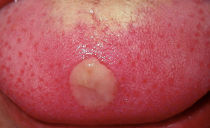
Inflammation of the papillae on the root and tip of the tongue, causes of enlargement (hypertrophy)
Papillae of the tongue are structural formations that take part in the perception of the touch and taste of food. By roughening the tongue, they help hold and mechanically process food. Many people think about the presence and purpose of the papillae only when they become inflamed, increase and begin to cause discomfort.
Inflammation of the papillae on the root and edges of the tongue can occur for various reasons: both against the background of dental diseases, and because of acute or chronic pathologies of internal organs.
Content
Anatomical and physiological features of the papillae
Both in children and in adults papillae cover the entire front surface of the tongue: back, tip, root and edges. Their surface is formed by an epithelium that is not keratinized throughout life.
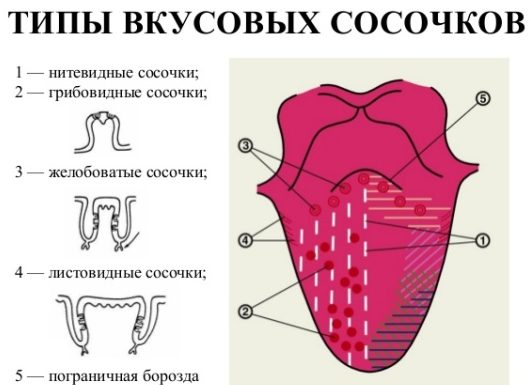
By structure and function, doctors divide the papillae into the following types:
| Variety | Location (language section) | Functions |
|---|---|---|
| Threadlike | Edge surface | They are responsible for the sense of touch and help to hold food, do not participate in the perception of the taste of food |
| Conical | Edge surface | Responsible for the sensation of pain and temperature, contribute to the mechanical processing of food |
| Grooved | Root | Perception of bitterness |
| Leaf-shaped | Plot of tongue near the palatine arches | Perception of bitterness |
| Mushroom-shaped | The entire surface except the central back | Sweet perception |
Despite the fact that only gutter-shaped, mushroom-shaped and leaf-shaped papillae are responsible for the perception of taste, all their varieties are equally important for humans. Any change associated with them indicates a malfunction in the body and causes discomfort.
Tongue papillae increased - causes
Hypertrophy (increase) of the papillae occurs due to inflammation of the mucous membrane of the tongue. Not only the sizes of structural formations change: they can turn red or black, become covered with a touch of different shades. Visible changes may be accompanied by pain, a sensation of the presence of a foreign body in the oral cavity, itching, loss of taste sensitivity or its distortion due to damage to taste buds.
The main causes of inflammation of the papillae of the tongue are:
- Exposure to aggressive food components.
- Thermal burn or hypothermia.
- Injuries caused by teeth, tartar, sharp objects, hard bristles of the toothbrush, rough food, uncomfortable or new dentures.
- Consequences of the piercing.
- Side effects of taking medication.
- Gastroesophageal reflux is a pathological phenomenon in which food and digestive juice from the stomach fall back into the oral cavity. A similar situation occurs during vomiting.
- Malnutrition, leading to a lack of nutrients in the body.
- Infectious inflammation provoked by various pathogens: bacteria, fungi, viruses.
- Allergy.
- Internal malfunction of a metabolic or hormonal nature.
- Chronic diseases of the internal organs.
- Consequences of smoking and frequent drinking.
Why are the papillae of the tongue inflamed, photo
It is not always possible to figure out independently why the papillae inflamed on the root or tip of the tongue. Sometimes the reason is obvious - when an injury or burn occurs. But to establish a connection between inflammation of the tongue and internal diseases only doctors can do it after a thorough diagnosis.
Dental reasons
In most cases, the reason that a person has inflamed and enlarged papillae on the root or along the edges of the tongue is glossitis, developing due to infection of the oral mucosa. Symptoms of the inflammatory process vary depending on the pathogen.
Fungal glossitis
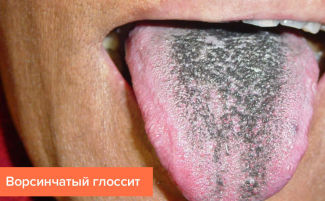
Under the influence of pathogenic fungi, a yeast, mycotic or villous form of glossitis develops. As a result of the vital activity of fungi, a white coating accumulates on the surface of the grooved taste buds, while trying to remove it, the mucous membrane of the taste organ begins to bleed. A sour smell is felt from the patient’s mouth, and the child may experience an increase in temperature.
Enlarged papillae at the root of the tongue may resemble red villi. The doctor pinches them, treating with dissolved copper sulfate. In addition, mouthwash with antiseptics and local treatment of wounds with antifungal agents are indicated. Severe forms of the disease must be treated with antifungal drugs for oral administration.
Bacterial glossitis
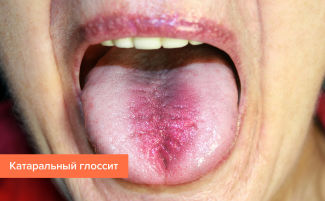
Bacterial infection of the mucous membrane of the tongue leads to the development of catarrhal or ulcerative glossitis, stomatitis. Inflamed parts of the taste organ are covered with white or red ulcers, aphthae, on which a plaque of different shades accumulates. There is pain, swelling, bleeding.
To find an effective antibiotic, you need to determine what types of bacteria inflamed papillae. In addition to antibiotic therapy, mouthwashes and antibacterial ointments are prescribed.
Viral glossitis
Viral particles provoke a herpes infection. Between the layers of soft tissues of the tongue, fluid accumulates, and on the tip - watery white or red bubbles appear.
During the treatment of viral glossitis, bubble rashes should be treated with antiviral gels. In addition, mouthwash with antiseptic drugs is indicated.
Internal causes
Due to infectious and non-infectious diseases of internal organs, other forms of glossitis may develop:
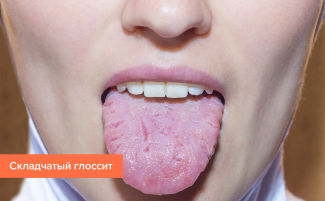
- Desquamative. It is accompanied by the formation of a “geographical language”, covered with white and red spots, separated by dark lines. Inflamed and enlarged papillae in the tongue, leading to the formation of desquamative glossitis, are a consequence of liver diseases, hematological diseases, metabolic disorders. In the process of treating the disease, observation by a therapist, gastroenterologist, hematologist is necessary.
- Gunter. It develops with a lack of vitamin B12 and folic acid, resulting in anemia. In both children and adults, the tongue with such a disease becomes raspberry red and shiny, as if polished. To eliminate inflammation, you need to take pharmacy vitamins.
- Interstitial. It is accompanied by a modification of muscle tissue, hypertrophy of the grooves in the tongue. If there are symptoms of this form of glossitis, the therapist sends the patient to the venereologist, since the cause of this inflammation is syphilis.
- Atrophic. It occurs due to an excess of vitamins A and E or permanent damage to taste buds in chronic inflammation. Over time, the patient's taste perception weakens - it is almost impossible to eliminate such a defect.
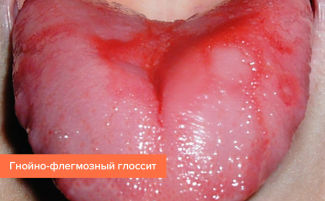
Photo of different forms of glossitis
Diagnostic measures
If you find the first signs of glossitis, you should definitely contact a dentist, and if necessary, a therapist and specialist specialists. Such examinations may be needed:
- A smear from the surface of the tongue to identify the bacterial flora.
- PCR tests for the presence of bacterial, viral, fungal infections.
- Histological and cytological laboratory analysis (if cell degeneration is suspected).
- Blood tests - general, biochemical, for hormones, for the presence of pathogens of AIDS, syphilis, hepatitis and other infectious diseases.
If during the diagnosis a fungal or bacterial infection is detected, it is necessary to check the sensitivity of the pathogenic flora to antibacterial and antifungal drugs.
After the examination, the patient can be referred for further observation and treatment by an endocrinologist, immunologist, allergist, and otolaryngologist.
General treatment recommendations and consequences
The formation of small vesicles or sores, the manifestation of white or pink papillae on the tongue, the proliferation of villi are the first symptoms of the inflammatory process, which in the future can lead to hypertrophy of the grooved, mushroom-shaped and other types of papillae.
The dangerous consequences of glossitis are suppuration, the spread of infection to the respiratory and digestive organs. The pain that accompanies an increase in receptor structures interferes with talking and eating, and in babies it causes severe anxiety and even weight loss. Therefore, any symptoms of glossitis require immediate treatment. The tactics of treating inflammation of the papilla of the tongue depends on the cause of its development.
Treatment of papillae of the tongue, inflamed due to injuries and burns
Burn and traumatic injuries of the mucous membrane of the tongue lead to the development of papillitis. In the absence of other alarming symptoms - fever, severe swelling and suppuration of tissues - papillitis can be managed at home. At home:
- Rinsing the oral cavity with disinfectants. It is better to take decoctions of medicinal herbs, for example, calendula.
- Processing the tongue with agents that accelerate the healing and restoration of soft tissues. Solcoseryl ointment, Lugol's solution, Chlorophyllipt, sea buckthorn oil can be used.
- The use of analgesics: Lidocaine, Anestezin. It is better to consult a doctor about the dosage and regimen of taking painkillers.
During the treatment of inflammation of the taste buds of the tongue, you need to adhere to a special regime that allows you to create sparing conditions for soft tissues damaged by papillitis:
- It is undesirable to smoke and drink alcohol.
- Do not eat food with a sharp salty or spicy taste.
- Temporary removal of dentures may be necessary.
If the prosthesis became the cause of inflammation of the papillae of the tongue, you should definitely contact your dentist to correct the shape or completely replace the inconvenient design.
Treatment of infectious inflammation
With inflammation of the mucous membrane of the oral cavity, glossitis and papillitis, you must adhere to the following rules:
- With an increase in papillae on the root and edges of the tongue, you can not drink alcohol-containing drinks, it is undesirable to smoke.
- Food should be moderately salty, without sharp spices, not hot and not very cold.
- If the cause of the appearance of red papillae on the tongue is an infection or disease of the internal organ, the patient has a fever, you must go to the doctor to find out why the inflammation developed. Such inflammatory processes pose the greatest danger to children, so you need to contact a pediatrician immediately.
Papillitis and glossitis are serious diseases that not only cause discomfort, but also entail other dangerous consequences. If a person noticed that he has enlarged papillae on the tip or back of his tongue, he should immediately consult a doctor to identify and cure the disease at an early stage. Mild forms of glossitis can lead to the development of more severe, accompanied by the complete death of the enlarged papillae and the risk of poisoning the body with toxins of microorganisms.
Inflammation of the papillae in children
Most often, the cause of inflammation of the papillae in the tongue of children is desquamative, allergic, traumatic or fungal glossitis. In children, inflammation of the papillae at the root of the tongue proceeds in a more acute form than in adults. Therefore, if the baby's mucous membrane of the oral cavity begins to become inflamed, it is necessary to immediately consult a specialist. Treatment of inflammation and enlargement of the papillae in the child’s tongue should be carried out in strict accordance with the recommendations of the pediatrician.