White plaque in the hole after tooth extraction: photos, causes and treatment
When a sore tooth is removed, the patient feels relief. A few days after the operation, the wound heals, and all the troubles are left behind. But during the healing period of the injured gum, one should especially carefully monitor its condition. AND if something appears in the hole that was formed after the person had the tooth removed, you should immediately consult a dentist and find out the cause of this phenomenon.
Content
Natural causes of white plaque on the wound formed after tooth extraction
After tooth extraction, an open wound remains in the oral cavity, through which, if there were no human immunity, any pathogens would penetrate. But such protective reactions of the body exist, and they start immediately after removing the root from the hole.
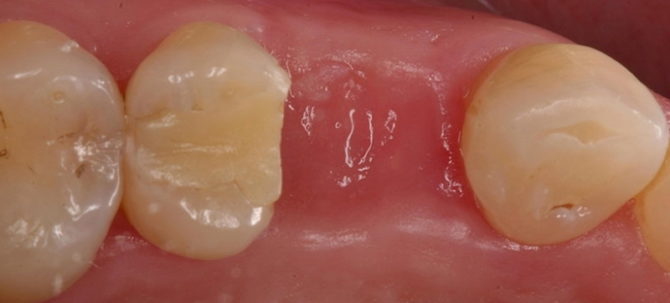
Human blood contains substances that, when the walls of the vessels are disturbed, form a thrombus of fibrin, which prevents the opening of bleeding. In the oral cavity, this process is also facilitated by the special components of saliva. Part of the fibrin settles on the surface of the wound. In some people, this layer is practically not noticeable, in others, a visible fibrinous deposit of white color forms, as in the place of a torn tooth in the photo on the right.
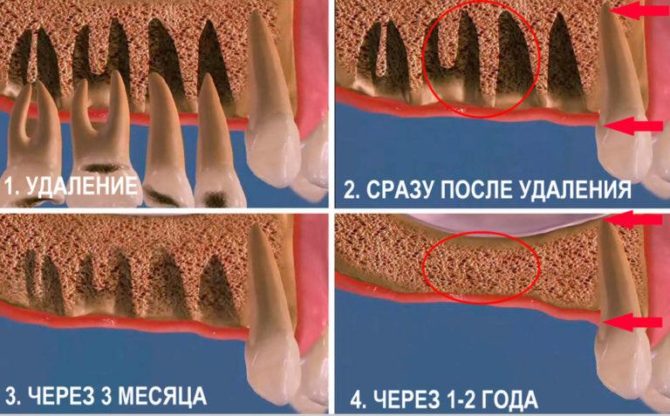
If tissue regeneration proceeds without complications, fibrous plaque disappears over time. The void formed inside the hole is filled with epithelium and connective tissue, after which bone tissue forms in this place. The healing process of bone tissue after tooth extraction is shown in the photo:
A few days after extraction, the gum near the hole becomes paler. This means that the inflammatory process, which always develops after surgery as a natural protective reaction of the body, subsides. The rush of blood to the wound decreases, and the color of the mucous membrane of the gums becomes the same.
When white plaque at the site of the extracted tooth is dangerous
White plaque at the site of a torn tooth does not always occur as a natural phenomenon. Sometimes this symptom indicates a developing complication due to dentist errors during tooth extraction or improper patient behavior in the postoperative period:
- White spots near the hole, accompanied by redness and swelling of the mucous membrane of the gums, indicate infectious inflammation and suppuration, that is, the development of alveolitis. The hole becomes inflamed with inadequate antiseptic treatment during surgery, after being injured or premature loss of a blood clot. If the sharp edge of the hole forms, it will irritate the surface of the wound and open the germs to the path inside the hard tissues of the jaw. Especially often alveolitis occurs after the removal of wisdom teeththat is associated with increased invasiveness of the operation.
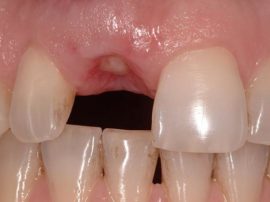
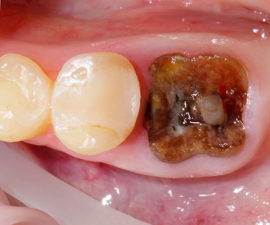 If the tooth has crumbled upon grasping with forceps, fragments of the root may remain inside the hole, as in the photo on the right. They interfere with the healing of the gums, injure the surrounding soft tissue and can provoke suppuration. Most often, fragments remain in the hole after the extraction of wisdom teeth, which is associated with their uneven roots.
If the tooth has crumbled upon grasping with forceps, fragments of the root may remain inside the hole, as in the photo on the right. They interfere with the healing of the gums, injure the surrounding soft tissue and can provoke suppuration. Most often, fragments remain in the hole after the extraction of wisdom teeth, which is associated with their uneven roots.- In case of inaccurate chewing of food after tooth extraction, food particles can get into the hole and get stuck in it.After a few hours, they will begin to rot and become a hotbed of infection.
Without appropriate treatment, inflammation of the well can not only lead to the spread of infection to nearby tissues and internal organs, but also to the development of tumors.
Anxiety symptoms
In the normal course of the wound healing period formed after tooth extraction, unpleasant postoperative sensations pass quite quickly. Bleeding stops after about 3 hours (it can be longer if the wisdom tooth is removed), pain and swelling subside after 2–4 days, a blood clot and fibrous plaque resolve a few days after extraction.
With the development of complications, the following symptoms may appear:
- The pain intensifies, acquires a "shooting" character, spreads to the jaw, ear or temple.
- Swelling increases, the lymph nodes in the face swell and become hard.
- Blood does not stop after 3 hours, or bleeding resumes some time after surgery.
- There is a febrile condition.
- The sensitivity of the skin near the area of the jaw where the tooth was pulled out is lost.
- It becomes difficult to move the jaw.
- White or yellowish liquid flows from the well.
- The wound is covered with a thick layer of plaque, from which an unpleasant odor emanates.
Is it necessary to remove the white plaque formed on the gum after tooth extraction
To determine whether it is necessary to take any therapeutic measures, you need to find out the cause of the appearance of white plaque on the postoperative wound by visiting the dentist again. If the doctor does not notice any signs of pathology, then the hole is covered with natural fibrin plaque. You can not remove it, since it is a protective barrier for pathogenic microorganisms.
If a person tries to remove fibrous plaque from a hole without consulting a dentist, he will provoke infection with further unpleasant consequences.
If a white plaque formed after tooth extraction is a sign of an inflammatory process, it is necessary to start treatment as soon as possible:
- If fragments of the root or stuck pieces of food are found, they are removed and the wound is thoroughly treated with antiseptics. The dentist can prescribe a course of antibiotics to the patient so that the inflammation does not affect a larger part of the gums.
- With the development of infection, the doctor puts a tampon with medicine in the hole. Drugs for oral administration, as well as rinsing with antiseptics, may be prescribed.
- If a tumor has formed due to prolonged inflammation, it is removed surgically.
What can not be done
If white plaque develops in the hole after tooth extraction, do not self-medicate before visiting dentistry. Attempts to provide first aid at home can lead to more serious complications:
| Patient Actions | Effects |
|---|---|
| Mouth rinse | Flushing of the protective fibrin layer, loss of a blood clot with the subsequent development of alveolitis |
| Do-it-yourself attempts to remove a clot, tooth residue, food or pus | Infection, which can spread not only to the soft, but also to the hard bone of the jaw |
| Toothbrush in the area of a torn tooth | Damage to the fibrin layer, bleeding, infection of the postoperative wound with an infection |
| Applying a warm compress | Increased blood circulation leads to bleeding, and in the presence of suppuration, the formation of pus accelerates, the likelihood of infection of the internal organs increases |
| Medication | Individual intolerance reaction, unwanted side effects |
| Smoking in the first few hours after surgery | Burn of the injured gingival mucosa, damage to the fibrinous layer and the development of the inflammatory process |
If the patient has the opportunity to contact his dentist, he may ask what painkillers and antipyretic drugs can be taken before visiting the dentistry.
In most cases, you should not be afraid of white fibrinous plaque in the part of the gums in which the teeth had to be pulled out. This phenomenon is a natural reaction by which the body has protected itself from infections. But if the hole becomes covered with a thick coating with an unpleasant odor, swells and turns red, and the patient's condition worsens, you need to visit the dentist again to treat the complications that have arisen.