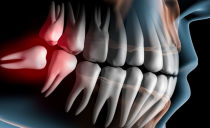
What is curettage of periodontal pockets, methods of curettage
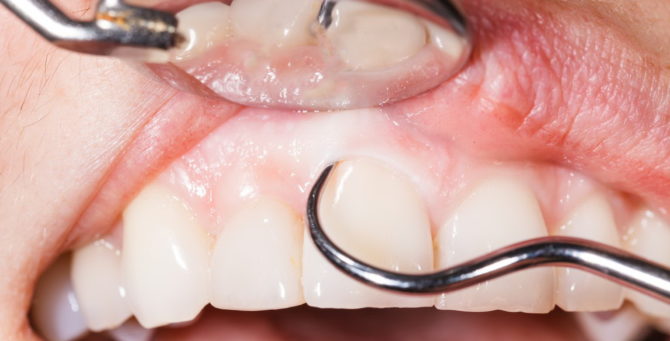
Closed or open curettage of periodontal pockets is the cleaning of granulation tissue and subgingival deposits. The procedure is carried out before the treatment of major periodontal diseases to increase the effectiveness of further medical measures. Manipulations are performed in the dental clinic using professional tools.
Content
When is subgingival scrubbing performed?
The main indications for the procedure are:
- severe bleeding gums;
- periodontitis of various degrees of severity;
- the formation of a noticeable gap between hard dental and soft gingival tissues;
- calculus deposition.
The gum tissue must be dense, otherwise the procedure will be ineffective. It is also advisable that the patient has no bone pockets, since curettage is pointless if they are present.
Read more about the indications for cleaning periodontal pockets in the video:
Contraindications for cleaning gingival pockets
The main contraindications to curettage brushing include:
- the release of purulent contents from the gingival pocket;
- the presence of an abscess in the oral cavity;
- bleeding disorder;
- bone pathology;
- some cardiological pathologies;
- inflammatory process in the body (acute respiratory infections, flu);
- fibrous tissue growth;
- anomalies in the structure of the jaw and the position of the dental units;
- underdevelopment of the jaw;
- any infection in the oral cavity in the acute stage;
- high tooth mobility.
Before the procedure, a diagnosis is always prescribed. If any complications and pathologies are detected, gum curettage is prohibited.
If the patient has metal crowns, then before the procedure they must be removed and replaced with temporary plastic ones. This is due to the fact that during the session the doctor removes the crowns and completely cleans all the teeth in order to achieve the maximum effect. Teeth with metal crowns are partially cleaned.
How professional brushing differs from gingival curettage
Professional cleaning involves processing the external surface of the tooth, and thanks to curettage, not only the teeth themselves are cleaned, but also periodontal pockets.
The procedure allows you to:
- to clean the dentition;
- clean the granulate;
- remove periodontal pocket;
- eliminate bleeding and gum inflammation.
Performing curettage toothbrushing according to compulsory medical insurance
The curettage procedure is most often performed on a paid basis, but in some clinics it is possible to order it according to the compulsory medical insurance policy. More detailed information can be found in the organizations themselves by calling or reading the information on the website.
A curettage procedure is an effective way to clean your mouth. It allows you to regress caries and periodontal disease.
Toolkit Used
Open and closed curettage of periodontal pockets is carried out using mechanical, laser or ultrasonic instruments.The effectiveness of cleaning and the number of necessary sessions depend on the choice of tools.
Mechanical tools in dentistry
To clean the periodontal pockets are used:
- Rasps or files with a large number of faces needed to remove large particles of sediment.
- Chisels used to remove formations from the approximate surfaces of the teeth.
- Scalers:
- Crescent - are needed to remove the pre-gingival stone and plaque.
- Hoe-like - thanks to them it is possible, without injuring the bottom of the periodontal pocket, to remove dental deposits from the buccal, lingual, distal and medial surfaces.
- Curettes:
- Special with one cutting face - designed to work on the same tooth surface.
- Universal - have 2 cutting faces and can be used to clean subgingival deposits of all tooth surfaces.
- Zone-specific - designed to effectively clean a specific part of the tooth.
- Finishing - used to cleanse deep gingival pockets.
- Furcational - used to work in the root furcation zone.
- Dental excavators needed to remove massive deposits.
All tools have a similar structure: a handle, a working part and a shoulder. They can be made of metal, plastic or Teflon, and also have diamond spraying. The choice of a specific tool depends on the severity of the pathology and the age of the patient.
Plastic and Teflon
Plastic and Teflon tools are used to remove soft plaque in adults and children. For cleaning implants, special plastic products are used - implackers.
Diamond coated
Diamond coated tools are used if periodontal cleaning requires excision of the gums. They are characterized by the presence of a curved shoulder and a semicircular working part.
Tool sharpening
All instruments used for periodontal curettage of the gums and teeth should be sharpened and disinfected. For sharpening dental curettage instruments are used:
- Arkansas natural stone used regularly;
- synthetic stone India, necessary for processing a blunt tool;
- ceramic stone;
- composite stone used to sharpen heavily worn parts.
To check the quality of sharpening tools in dentistry, a simple plastic stick is used. A properly sharpened tool removes microscopic chips from it, and does not slip on the surface.
Careful sharpening of the instruments is performed before each curettage procedure, ensuring its high efficiency.
Ultrasound in Periodontics
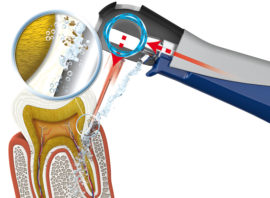 Ultrasound is most commonly used to remove deposits from periodontal gingival pockets., since it allows you to do the procedure:
Ultrasound is most commonly used to remove deposits from periodontal gingival pockets., since it allows you to do the procedure:
- painless;
- fast;
- as efficient as possible.
Varieties of procedure
In modern dentistry, there are 2 main types of curettage: open and closed. Outdoor is made in the most severe cases. Most often, during this procedure, you have to cut the gum. Closed is indicated during medical whitening of teeth or during their cleaning from tartar. The duration of all varieties of the procedure is 2-3 hours.
Flap excision surgery
Patchwork curettage of the gingival pockets involves cleaning the deep surfaces of the gums and brushing the teeth, including their roots. After the operation, materials that stimulate the growth and development of tissues can be used in order to restore them as soon as possible.
During the procedure, the periosteal surface of the gum is cut out, after which all soft and internal tissues are carefully processed. In the postoperative period, the patient needs increased control over the state of the gums, since sometimes after curettage the necks of the teeth are exposed, the structure of the alveolar processes changes, or the sensitivity of the dentin increases.
Laser curettage of periodontal pockets
Laser curettage is performed by introducing a special laser device under the gum. The laser acts on the periodontal cavity, coagulating the proliferation of connective tissue and killing pathogens. After this procedure, the treated area is covered with special antiseptic agents. The laser is usually prescribed for mild pathologies.
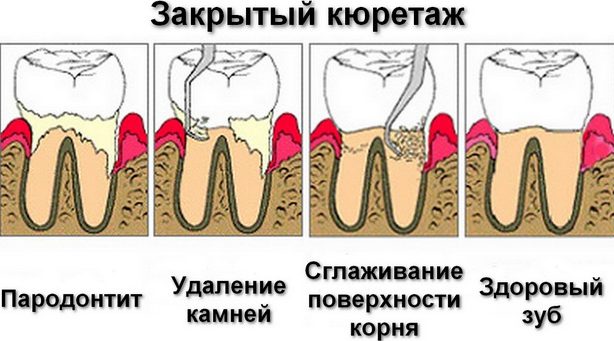
Closed curettage of periodontal pockets
A closed curettage procedure is called that way because it is performed blindly - the dentist does not see the problem area. This method of cleaning periodontal pockets is used only in the presence of mild pathologies.
Stages of closed curettage:
- The introduction of a local anesthetic.
- Cleaning the walls of the teeth from hard plaque.
- Scraping granulation.
- Cleaning periodontal pockets with an antiseptic.
- Apply a protective dressing to the gums with healing components.
For several hours after the completion of the closed curettage session, the patient is contraindicated in eating and drinking. Then, within a week, he should regularly gargle with antiseptic drugs.
More information about the closed curettage of periodontal pockets is described in the video:
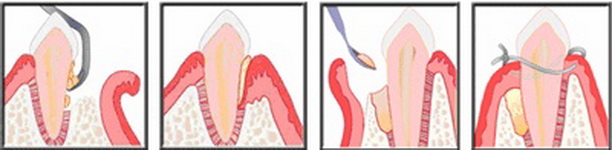
Open curettage of periodontal pockets
Open curettage is a full-fledged surgical operation performed with a pocket depth of more than 5 mm. In this case, a good overview of the pathological site is required, and therefore gum tissue is excised.
A few days before the curettage, a person is prescribed medication with anti-inflammatory drugs, as well as splinting of mobile dental units.
During one open curettage session, only 4-6 teeth pockets are cleaned at a time. Stages of the procedure:
- Sensing periodontal pockets to measure their depth.
- Application of anesthetic gel to the gums.
- Anesthesia of all teeth to be treated.
- The product of a horizontal incision of the gums and removal of the flap.
- Curettage of the walls of the holes and teeth.
- Grinding the walls with a milling cutter.
- Antiseptic processing of the operation site.
- Application to the wound surface of drugs that stimulate healing and osteosynthesis.
- Suturing.
After the operation, the patient is prescribed an antiseptic mouth rinse. With high sensitivity of enamel, anesthetics are indicated.
Read more about the open curettage of periodontal pockets in the video: