Inflammation of the oral mucosa: causes and treatment
The treatment of inflammation of the oral mucosa largely depends on the type of pathogen, due to which the lesion developed. That is, first you need to diagnose and establish the etiology of the disease, and only then proceed with drug therapy.
Content
Classification of inflammatory diseases and their symptoms
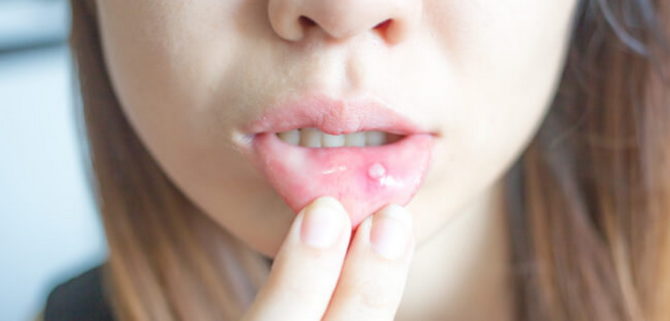
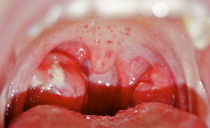
Any inflammatory process in the oral cavity is called stomatitis. The disease is characterized by the onset of plaque, redness of the mucous membrane and the appearance of ulcers, aphthae or other rashes on it. Plaque and rashes can be localized on the gums, tongue, lips, palate, or the inside of the cheeks. The disease is accompanied by fever and lymphadenitis. The patient has a severe pain in the oral cavity, it is difficult for him to chew food and drink water.
The causative agent of stomatitis can be Candida albicans fungus, herpes virus, bacteria, trauma or allergies.
There are several types of inflammation of the oral cavity:
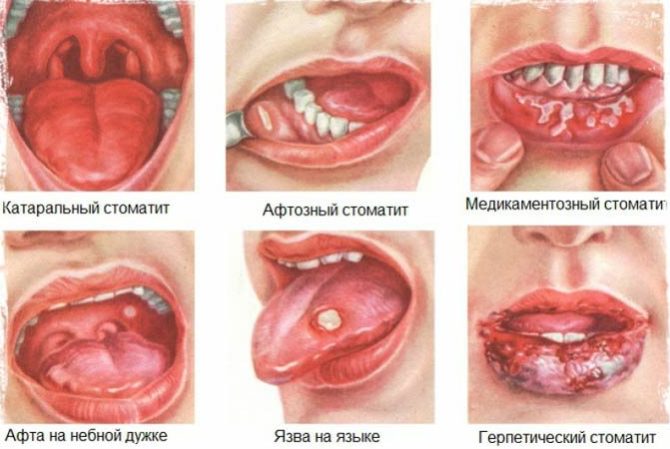
- Catarrhal. May be accompanied by swelling, redness, the appearance of pustules or numerous erosions in the mouth and lips, plaque on the mucous membrane, increased salivation, pain in the mouth, bleeding gums. Catarrh inflammation develops due to caries, chipping of the crown, tartar and lack of sufficient hygiene.
- Traumatic. It is characterized by redness, hyperemia, irritation of the mucous membrane and the appearance of erosion. It occurs due to various mechanical damage.
- Herpetic. It occurs due to infection or activation of the herpes virus. In addition to traditional changes, lymphadenitis, general weakness and a strong increase in temperature are observed.
- Candidiasis (thrush). It occurs due to the activity of Candida albicans fungi. The disease is characterized by flushing of the tongue, the inner surface of the cheeks, gums and the appearance of abundant white plaque. Most often, candidiasis affects infants.
- Aphthous. It is manifested by the appearance of ulcers. First, the mucous membrane swells, turns red, and then aphthae covered with a serous coating appear on it. The lesions are painful when you touch the tongue.
- Allergic. Represents the body's reaction to any stimulus: drugs, food, coloring matter. This type of inflammation is characterized by standard allergy manifestations: swelling, pain in the mouth, severe itching, spot burning, the appearance of reddened spots on the lips and on the inside of the cheeks.
Signs of glossitis
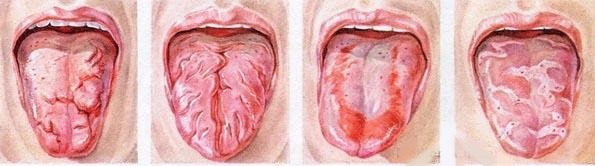
Inflammation of the tongue is considered separately from other forms of stomatitis, such a pathology even got its own name - glossitis. The disease often accompanies various dental pathologies and indicates the presence of infection in the body. The following signs indicate that a person has an inflamed tongue:
- pain and swelling of the tongue;
- violation of taste perception;
- swelling of individual papillae of the tongue;
- the appearance of spots on the tongue;
- redness of the tongue;
- enhanced salivation;
- the appearance of rashes and ulcers.
In the tongue, multidirectional folds, curd or varnish coating, purulent pimples with a bright border and other formations may appear.Any change in the appearance of the tongue should alert and become an occasion for immediate medical attention. Especially if it becomes painful to swallow, or there are problems with pronunciation.
Signs of gingivitis
Gingivitis is called pathological gum disease.arising due to the abundance of plaque, stone, oral contraceptives, immunosuppressants or irritation during teething (milk or wisdom teeth). All these factors lead to gum disease only if a person systematically ignores the rules of hygiene. That is, the growth of new teeth is not always accompanied by an inflammatory process.
Gingivitis can be recognized by swelling, redness, bleeding, hyperthermia, and sore gums. Sometimes the connection between the gum and the tooth is broken, which causes it to stagger. Almost always gingivitis is accompanied by halitosis - stink from the mouth.
Causes of inflammation of the mucous membrane in the oral cavity
Often inflammation of the mucous membrane of the oral cavity and tongue occurs due to reduced immunity and poor oral hygiene. The mucous membrane, which is not given proper attention, becomes susceptible to various pathogens - bacteria, viruses, fungi - and therefore it is easily infected. Also occurs when the tongue or the inside of the cheeks is injured with a sharp object, a tooth fragment, a chemical substance or hot food - under the influence of irritating factors, the susceptibility of the mucous membrane to infections increases.
Predisposing factors are needed for primary infection, if the pathogen is in the body in a vegetative state or has already infected other cells and tissues, then special “entry gates” for the penetration of bacteria or fungi are not required. Pathogenic microflora will be introduced into the oral cavity with blood flow from the main infectious focus.
In adults, pain can be localized in the area of the oral mucosa due to smoking. Nicotine is a very irritating factor. It corrodes the mucous membrane and provokes its inflammation and hyperemia. In adult smokers, stomatitis is more common than in non-smokers.
Factors that provoke inflammation in the oral cavity
The factors that provoke the development of inflammation in the oral cavity include:
- frequent stress;
- mental disorders;
- chronic lack of sleep;
- constant intoxication of the body: alcoholism, smoking, drug addiction, work in hazardous industries;
- respiratory diseases;
- HIV and hepatitis, especially if you do not have supportive procedures;
- hormonal disruptions during menopause, puberty or pregnancy;
- hypovitaminosis;
- inflammatory processes in the throat;
- the presence of intestinal parasites.
Problems with the mucous membrane in the mouth reflect the general condition of the body and often indicate more serious pathologies of the internal organs.
Medication inflammation
Taking certain medications may be accompanied by side effects, sometimes referred to as drug disease. Most often, such complications are associated with the use of:
- antibiotics of all groups;
- pyramidone;
- sulfonamides;
- novocaine;
- preparations containing iodine, phenol and heavy metal compounds.
The side effect of drugs is due to their chemical structure and often manifests itself against a background of weakened immunity and concomitant diseases. Most often, taking such drugs leads to the development of catarrhal or allergic stomatitis.
In children, irritation of the mucous membrane in the mouth often occurs due to intestinal dysbiosis or vitamin deficiencyresulting from prolonged antibiotic therapy. Dysbacteriosis, which developed with antibiotics and sulfonamides, leads not only to candidiasis, but also to a change in the natural color of the tongue to black.That is why, in parallel with the treatment of soft tissues of the oral cavity, it is necessary to restore the work of the digestive tract.
How to treat the oral cavity with inflammation
Inflammation of the soft tissues of the oral cavity appears due to a variety of reasons, therefore, it is possible to effectively treat the disease only after adequate diagnosis. Sometimes sores in the mouth can be cured with the help of diet and folk remedies.
Therapeutic diet
To ulcers in the oral cavity heal faster, you should give up smoking or reduce its intensity. It is necessary to remove foods from the diet that cause allergies and lead to irritation of the mucous membrane:
- citruses: tangerines, oranges, pomelo, grapefruits;
- hot coffee and tea;
- dishes with pepper (black, red, chili);
- salted dishes.
During the treatment period, it is worth switching to a salt-free diet altogether to avoid problems with irritation of the soft tissues of the oral cavity. In addition, it is recommended to rinse your mouth with antiseptic solutions after each meal.
Traditional medicine
If the soft tissues of the oral cavity are inflamed and sore, it is necessary to moisturize them with high quality. Frequent rinses will help relieve inflammation and hyperthermia, and get rid of infection. In the inflammatory process on the mucosa, it is recommended to use such folk remedies:
 soda-salt solution (they can rinse your mouth every hour);
soda-salt solution (they can rinse your mouth every hour);- a decoction of chamomile;
- infusion of red elderberry flowers;
- expired kefir, which stood for 8-10 days in the open state in the refrigerator;
- red mountain ash juice;
- solution for rinsing from tea tree oil (you can do it with the addition of aromatic oils);
- tincture of rose petals.
If there are no herbs against inflammation on hand, you can rinse your mouth with plain water or periodically dissolve a piece of ice: cold will reduce the intensity of blood flow to the infected area, which will relieve pain, redness and inflammation.
Oral soft tissue inflammation can be treated with aloe juice. This plant has amazing anti-inflammatory and antibacterial properties. Aloe juice should be applied directly to the affected area 3 times a day. For the best effect, you can make aloe lotions on the inflamed area or rinse your mouth with plant juice dissolved in water. Such measures will help restore the integrity of the mucosa.
When ulcers appear in the oral cavity, people usually do not go to the doctor, but if aphthae are painful, swollen, there are many, and they do not go away within 12-14 days, it is worth visiting the clinic. It is dangerous to treat such pathologies on your own.
What medications are used to treat inflammation
The choice of drugs depends solely on the type of infection that caused the pathology. For any infectious lesion, it is useful to take painkillers or rinse the oral cavity with such means. They will help reduce pain and inflammation of the mucous membrane in the mouth, but will not eliminate the cause of the disease. Anesthetics fight solely with symptoms, they cannot restore the condition of the oral mucosa.
You can purchase over-the-counter medications that effectively treat mouth ulcers, regardless of their etiology:
- Corticosteroid ointment Triamcinolone.
- Blistex.
- Campho Fenik.
- Zovirax.
- Denavir.
In case of a viral infection, it is recommended to take medications based on acyclovir. They will help relieve painful symptoms, restore tissue integrity and cure the disease at the initial stage. Such drugs are allowed to be taken by both adults and children, but before purchasing them, you must familiarize yourself with the contraindications and consult with a specialist.
A doctor should prescribe medication. With improper drug therapy, the inflamed mucosa in the mouth can cause a generalization of the infection.
Any inflammatory processes in the oral cavity need timely treatment.If you ignore the inflammation of the mucous membrane, the infection can spread to other tissues and organs.