Conduction anesthesia in dentistry - what is it, types
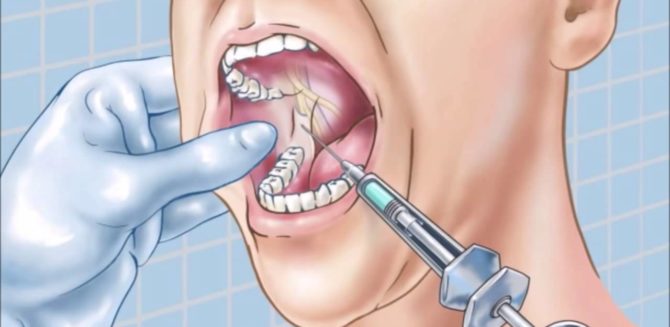
Conduction anesthesia has occupied a special place in dentistry. She is the most popular option for local anesthesia. The procedure is used for both simple and complex dental treatment.
Content
What is conduction anesthesia
Conduction anesthesia differs from other methods of regional anesthesia in that it blocks the work of nerves in a certain area. It is introduced into the body by injection into the part of the oral cavity where treatment will be carried out. Sometimes an injection is made into the nerve itself, thereby ensuring its complete shutdown for a while.
This type of local anesthesia has many advantages:
- It does not affect the nervous system from the side of the brain, therefore it does not entail consequences associated with its work.
- The action of one injection can last for 6-8 hours, so this method of anesthesia is used even with complex surgical intervention.
- Anesthetic acts quickly enough, so treatment can be started immediately.
- Conduction anesthesia is used even in pediatric dentistry.
- Such anesthesia has been available for quite some time, so today it is used even in the smallest clinics.
Of the shortcomings of conduction local anesthesia, only a slight pain from the injection itself can be noted. If the injection is given to children, then a freezing gel is applied to their gums.
Contraindications to conduction anesthesia
Conductor local anesthesia is a fairly safe method of pain relief, but even it has contraindications, among which:
- Allergy to the individual components of the anesthetic. Contraindication can be circumvented by simply replacing the solution or using another method of freezing nerve endings.
- Serious disturbances in the cardiovascular system. First of all, this group of contraindications includes heart attacks and strokes.
- Diabetes mellitus, especially the first type.
- Any abnormalities in the endocrine system.
In addition to the absolute, there are relative contraindications. For example, infectious diseases. If available, the dentist simply reschedules the date of the procedure to a more favorable time.
Types of Anesthesia
Conduction anesthesia is so popular in dentistry due to the fact that with its help you can only act on a separate area of the nervous system. Based on the injection site, this type of anesthesia can be divided into the following varieties:
- mandibular;
- torusal;
- mental;
- tubular;
- incisor;
- palatine.
Incisor
Incisional anesthesia is necessary when treating teeth in the smile area. It allows you to disable the nerves in the front of the upper jaw.
Incisional regional anesthesia can be extraoral and intraoral. In the first case, the specialist makes an injection into the nasolabial cavity, the syringe itself is inserted into the nostril. In the second, an injection is made into a small depression behind the incisors.
When using incisive anesthesia, the risk of bleeding in the injection area is greatly increased. If you follow the rules of hygiene and protect the damaged area from bacteria, there will be no consequences.
Heavenly
Palatine conduction anesthesia is used in serious operations. Injection is done near the line connecting the soft and hard palate.As a result, anesthesia of a large area of the upper jaw occurs, several nerves are turned off at once.
Usually, after application of palatine anesthesia, prosthetics, bone tissue in the alveolar bone, or implantation are performed.
Infraorbital
Infraorbital analgesia is used to treat fangs, anterior incisors, and premolars. It allows you to disable peripheral branches of the infraorbital nerve. Such local anesthesia can be extraoral and intraoral. In the first case, the drug is administered intra-channel, an injection is made in the immediate vicinity of the nerve. In the second, the injection is introduced into the crease, which is located between the central and lateral incisors.
This option of anesthesia is the safest, since it does not affect the nerves themselves - the drug is injected near them.
Mandibular
Mandibular regional anesthesia is used to restore the teeth of the lower jaw. The method is necessary to disconnect the lower tracheal nerve.
Technique for the administration of an anesthetic drug:
- An anesthetic is injected into the lower jaw, in an area that is 1 cm deeper than the wisdom teeth. The needle penetrates the soft tissue to touch the bone.
- The tool is injected directly into the base of the lower jaw, in the very middle. This method of administering an anesthetic helps to almost completely anesthetize the lower part of the face by disconnecting several nerves at once. Since the method can be dangerous if used incorrectly, they resort to it only in cases where other methods of pain relief are not available.
Torusal
With the torus form of conduction anesthesia, the drug penetrates the mandibular roller. The method is safe for the patient and is used before complex treatment, as it allows to anesthetize most of the lower area of the face.
Of the disadvantages of torusal anesthesia, it is worth noting hematomas, which almost always form after freezing nerves in this area. The fact is that an injection is made into soft tissues, which are penetrated by blood vessels and nerves.
Mental
With mental anesthesia, nerve impulses in the premolar region, incisors, lingual surface of the jaw, chin and lower lip are blocked. Therefore, this technique of introducing local anesthesia is used to treat precisely these parts of the jaw.
An injection is made into the chin hole near the base of the nerve trunk. It is located behind the lower lip in the area between the 4th and 5th teeth. The needle is inserted all the way to the bone, so mental regional injection is very difficult to tolerate.
Tubular
Local tuberculosis is used to anesthetize the posterior region of the lower jaw. It is usually used in the complex and simple treatment of chewing teeth and when removing eights.
Depending on the injection site, two techniques for carrying out tubercular anesthesia are distinguished:
- The drug is injected into the cheek-alveolar ridge. It is located on the side of the nose, near the crease, which usually forms with a broad smile. Before the injection, the specialist clamps the soft tissues to accurately get the needle into the desired nerve.
- The tool is injected into the area under the second molar. Before this, you need to fix the mouth and lips well so that they do not interfere with the injection.
Conduction anesthesia is an anesthesia technique used in dentistry to treat all teeth. In the vast majority of cases, specialists choose this particular option of local anesthesia. Refusal from it can only be associated with an allergy to certain components of the drug.