Increased salivation: symptoms, causes, types and methods of treatment
Hypersalivation or ptyalism is disorder characterized by increased saliva. The causes of increased salivation in both women and men can be very different, including those associated with serious diseases.
Content
Symptoms and manifestations of hypersalivation
The dominant symptom of adult pialism is copious salivation, exceeding the norm by more than 2 times. The phrase "crush saliva" is relevant for a person with excessive work of the salivary glands. Against the background of the main manifestation, the following occur:
- Frequent swallowing. A large amount of fluid in the oral cavity forces a person to reflexively swallow.
- A constant desire to spit.
- Speech Disorders. Excessive salivation makes it difficult to talk freely. Excess liquid substance in the oral cavity causes a sensation of lisp, swallowing sounds, squelching in the speaker. The speech becomes dull and intermittent.
-
Excessive salivation leads to a violation of the integrity of the skin of the lips, cheeks, and chin. Moisture accumulates in the corners of the mouth and may appear on the lips. This leads to scabs and cracks. Trying to wipe the saliva flowing out of your mouth with a handkerchief or tissue causes skin irritation.
- Inflammatory, infectious lesions of the lips, corners of the mouth, cheeks, chin. Unwillingness to constantly “drool” and attempts to wipe the mouth dry lead to mechanical irritation of the entire lower part of the face. This creates favorable conditions for the occurrence and development of foci of inflammation and infectious lesions.
- Violation of taste perception: increase or decrease in sensitivity, inadequate taste reaction.
- Bad smell.
- Dehydration. The body loses a large amount of water with excessive salivation, vomiting.
- Aspiration pneumonia. In violation of swallowing function, impaired consciousness, salivary fluid enters the lower respiratory tract, causing obstruction - obstruction.
Disease background
The main causes of increased salivation in adults include:
- Inflammatory processes in the oral cavity and pharynx: gingivitis, tonsillitis, periodontitis, stomatitis, acute respiratory viral infections. In this case, increased salivation is a protective reaction of the body, allowing you to free the oral cavity from pathogenic microbes, pathogens, and tissue breakdown products.
- Digestive tract disorders: ulcers, gastritis, neoplasms, pancreatitis, cholecystitis. Microorganisms entering the oral cavity from the gastrointestinal tract irritate the glands and gums. This provokes the development of ptyalism.
- Neuralgic disorders: brain injuries, cerebral palsy, trigeminal inflammation, Parkinson's disease. These pathologies are accompanied by impaired swallowing and respiratory function, enhanced by secretion of the salivary glands with nausea and vomiting.
- Paralysis of the muscles of the maxillofacial region. If the facial nerve is damaged, a person is not able to control the facial muscles, which leads to salivation.
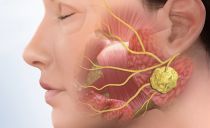
- Mumps is an inflammatory process in the salivary glands. The disease is the cause of not only profuse salivation, but also swelling of the face and neck (mumps).
- Irritations of a mechanical nature. This includes dental procedures, manipulations, damaging gums: removal of stone, tooth, implantation. Pentalism in this case is temporary.
- Medical ptyalism. It is a side effect when taking medications that have an irritating effect on the salivary glands, which causes their activation. In this case, excessive salivation is temporary and disappears after stopping the medication.
- The onset of menopause can also be accompanied by increased work of the glands, accompanied by frequent hot flashes and excessive sweating. Over time, the process of producing saliva returns to normal.
- Increased salivation may cause pregnancy. The resulting toxicosis provokes profuse salivation, accompanied by nausea and vomiting.
The cause of severe salivation can be a hormonal imbalance that occurs against a background of thyroid dysfunction.
Types of disease
According to the development mechanism, ptyalism is classified into the following types:
| True | False |
|---|---|
| The disorder is associated with increased salivary gland function., which causes their increased secretion.
According to the factor of occurrence, true ptyalism is divided into 4 types:
|
Excessive salivation resulting from a disorder of swallowing function, when the mechanism of the process is disturbed. The problem is not with the quantitative changes in the excreted fluid, but with the frequency of swallowing it..
In diseases of the nasopharynx, nervous system, muscles of the face and jaw, swallowing causes discomfort and causes pain (tonsillitis, cramps, sore throat). Therefore, a person swallows saliva less often than the norm requires. As a result, there is an accumulation of fluid in the mouth. |
Excessive salivation may be permanent or temporary. The form of the disorder, when the amount of salivary fluid has increased significantly, it is excreted both day and night, is caused by serious pathologies, requires specialist intervention.
A temporary increase in the amount of saliva can be caused by irritants, the absence of which will stop the disorder itself. For example, after childbirth ptilism caused by toxicosis disappears, and the dosage form of the disease disappears after stopping the drug.
Profuse salivation in a dream
Normally, the activity of the glands that produce saliva during nighttime sleep is reduced. If, after waking up, it is discovered that the pillow is wet, then there has been a spontaneous activation of the salivary glands. This is why drooling while sleeping in an adult.
 This happens when the salivation increases, the body relaxed during sleep does not have time to react, the fluid is not swallowed, and as a result, saliva flows abundantly. The occurrence of such isolated cases is not a violation and a sign of the existing pathology. But manifestations that occur constantly require the intervention of a specialist: plentiful salivation during sleep can be associated with a serious illness.
This happens when the salivation increases, the body relaxed during sleep does not have time to react, the fluid is not swallowed, and as a result, saliva flows abundantly. The occurrence of such isolated cases is not a violation and a sign of the existing pathology. But manifestations that occur constantly require the intervention of a specialist: plentiful salivation during sleep can be associated with a serious illness.
Among the main factors that provoke night hypersalivation, there are:
- Lack of teeth, creating holes in the dentition through which saliva can flow from the mouth at night.Wrong bite makes it impossible to close contact of the dentition, as a result of which the phenomenon occurs.
- Diseases that provoke a violation or complete absence of nasal breathing: a common cold, a runny nose, in which the mucous membrane swells, or snot, otolaryngological diseases, curvature of the nasal septum go - all these are the reasons that saliva flows during sleep. Violation of nasal breathing causes the sleeper to actively breathe with his mouth without closing his lips, so the accumulated moisture flows out. In such cases, the flow of saliva is accompanied by snoring. Most often, when the disease is eliminated, the accompanying signs disappear, including ptyalism.
The reason that drooling in adults can be a good sleep. In this case, the person is not able to control his reflexes, there is no timely swallowing of the liquid, it collects in the mouth - excess flows out.
Hypersalivation during pregnancy
Frequent salivation in women is often caused by such an exciting and important stage as pregnancy. Numerous changes that occur in the female body can provoke various disorders, including ptyalism.
The main causes of abundant salivation in the expectant mother:
 Heartburn. When an acid imbalance occurs, a lot of saliva is released, which is a protective reaction from an increased level of acid.
Heartburn. When an acid imbalance occurs, a lot of saliva is released, which is a protective reaction from an increased level of acid.- Reaction to medication. The internal transformations that a pregnant woman undergoes may manifest in an inadequate perception of drugs.
- Toxicosis. Increased salivation and nausea, vomiting occurs before, during and after a meal. A similar condition may occur even before water consumption. With toxicosis, the syndrome often has no connection with a real increase in the work of the salivary glands. A pregnant woman tries to cope with nausea and suppress vomiting, so she swallows less often. As a result, there is a feeling that the fluid begins to accumulate in the oral cavity.
Usually, excessive salivation does not cause complications in expectant mothers, does not threaten the fetus. But it is necessary to control the condition, since sometimes current saliva can be the result of serious diseases.
With uncontrolled ptyalism, the occurrence of such complications is possible:
- Violation of adequate taste perception, rejection of food.
- Dramatic weight loss. Carrying a child requires significant energy costs, a large number of nutrients and elements. Rational nutrition is necessary for a favorable pregnancy, fetal development. Unwillingness to consume food causes a decrease in weight.
- Dehydration
- Violations of the psycho-emotional background, insomnia.
- Deterioration of the condition and color of the skin of the face.
- Infectious lesions.
Diagnostic measures
The main task of diagnosis is to determine the cause of severe salivation. Diagnostic measures include:
- Collection of patient complaints, examination of the patient’s medical records. Purpose: to identify the time of occurrence of primary symptoms, to identify diseases that could trigger salivation.
- Life analysis, the presence of bad habits. One of the common causes of hypersalivation in adults is smoking.
- The first appointment with a specialist includes a physical examination: a visual assessment of the condition of the oral cavity, nasopharynx, palpation of the head, muscles of the face, neck.
- General blood tests, urine tests that must be done to identify the cause of salivation.
- Study of salivary fluid.
- Referral to a narrower specialist: dentist, neurologist, otolaryngologist.
Based on the diagnosis, the doctor determines the optimal treatment for hypersalivation.
Effective treatment regimens for excessive salivation
The most common methods of treating increased salivation include classical and folk methods. The first is based on taking special medications and conducting special medical manipulations that can effectively combat hypersalivation or its cause.
Having carried out the necessary diagnostic measures, the therapist can refer the patient to a narrower specialist to accurately identify the factor that caused excessive salivation:
- Dental problems: lack of teeth, inflammation in the oral cavity, malocclusion and other diseases that can cause excessive salivation, are corrected by a dentist.
- A neurologist using massages or exercise therapy will eliminate neurological pathologies, which will reduce the amount of salivary fluid.
- Gastrointestinal diseases, helminthic invasions are treated by a gastroenterologist, as a result of which the secretion of glands is reduced.
If a situation arises when it is required to treat directly hypersalivation, apply:
- Radiation therapy, due to which the salivary ducts are blocked by scars.
- Surgery, in which glands that excrete too much saliva are selectively removed.
- Cryotherapy Its essence is to increase the frequency of swallowing, which reduces the amount of fluid.
- Botox injections that paralyze secretion production.
- Drugs that suppress excessive salivation in humans.
 The folk method is based on herbal medicine. Adequate use of folk remedies causes positive feedback and comments from practicing dentists. Doctors often prescribe herbal rinses and compresses from infusions of medicinal plants, which reduce the release of salivary fluid. The dominant direction of herbal medicine is rinsing the mouth with various tinctures, decoctions:
The folk method is based on herbal medicine. Adequate use of folk remedies causes positive feedback and comments from practicing dentists. Doctors often prescribe herbal rinses and compresses from infusions of medicinal plants, which reduce the release of salivary fluid. The dominant direction of herbal medicine is rinsing the mouth with various tinctures, decoctions:
- decoction of oak bark;
- camomile tincture;
- a decoction of the fruits of viburnum;
- vegetable oils;
- alcohol tincture from a shepherd’s bag.
Pentalism can occur at any age, for different reasons. Regular examinations by a specialist will help to identify and get rid of pathologies, against which hypersalivation occurs, to prevent the occurrence of new diseases and serious complications.