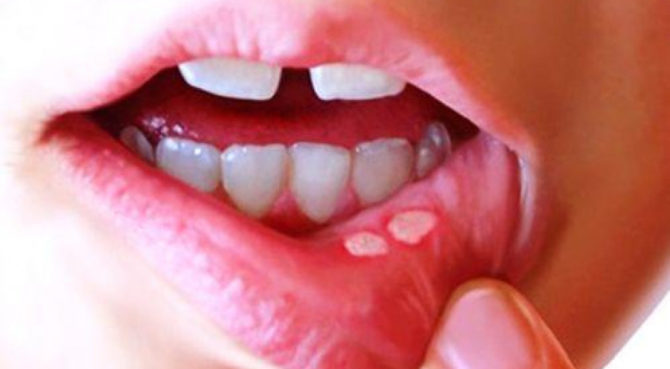
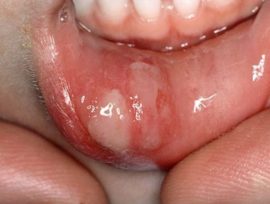
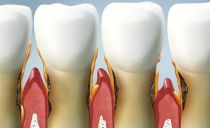
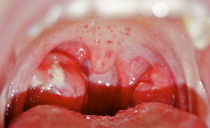
Aphthous ulcers in the oral mucosa look like white spots with a red rim. Such formations can be round or oval. Ulcers occur singly or in the form of extensive foci. Most often, the inflammatory process affects the front of the mouth: the inner side of the cheeks, lips. This is due to the fact that it is this area of the oral cavity that is most affected by damage: bites during meals and the formation of scratches. Less often, the location of the aft becomes the mucous membrane of the tongue.
The average period of the course of the disease is 8-10 days. Usually, aphthae quickly heal without leaving scars.
Specialists call the following causes of aphthous stomatitis:
- Low immunity. According to doctors, this is the main reason for the development of the disease. Aphthae inside the mouth are formed in people who often suffer from colds and viral diseases against a background of reduced immunity.
- The disease often occurs with a complicated course of tonsillitis, pharyngitis, gastrointestinal diseases.
- Inadequate oral hygiene.
- Sometimes the cause of aphthous stomatitis is the penetration of pathogenic microorganisms such as L-shaped staphylococci, herpes viruses, measles, adenoviruses, diphtheria bacillus.
- Inflammation of the mucous membrane can be the result of an allergic reaction of the body to certain foods, drugs.
The provoking factors in the development of the inflammatory process are also: hypothermia, hereditary predisposition to the disease, vitamin deficiency, diseases of the teeth and gums. One or several unfavorable factors can provoke the formation of aphthous ulcerations.
Types of aphthous stomatitis
Aphthous stomatitis is much less common in children than in adults. This is due primarily to the lack of serious pathologies of the digestive system, the best condition of the teeth and body. In adults, with constant malfunctions of the immune system, the acute form of the disease becomes chronic.
The description of these two forms in dentistry looks like this:
- Acute gingivostomatitis. Acute aphthous stomatitis develops against a background of diseases of viral origin. Usually affects children up to three years after they are ill with diphtheria, measles, rubella, whooping cough.
- Recurrent chronic aphthous stomatitis. The causes of the transition of the inflammatory process into a chronic form are staphylococci, viruses, impaired immunity and allergies. Constant relapses are also observed in people with gastrointestinal diseases or in those who have a genetic predisposition to inflammation of the oral cavity.
There is another classification of the disease: the nature and severity of mucosal lesions. In addition to acute and chronic aphthous stomatitis, such types of this pathology are distinguished in dentistry:
-
Fibrinous. Aphthae acquire a grayish tint, ulcerations pass on their own within a few weeks. When moving from an acute form to a chronic disease, it occurs up to three times a year. In cases where the disease is not treated, such ulcers remain on an ongoing basis.
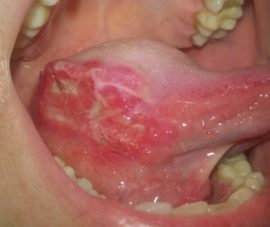
- Necrotic. The underlying cause is inflammatory diseases of infectious origin. With the development of this form of the disease, cell death of the mucosa occurs. Ulcers do not cause a person painful or uncomfortable sensations, but over time they expand in size, forming large lesion foci. Such aphthae heal for a long time.
-
Glandular. This form of the disease affects the salivary glands. Aphthous ulceration gives a person severe pain, and after treatment frequent relapses are possible.
- Scarring. Pathology is accompanied by the formation of aphthae of a sufficiently large size - up to 1 cm. After healing, they leave scars after themselves. The treatment process is long, the symptoms of the disease can last up to three months.
- Deforming. This is one of the most severe forms of pathology. It is characterized by the formation of large ulcers that leave scars after healing. These scars can change the structure of the mucosa, deform its surface. Only an experienced and highly qualified specialist should treat this form of inflammation, since the therapy is complex and lengthy.
-
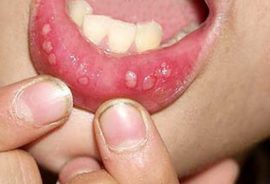
Herpetic. Most often occurs in infants. Moreover, there are times when children are already born with such a disease, having been infected by a mother who does not have immunity to the pathogen. Aphthae have the appearance of small bubbles, but they scare with their quantity, which can reach 30 pieces. The mucous membrane of the mouth with severe inflammation can turn red. In young children, the disease at the beginning of development is often accompanied by fever and eye damage.
Each of these types of aphthous stomatitis has its own characteristic symptoms.
Symptoms of aphthous stomatitis
Symptoms of aphthous stomatitis largely depend on the type and form of the disease. If the disease has a mild form, symptoms at the initial stage can not always be noticed. Sometimes it is so insignificant that patients do not attach any importance to it. Over the entire period of the disease, only 1 afta can form in the mouth. But more often, the inflammatory process gives a person a lot of painful and uncomfortable sensations.
Acute aphthous stomatitis arises suddenly and is characterized by pronounced symptoms. First, the patient complains of a general malaise characteristic of colds and viral diseases, and an insignificant increase in temperature may soon occur.
The acute form of aphthous stomatitis is also manifested by the following symptoms:
- severe headaches;
- swollen lymph nodes that are painful on palpation;
- temperature increase up to 38 ° C;
- bad breath due to sores;
- violation of the stool: constipation is replaced by diarrhea.
With the development of herpetic aphthous stomatitis, a slightly different clinical picture is observed:
- severe fever (this is how the disease manifests itself in young children and infants);
- pronounced pain, due to which the child is constantly acting up;
- disturbance of night sleep due to poor health;
- decreased appetite, the child may refuse to eat for several days.
When chronic recurrent aphthous stomatitis develops, the following symptoms occur:
- insomnia or drowsiness;
- irritability;
- loss of appetite;
- increased salivation;
- swollen lymph nodes;
- bouts of vomiting (in children);
- the formation of irritations in the corners of the mouth.
With any form of the disease, a person feels pain while eating. During a visual examination of the tongue, you can notice a white coating on it, and on the inside of the cheeks and lips - vesicles or ulcers.
Treatment of aphthous stomatitis
Treatment of aphthous stomatitis depends on the form of its course. If the inflammatory process has a viral nature of origin, therapy is carried out at home. It is based on a sparing diet with the exception of spicy, salty, acidic and solid foods that irritate an already inflamed mucosa.
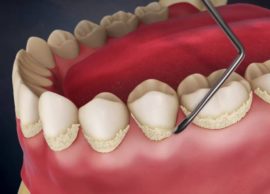
A mandatory action in the treatment of aphthous stomatitis, regardless of its form, is the removal of plaque and stone. These deposits can contain a large number of pathogenic agents, which caused the development of pathology. The absence of such an action on the part of a specialist is the main reason why it is not possible to cure a patient of stomatitis.
To treat foci of inflammation, dentists recommend lubricating the ulcers with boric acid, hydrogen peroxide or rinsing the mouth with a decoction of chamomile. In the presence of ulcerative formations in the throat, rinsing with the indicated means is also recommended.
For relief of a pain syndrome are applied:
- Lidochlor.
- Hexoral.
- Anestezin.
Patients with a predisposition to allergies are prescribed a suspension of Diphenhydramine to rinse the mouth and throat.
 To cure chronic recurrent stomatitis, you need to rinse your mouth with chlorhexidine and treat ulcers with local glucocorticosteroids. For this, in dentistry are used:
To cure chronic recurrent stomatitis, you need to rinse your mouth with chlorhexidine and treat ulcers with local glucocorticosteroids. For this, in dentistry are used:
- clobetasol ointment;
- Fluocinonide ointment;
- Dexamethasone rinse.
Dentists often prescribe anti-inflammatory drugs with anesthetic effect to patients: Camistad, Clobetasol, Trasilol, Xicain and Benzocaine. You can not do without them when a severe pain syndrome appears, but prolonged use of these medications is unacceptable, since adverse reactions are possible.
With the re-occurrence of signs of aphthous stomatitis, it becomes advisable to use local antibacterial drugs: Tantum Verde, Oracept. In the fight against aphthae, regardless of their origin, Stomatophyt-A balm has proven itself well. The medication consists of medicinal extracts and anesthetic. Apply it with a cotton swab to the places of localization of aft.
When the ulcers heal, it is necessary to continue treatment with epithelizing drugs that will restore the mucous membrane. Among such tools in dentistry, Solcoseryl gel is actively used.
Allergic stomatitis must be treated with antihistamines for oral administration. Ointments, solutions and suspensions of local action with an anti-inflammatory effect are also used. To rinse the mouth and throat, decoctions of oak bark, chamomile, sage, calendula and other soothing herbs are used.
How to treat aphthous stomatitis in children
Treatment of childhood aphthous stomatitis has its own characteristics. If characteristic symptoms occur, you should visit the office of the pediatrician and dentist. A mandatory action should be to follow a sparing diet, which will eliminate irritation of an already inflamed mucous membrane.
 Antihistamines are prescribed for children, designed to relieve swelling and reduce the allergic reaction:
Antihistamines are prescribed for children, designed to relieve swelling and reduce the allergic reaction:
- Tsetrin.
- Diazolin.
- Claritin.
- Telfast.
- Zodak.
- Suprastin.
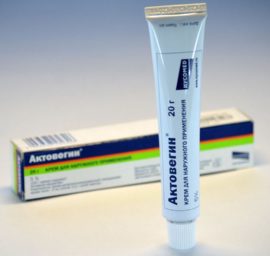
Immediately after the elimination of severe inflammation, when the acute phase subsides, Actovegin gel is included in the course of treatment of aphthous stomatitis in children. The action of this drug is aimed at accelerating the process of regeneration of damaged cells, wound healing and restoration of the mucous membrane.
Treatment is not complete without immunomodulators. From this group of drugs, children are prescribed the use of toothpaste with lysozyme, glucose oxidase, lactoferrin. Enzymes have a beneficial effect on the affected mucous membrane, increasing its resistance to viruses and bacteria.
The tactics of therapy should be prescribed by a specialist, self-medication of aphthous stomatitis can cause serious complications.
Dietary recommendations
Given that the patient may experience a deterioration in the use of irritating food, it is important to adhere to a sparing diet. It is built on such rules:
- Food should consist of finely chopped and mashed food.
- All products must be thermally processed, before use they must be boiled or doused with boiling water.
- You can’t eat hot or cold food, food should be at room temperature.
- Each time after eating, it is necessary to rinse the oral cavity with water or a decoction of herbs to remove food debris.
- If aphthous ulceration is so inflamed that eating is uncomfortable, you must use a wide tube during meals.
To prevent the occurrence of an ailment, it is recommended to regularly visit the dentist's office, monitor oral hygiene, and timely treat diseases that can lead to a decrease in immunity.