Causes of red rash in the palate, in the throat and on the oral mucosa in adults and children
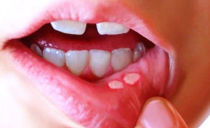
Enanthema - this is what doctors call a rash in the oral cavity. Rashes on extremely sensitive mucous membranes of the tongue, palate, gums, inner side of the lips, cheeks, back wall of the throat cause a lot of trouble and require immediate treatment. In both an adult and a child a red rash in the palate and mucous membranes of the mouth is a sign of an infectious disease or an allergic reaction.
Content
Allergic reaction in adults and children
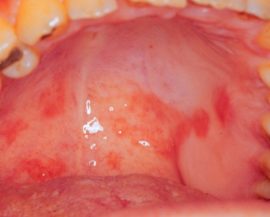
Various rashes in the mouth often accompany allergies. Usually it is manifested by the appearance of red dots in the upper sky and in other parts of the oral cavity, but it can also be accompanied by the appearance of small pimples or vesicles - papules, vesicles.
The appearance of allergic rashes is often accompanied by swelling of the mucous membranes and soft tissues. Inflammation and swelling can quickly spread and cause a life-threatening complication - Quincke's edema. Therefore, even the smallest symptoms of an allergy cannot be ignored. The appearance of any rashes in the oral cavity is an occasion for urgent medical attention, especially if the allergen that caused such a reaction is unknown.
The most common allergens:
- food products;
- chemicals in food (colorants, flavors);
- plant pollen;
- medical preparations and their components;
- materials of dentures and fillings;
- household chemicals (toothpastes, rinses, fresheners);
- children's toys, teethers, nipples and soothers made of substandard materials.
To stop the spread of red rash and swelling towards the throat, to the respiratory system, it is better to take an antihistamine before going to the doctor: Diazolin, Suprastin, Tavegil. It is especially necessary to act quickly if a rash is found in the throat of a child. Many babies are prone to allergic reactions in the form of enanthema, any parent should be ready for this.
The main difference between an allergic rash and an infectious rash is that it is not accompanied by fever and general weakness. Red dots in the sky in the child’s mouth, accompanied by fever and intoxication symptoms, indicate an invasion of a viral, bacterial or fungal infection in the body.
Infectious diseases for children
Many infectious diseases manifested by a rash in the palate are known as "childhood". But this does not mean that adults are not susceptible to infection. Having overcome such diseases once, a person receives lifelong immunity. But if you do not get the same chickenpox in childhood, there is a risk of contracting this infection in adulthood.
Rubella
With rubella, red spots may first appear in the baby’s sky, and then on the face and body. Typically, in childhood, rubella passes easily and without complications, with the exception of babies up to a year. These babies suffer the disease very hard, so the red specks in the mouth, which quickly merge into spots, should alert parents: this may be the first symptom of rubella. This disease is dangerous for adults who have not been ill with them in childhood, especially for pregnant women.
Measles
As with rubella, with measles, a rash in the mouth can appear earlier than on the body - sometimes in a day or two. But the nature of the rash is very different: with measles, the rashes look like dots of white or pale gray, resembling semolina. Their clusters in the upper sky, tonsils and posterior wall of the throat are surrounded by a pinkish border, this phenomenon is called Belsky-Filatov syndrome.
Chicken pox
With chickenpox, a red rash in the oral cavity should alert, as it indicates a complicated course of the disease. Bubbles filled with liquid can shower on the gums, tongue, inner surfaces of the baby’s lips and cheeks, often found at the top - on a hard and soft palate. Breaking through, they form ulcerations in the oral cavity.
Scarlet fever
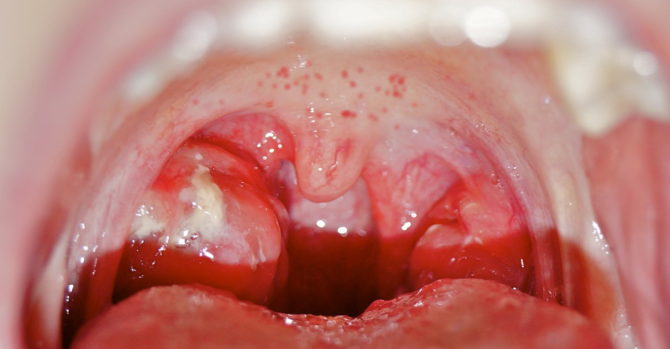
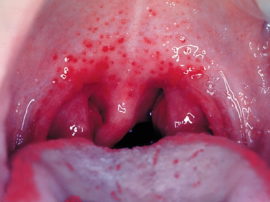 With scarlet fever, a small red rash covering the baby’s body can also appear in the upper sky. The mucous pharynx with scarlet fever is bright red, the regional lymph nodes and tonsils are enlarged, the tongue acquires a raspberry color and is covered with a white coating - see photo.
With scarlet fever, a small red rash covering the baby’s body can also appear in the upper sky. The mucous pharynx with scarlet fever is bright red, the regional lymph nodes and tonsils are enlarged, the tongue acquires a raspberry color and is covered with a white coating - see photo.
Rashes-specks are usually accompanied by very high fever and vomiting, and with a severe form of the disease - convulsions, blurred consciousness.
Roseola
Since the disease begins with a high temperature, and after a couple of days when the temperature drops, a rash appears, roseola is often mistaken for acute respiratory viral infections and an associated allergy to drugs. Small red spots and vesicles in the throat and in the sky precede the appearance of the same rashes on the body. Their presence is accompanied by redness of the pharynx and pain when swallowing.
The difference between a rash in the mouth and on the body with roseola from any other is that with pressure it disappears.
Common Infectious Diseases
Infections of varying severity periodically complicate a person’s life, without leaving behind antibodies and immunity against the pathogen. Therefore, specks on the back of the throat, vesicles on the gums and red dots in the sky can appear in the mouth of any adult, and not just in infants or adolescents.
Relapses of infectious diseases result from weakened immunity. with flu, acute respiratory or enterovirus infections, chronic diseases, hypothermia, stress. Many of them are accompanied by a red rash and blisters in the sky, hemorrhages and erosion.
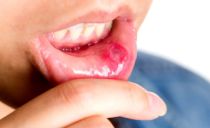
Herpes
Many mistakenly believe that a blistering rash with herpes affects only the lips from the outside. In fact, it can be localized in any part of the oral cavity, skin, and even on the mucous membranes of the internal organs.
The carrier of the herpes virus is the vast majority of people, since once they enter the body, the viral particles remain in it throughout life. With weakening of the body's immune defenses, the virus is activated and manifests itself as a red rash on the face, oral mucosa.
Bursting, the vesicles become foci of inflammation and secondary infections. Mild herpetic damage to the mucous membranes can develop into a necrotic ulcerTherefore, careful care is necessary for the inflamed areas of the oral cavity.
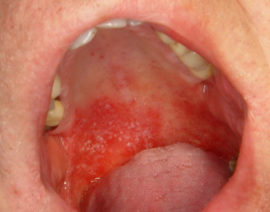
Stomatitis
Stomatitis is an inflammation of the oral mucosa. The disease can have a fungal, bacterial and viral etiology, often detected in newborns. In both a child and an adult, the disease is recognized by red spots in the mouth, covered with white or yellowish (with fungal stomatitis - curd) plaque. Without proper treatment, spot aphthae form at the spot of spots, which are accompanied by constant pain.
Stomatitis is a disease that can have a different etiology. If the disease is caused by a viral infection, you need to treat it with antiviral agents. If bacteria - antibiotics. And if fungal agents - special antifungal drugs.Since it is difficult to independently identify the pathogen, it is better to consult a dentist or therapist.
Pathogens of other extremely serious infectious diseases can also cause stomatitis, accompanied by ulcerations and red spots in the mouth:
- typhus;
- staph infection;
- herpes zoster and red lichen;
- meningococcal infection;
- lupus erythematosus;
- syphilis.
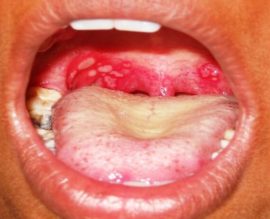
Enteroviral vesicular pharyngitis (herpetic sore throat)
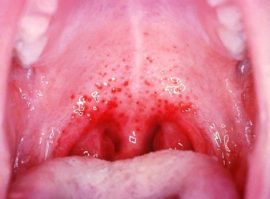 The disease received its second, more widely known name because of the similarity with both tonsillitis and herpes: watery papules are localized on the tonsils and palate.
The disease received its second, more widely known name because of the similarity with both tonsillitis and herpes: watery papules are localized on the tonsils and palate.
However, the treatment of this disease is significantly different from the treatment of both herpes and sore throats. Therefore, with the appearance of rashes on the glands, it is very important to correctly diagnose what only a doctor can do.
Mononucleosis
Mononucleosis is an infectious disease in which a spotted rash on the body is sometimes accompanied by a rash in the mouth in the form of pinkish papules in the soft palate and glands. They do not cause much discomfort and usually go away on their own within a few days. Complications usually occur only in infants up to two years old.
Mostly children aged 3-5 years get sick with mononucleosisbut adults who have not had it in childhood are not immune from infection.
Due to the similarity of symptoms of mononucleosis with angina and pharyngitis, it can only be diagnosed by a blood test.
How to relieve enanthema discomfort
Determining by eye what caused the appearance of papules, white or red dots in the throat of a child or adult, is not always possible even for experienced specialists. Such a symptom, in addition to infections, can indicate chronic and even cancer diseases of internal organs and systems. Most often, the true cause of the rashes can be found out only after passing the tests. Therefore, the first thing a sick person should do is consult a doctor.
It is impossible to eliminate rashes in the oral cavity without a comprehensive treatment of the underlying diseasethat caused this symptom, according to the scheme prescribed by the doctor. In anticipation of a medical examination, you can only try to alleviate the painful sensations at home. After all, the presence of a rash in the palate and mucous membranes of the baby makes it difficult to breastfeed, while older children interfere with thoroughly chewing food, swallowing and even talking. It is also difficult for an adult to endure constant irritation on the tongue, cheeks, gums or in the larynx.
To reduce discomfort in the mouth, you can use rinses and baths with decoctions of chamomile, sage, yarrow or oak bark, treat red pimples and spots with solutions of Furacilin, Chlorhexidine or Miramistin. An antihistamine tablet will help relieve swelling and itching. With herpes, antiviral ointments based on acyclovir come to the rescue. But rinsing, bathing and taking drugs do not eliminate the need for urgent consultation with a specialist doctor.