Trigeminal inflammation on the face: symptoms and treatment
The trigeminal nerve is an important component of the entire human nervous system. He is responsible for almost all processes that occur with the face - facial expressions, sensitivity, work of the jaw. Inflammation of the trigeminal nerve is a rather complicated problem, as it is accompanied by significant pain and, in the absence of treatment, severe consequences.
Content
Localization
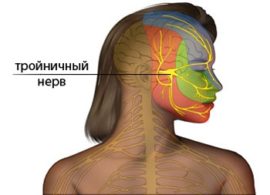 To understand where the trigeminal nerve is located, you can take a look at the photo.
To understand where the trigeminal nerve is located, you can take a look at the photo.
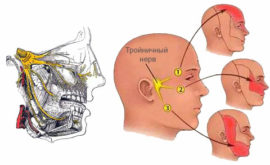
The trigeminal nerve originates in the temporal zone (near the ear), and then triple branching emerges from it. Branching consists of three different directions:
- Eye branch.
- The branch leading to the upper jaw.
- Mandibular nerve.
In turn, there are still many other small vessels that spread throughout the face from the main large branches of this nerve process. Thus, this nerve process controls the work of all the facial muscles.
Causes of inflammation
Trigeminal neuralgia (trigeminal neuralgia) is a disease accompanied by a strong inflammatory process. The causes of inflammation of the trigeminal nerve may be pinching or circulatory disorders. The following internal states are capable of provoking compression:
- tumor formations;
- injuries and adhesions;
- pathological expansion of the vessels of the brain;
- congenital malformations of the skull bones.
External factors that cause inflammation include:
- dental problems (gingivitis, periodontitis, periodontal disease, improper treatment or prosthetics);
- inflammation of the sinuses.
Trigeminal inflammation on the face can also be triggered by various diseases of the nervous and cardiovascular systems:
- atherosclerosis;
- multiple sclerosis;
- Cerebral palsy;
- epilepsy;
- meningitis;
- encyphalopathy.
The trigeminal nerve on the face can become inflamed due to damage to the human body by severe viruses or infection (herpes, meningitis, neurospide, tetanus, botulism, tuberculosis, herpes zoster, malaria, polio, etc.).
Another cause of trigeminal neuralgia can be called severe hypothermia of the head and face. That is why children from childhood are taught to wear a hat before going out.
Trigeminal disease can sometimes be triggered by completely extraneous factors and conditions:
- allergic reactions;
- disruption of the endocrine system;
- hormonal disruptions;
- stress, depression, nervous breakdowns, neurosis;
- advanced age;
- the presence of parasites in the body;
- autoimmune diseases.
- lack of vitamins and minerals in the body.
Symptomatology
Symptoms of trigeminal inflammation can be divided into conditional primary and secondary signs.
Pain syndrome
The first and main symptom of trigeminal inflammation is pain. She can torment the patient for several days, weeks or months. After some time, even without appropriate treatment pain can disappear, but this in no way indicates that the disease receded.
The pain is localized in those places where the trigeminal nerve passes, that is, a person has only one part of the face that hurts. The starting points of the onset of pain can be the temple, the wings of the nose, the corners of the mouth, and the jaw. The location of pain in the jaw area very often prevents the doctor from determining the exact diagnosis.The fact is that the same manifestations are characteristic of toothache caused by problems with the teeth.
 Painful sensations in case of damage to the trigeminal nerve manifest as acute, piercing, short-term spasms. Such cramps are almost impossible to calm by taking painkillers. They can occur during palpation of the face, chewing, facial expressions, or simply out of the blue.
Painful sensations in case of damage to the trigeminal nerve manifest as acute, piercing, short-term spasms. Such cramps are almost impossible to calm by taking painkillers. They can occur during palpation of the face, chewing, facial expressions, or simply out of the blue.
Pain with trigeminal neuralgia is conditionally divided into two types:
- Typical.
- Atypical.
Typical pain manifests itself in sudden, paroxysmal cramps, spreading throughout the right or left side of the face. Such spasms are somewhat reminiscent of electrical discharges. Typical pain occurs abruptly and also abruptly disappears. Its duration does not exceed a couple of minutes, and the frequency can reach several times per hour, but after a couple of hours it completely disappears.
Atypical pain can be determined by prolonged, severe pain during the whole day or several days. Pain can be spread all over the face and be accompanied by a tick.
Secondary symptoms
If the trigeminal nerve is inflamed, then along with unbearable pain the patient may experience other manifestations:
- swelling and redness of the eyelids;
- uncontrolled, increased salivation;
- lacrimation of the eyes;
- violation of taste buds;
- numbness of the face;
- trouble sleeping;
- weakness and chills;
- muscle spasms;
- facial asymmetry;
- pallor and redness of the skin;
- dry or oily skin;
- rashes and itching on the skin of the face;
- headaches;
- painful tic on the face;
- distorted facial expressions and grimaces;
- increase in body temperature;
- insomnia, irritability, anxiety.
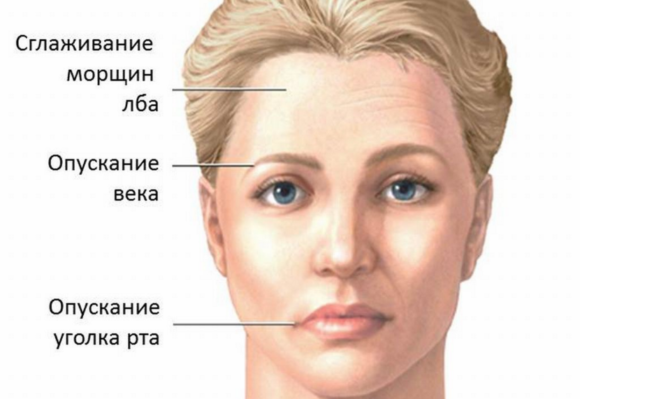
In the following image, you can see how the face changes with facial neuralgia:
Diagnostics
Human anatomy is such that it is not always possible to make an accurate diagnosis based on symptoms. That is why it is sometimes quite difficult to diagnose by eye whether the trigeminal nerve hurts or is it a matter of another disease.
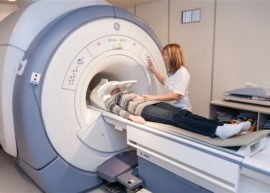 Any doctor in order to find the cause and source of the disease must conduct the correct diagnosis. When treating the trigeminal nerve, it consists in talking with the patient, examining and palpating his face, viewing a hospital card.
Any doctor in order to find the cause and source of the disease must conduct the correct diagnosis. When treating the trigeminal nerve, it consists in talking with the patient, examining and palpating his face, viewing a hospital card.
Highly Often, an MRI or CT scan should be done to accurately determine the diagnosis.. In Moscow, you can contact some treatment centers for electroneurography, electroneuromyography, or electroencephalography. Such instrumental research methods allow you to have a more accurate picture of the disease.
Treatment methods
Treatment of inflammation of the trigeminal facial nerve should be carried out in accordance with certain rules. First you need to remove the pain syndrome, then start treating the underlying disease that caused the neuralgia, and at the same time eliminate the inflammation that arose in the place where the trigeminal nerve is located. In order to thoroughly restore his health, the patient will have to lie in the hospital for at least a few weeks, and only then continue to be treated at home.
During the treatment of trigeminal facial nerve, the following medications can be used:
 Initial anesthesia (when the nerve just begins to become inflamed) can be carried out at the expense of spasmolytics like Ibuprofen, Spazmalgon, Analgin, Baralgin, etc. The course of taking such drugs should not exceed two weeks.
Initial anesthesia (when the nerve just begins to become inflamed) can be carried out at the expense of spasmolytics like Ibuprofen, Spazmalgon, Analgin, Baralgin, etc. The course of taking such drugs should not exceed two weeks.- If it is not possible to relieve pain with the help of weak analgesics, you have to seek help from stronger non-narcotic drugs - Ketanov, Deksalgin, Ketalgin, etc.
- Sometimes even such drugs can not do anything with pain - then circumstances force doctors to prescribe the use of narcotic painkillers - Tramadol, Morphine, Promedol, Nalfubin, etc.
- Until recently, treatment of the trigeminal nerve was usually carried out using the anticonvulsant drug carbamazepine. Today, for many doctors, this practice is a thing of the past. The fact is that these drugs have a large list of contraindications and are able to affect many internal organs.
- You can also calm tics and cramps with Gabapentin, Diphenin, Lamotrogin, or Valproic acid.
- Along with painkillers and anticonvulsants, a doctor may prescribe medication with a sedative effect, for example, diphenhydramine with analginum.
- Sometimes doctors have no choice but to prescribe antibiotic therapy. However, this practice is used only to treat the underlying disease.
- During treatment of the trigeminal nerve, antiviral drugs are sometimes used - this tactic is justified when the disease is caused by a viral infection.
Sometimes trigeminal neuralgia is treated with alcohol blockade. For this, the patient is given an injection with a solution of alcohol and novocaine. But in this case, doctors need to be aware that the patient may start bleeding or develop a hematoma at the site of skin puncture.
Another method of treating the trigeminal nerve is therapeutic massage. Many patients find this technique quite effective and most harmless.
Home treatment
Treatment of trigeminal inflammation at home is not possible. In order to recover from such a complex disease, you must first undergo a thorough diagnosis, and only then determine the treatment regimen. A prerequisite for proper therapy is a timely visit to a doctor. Only he will be able to identify this ailment and prescribe a medicine.
Before treating inflammation of the trigeminal nerve with folk remedies, it is necessary to consult a doctor. Sometimes doctors allow the use of alternative medicine as an adjuvant. But the main therapy should still be carried out medically.
Operation
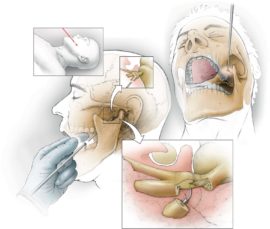 The figure shows how the operation to restore the trigeminal nerve.
The figure shows how the operation to restore the trigeminal nerve.
In cases where drug treatment does not give proper results, surgical intervention may be prescribed. The same tactic is relevant when pressure is exerted on the trigeminal nerve. The pressure of a brain tumor or vessel can damage and inflame a given nerve process.
There are two types of such an operation:
- Microvascular decompression.
- Radio frequency destruction.
The surgeon himself must determine the choice of operation. With microsurgical decompression, the posterior part of the cranium is trepanized, and a special material is laid in the gap between the root of the trigeminal nerve and the vessels pressing on it, which performs the function of laying. Such a technique does not allow the vessel to damage the root.
With radio frequency destruction, radio waves are directed to the affected areas of the roots and destroy them.
Complications
If in the presence of these symptoms in time you do not consult a doctor and do not cure neuritis, then the following consequences are very likely:
- hearing problems;
- violation of taste buds;
- constantly haunting pain;
- atrophy or paresis of the muscles of the face;
- disorders of the central nervous system;
- problems with the nervous system.
Summing up, it is worth saying that prevention is always the best treatment. And in order to prevent the trigeminal nerve from getting sick, stressful situations, hypothermia and acute viral diseases must be avoided.