Tooth pulpitis: what is it, causes and methods of treatment
Often a person himself is to blame for the fact that he needs to treat such a dental defect as pulpitis of the tooth, since root causes most often lie in non-compliance with oral hygiene. But unlike caries, pulp damage cannot be ignored for a long time, because it is accompanied by severe discomfort and pain. Therefore, sooner or later with this problem you have to go to the dentist.
Content
The essence of pathology
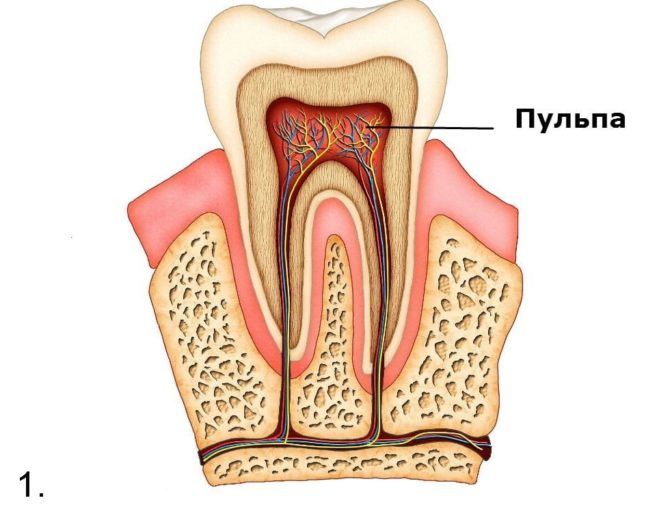
Externally, the teeth with pulpitis look very strong, they are covered with a rather thick layer of hard tissues, represented by enamel and dentin, in order to perform their functions. The tooth pulp suffers - the internal soft contents in which the nerve endings and blood vessels are located. Through this part, the crown and root receive the necessary nutrients.
With the defeat of any surface part of the tooth or infection through the blood in the pulp, the inflammatory process begins. Soft tissues swell due to intense rush of blood to provide local immune defense. The dental chamber is a limited space, so the pressure on the dental nerve increases, and the person begins to feel pain.
That's what pulpitis is in dentistry - pulp inflammation. It is very important to recognize it in time and begin treatment, because this pathological condition can have very dangerous consequences.
Many patients do not understand why pulpitis is dangerous. Due to the violent inflammatory process, a lot of pus can form - a mixture of destroyed pathogens of the infection and dead protective immune cells. An excess of purulent substance that does not fit in the pulp chamber, through the hole formed, goes into the gum - so fluxes and fistulas are formed, which are dangerous sources of infection. Hence, pathogenic microorganisms with blood can penetrate into any other organs of the body and provoke their inflammation.
Causes of Pulpitis
The reasons for the development of pulpitis can be various, but almost always this disease is associated with a violation of the integrity of the tooth, its pulp chamber and the penetration of infection. Non-infectious factors are extremely rare. The main causes of pulpitis:
- The formation of a deep carious cavity due to non-compliance with hygiene rules, malnutrition, metabolic problems, physical destruction of enamel. Pathogenic microorganisms penetrate the pulp through the crown of the tooth.
- The development of infection in the periodontal pocket in which the tooth is attached.
Microorganisms can enter the chamber through the roots in case of infectious diseases of the gums or careless actions of the dentist who performs manipulations with violation of sanitary standards.
- Penetration of pathogenic bacteria and viruses through the bloodstream from other organs. Pulpitis is a complication of rubella or flu.
- The spread of the infectious process from nearby organs. Sinusitis can provoke inflammation of the tissues of the upper teeth adjacent to the maxillary sinus.
- Tooth injuries, in which the internal cavity is opened. For this reason, pulpitis of the front tooth often appears.
- Incorrect treatment of caries, in which the carious cavity is connected to the pulp chamber.
- In rare cases, the pulp becomes inflamed without opening the chamber, with the deposition of insoluble salts on its inner wall and irritation of the nerve.
- Turning a tooth to install a crown without depulping leads to the development of pulpitis due to opening the cavity.
Disease classification
Depending on the nature of the course of the disease, the causes of its occurrence and the pathways of infection, these forms of pulpitis are distinguished:
| Pulpitis shape | Developmental stages |
|---|---|
| Acute pulpitis - the first stage of the disease, causes severe pain, especially at night. At first, a serous formation is formed, with time it turns into purulent. | Focal - the initial, serous stage of the disease, in which dentin begins to collapse at the site of contact with the carious cavity. The pain has a shooting character, periodically subsides and returns. Duration does not exceed 2 days. |
| Diffuse - further destruction of the pulp in the area of the crown and root. Toothache becomes longer, periods of decay are reduced. Pus appears. The source of discomfort is difficult to determine, the pain is given to other parts of the skull. Stage lasts up to 2 weeks. | |
| Chronic pulpitis is an acute complication. The pain syndrome is not intense, but sharp pain can occur with an exacerbation of the chronic form. | Fibrous pulpitis is often a painless form in which the patient may not notice the disease. Pulp and carious cavities may not be connected. Such a pathology can be cured. |
| Hypertrophic pulpitis is the stage of active destruction of the pulp under the extensive carious cavity. The tissue becomes dirty gray, smells unpleasant, the nerve atrophies. | |
| Gangrenous pulpitis is the stage of connection of the pulp cavity with the carious. Granulation occurs - cavity overgrowing with the formation of a polyp, which, when pressed, hurts and bleeds. |
Pulpitis Symptoms
The initial stages of chronic pulpitis can be almost asymptomatic. This is an insidious feature, since the patient does not attach due importance to a serious disease and does not go to dentistry. The acute form and exacerbations of chronic are always accompanied by severe pain, which have such features:
- As inflammation develops, seizures become longer and more frequent.
- Pain can change under the influence of temperature: decreases with cooling and intensifies with heating. If such a reaction is noticeable, then inflammation is already accompanied by the formation of pus.
- An attack may begin due to the ingestion of very sweet food in the cavity or when pressing on the crown.
- The more the pulp is affected, the more common the pain becomes. It can be felt in the opposite jaw, in the eye or ear.
Pulpitis differs from caries by a longer or constant pain, which subsides only after some time after elimination of the irritant, and not immediately.
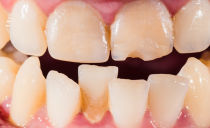
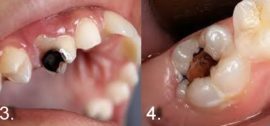 The pulpite tooth changes externally: its crown loses its whiteness, in the places where holes appear in the inner chamber, grayish spots of diseased soft tissues are visible. What pulpitis looks like, look at pictures 3.4.
The pulpite tooth changes externally: its crown loses its whiteness, in the places where holes appear in the inner chamber, grayish spots of diseased soft tissues are visible. What pulpitis looks like, look at pictures 3.4.
Periodically, bleeding may occur. Due to the intense rush of blood to the jaw, the gum swells, and then the cheek. The face may look asymmetrical, problems with diction are possible.
Diagnostics
To find out what caused the pulpitis of the tooth and begin the competent treatment of this disease, you need to consult a dentist. After listening to the patient’s complaints, having examined and identifying symptoms, the doctor can send for additional examinations: X-ray, odontodiagnosis.
During a dental examination, the doctor determines the signs of a violation. He probes and evaluates the sensitivity, as well as the mobility of the tooth in the gum.
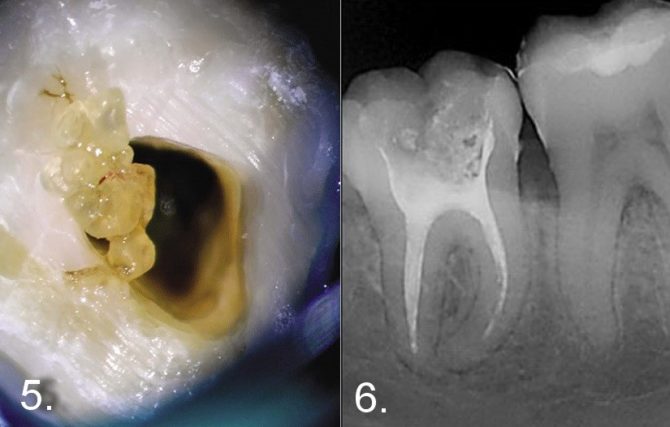
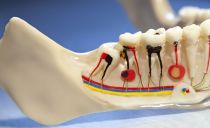
On the x-ray, pathological formations can be seen - denticles. They develop during dystrophic processes in the dental tissue and look like rounded dark spots (photos 5, 6). Denticles can be located inside the tooth cavity or in the area of the root canals.
The image may also display an internal granuloma - a clear, rounded bright spot inside the tooth, most often the front. After the diagnosis, the doctor decides which treatment method is most suitable in this case.
Treatment
Be sure to treat yourself if pulpitis is found during the examination. Leaving this dental problem unresolved, you can put yourself at risk for more dangerous diseases - sepsis, phlegmon, periostitis. With a prolonged purulent process, the tissues around the source of infection soften, due to which the teeth begin to stagger, and when performing manipulations in dentistry, a jaw fracture can occur.
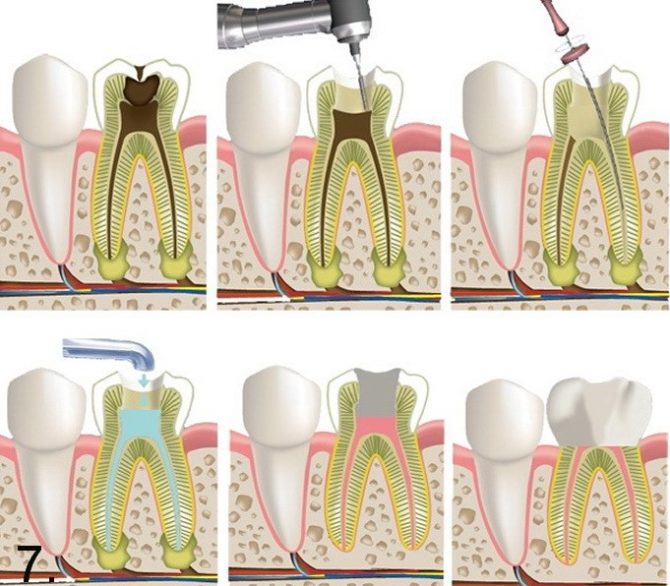
A pulpitis tooth can be treated in different ways, but it must be partially or completely depulped. - remove soft inflamed tissue from the inner chamber. There are such approaches:
- With vital amputation, anesthesia is done and depulpation is performed in the crown of the tooth, the nerve is not previously killed.
- With vital extirpation under anesthesia, all soft tissues are removed at a time. The operation is performed without first killing the nerve.
- With devital amputation, the nerve is first killed, often using arsenic paste. And then the coronal part of the pulp is removed. When killing a nerve, you will have to go to the dentist several times.
- With devital extirpation, after killing a nerve, the entire pulp is removed.
After depulpation, the canals and crown are filled, and then the tooth is treated with antiseptics to eliminate the infection. The picture number 7 shows the stages of treatment of a tooth affected by pulpitis:
After treatment, there is no pain, or they subside after 2-3 days. If the pain does not go away, you should consult a doctor.
Prevention
The picture of running pulpitis can scare anyone, so it’s better to do prophylaxis than to treat it and endure pain later. The main rule is to follow the usual rules of hygiene, two-time brushing in the morning and evening. In this way, caries, pulpitis, and all other diseases that can become their complications can be prevented.
You should eat right so that hard and soft tissues of the tooth receive a sufficient number of trace elements for their construction. Care must be taken to prevent various injuries. At least twice a year, it is necessary to undergo preventive examinations at the dentist so as not to miss the development of diseases that are not accompanied by noticeable manifestations, pain. If there is discomfort in the mouth, the visit to the doctor should not be postponed.
Pulpitis is an unpleasant and dangerous disease, which can result in the loss of one or even several teeth. But modern treatment methods allow you to save as much of the crown as possible. If you take the first step in time and turn to the dentist, the cured tooth will function as before. It is only necessary to be careful not to destroy the seal.