External and internal structure of human teeth: description, diagram, sectional photo
A person’s teeth are necessary for grinding food and have a unique structure that ensures the fulfillment of this function. They are classified into several groups - incisors, fangs, premolars and molars. This division is due to the features in their anatomy, purpose and teething - all of this will be discussed in the article.
Content
Teeth formation, their quantity and names
Teeth are formed in the prenatal period. This process is called odontogenesis and begins from the second month of pregnancy. By the 4th month we can talk about the anatomical structure, biochemical composition and histological structure of human teeth.
How many teeth do children and adults have, names
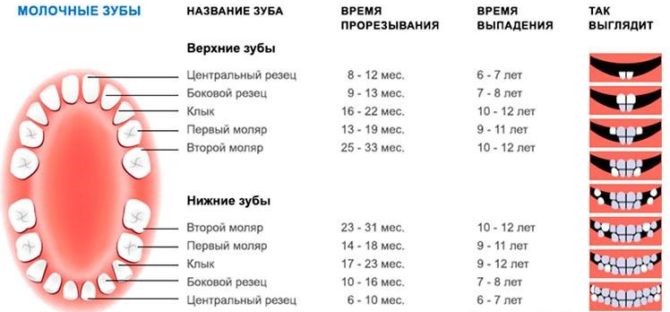
Children have 20 milk teeth, and in adults 28 or 32 molars, depending on the presence of wisdom teeth, which do not erupt in all. According to statistics, the formation of permanent teeth is completed by 25 years.
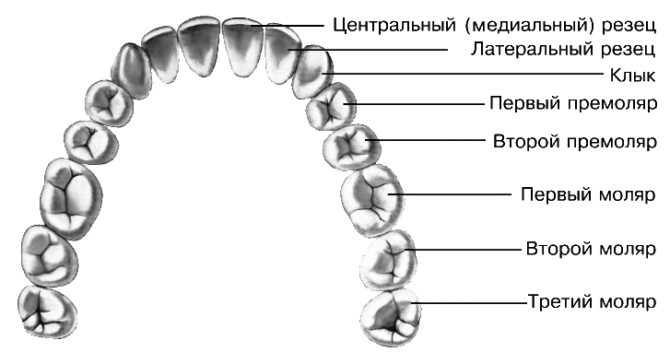
A tooth is the only human organ incapable of independent regeneration. To indicate each dental unit in dentistry, the oral cavity is conventionally divided into 4 segments: the left and right sides of the upper and lower jaw. All segments are symmetrical and include:
- two incisors;
- one fang;
- two premolar or small chewing teeth;
- three molars or large chewing teeth.
For life, each person has one change of teeth. By the age of 2.5 years, a milk bite is formed in children, consisting of 20 dental units. At the age of 6 years, the molar teeth are gradually replaced by indigenous ones, the process of their replacement ends by 11 years.
Dentistry in dentistry
To simplify the designation of dental units, dentists use a numerical term rather than their full name. Each individual tooth is assigned its own number in the sequence from 1 to 8. The number 1 denotes the central incisor, 8 - the wisdom tooth or figure eight.
In the patient's card, it is customary to indicate the serial number of the tooth with an Arabic numeral, and then the side (left or right) and belonging to the lower or upper jaw. To date, there are many tooth naming systems, but the most popular in Russia remains numerical.
When closing the jaws, the upper dentition should overlap part of the lower. If the bite is correct, the lower crowns are hidden under the upper by ⅓. Disturbed bite affects chewing function and aesthetics.
Classification, purpose of teeth and the structure of their root system
All teeth differ in appearance and purpose. Depending on the location and functional load, there are:
- The incisors are the front teeth. There are a total of 8, 4 on each jaw. With their help, biting and cutting solid food is realized.
- Fangs. The origin of the term "fangs" is associated with their similarity with the teeth of predatory animals. The number of fangs - 4 pieces, 2 on each jaw.
- Premolars. There are 8 premolars in the adult's mouth, the first four are located on the upper jaw, the second on the lower.They perform a chewing function.
- Molars. Total quantities - 8 pieces, are responsible for chewing food.
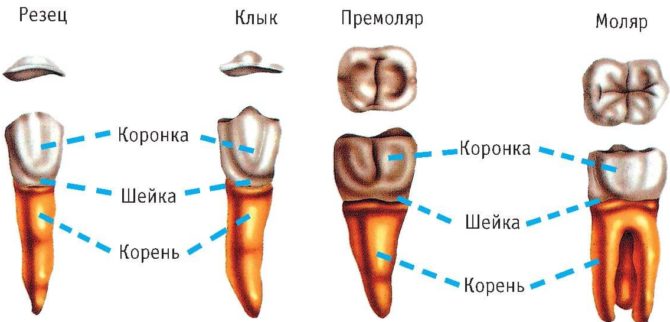
Forms of crowns and roots of incisors
Cutters are distinguished by the presence of a flat, chisel-shaped crown with pointed cutting edges. The largest sizes reach two central incisors of the upper jaw.
Lateral incisors of the lower jaw are larger than those located on top. All teeth of this species are united by the presence of one root of a flat, conical shape.
Forms of crowns and fang roots
The longest roots among all human teeth have fangs. Their task is to cut food into small components.
From the side of the tongue, a groove passes, dividing the tooth crown into 2 unequal parts. The shape of the crown is conical. And its edge is a single, clearly defined tubercle.
Shapes of crowns and roots of premolars
Premolars perform a chewing function. The first upper molar tooth has a prismatic shape, and from the cheek side it is rounded. The cutting surface is represented by volumetric rollers, between which there are wide natural recesses. The root is forked and flattened.
The main feature of the second premolar is the root system. It is distinguished by its conical shape and the presence of slight compression from the frontal side of the root.
The first premolar of the lower jaw has a rounded shape and two tubercles as a cutting base. The only root is flattened.
The second lower premolar is larger than the first and upper. Its contact surface is represented by two large tubercles, separated by natural recesses in the shape of a horseshoe.
Forms of crowns and roots of molars
The first upper molar is the largest tooth. It has a rectangular crown. The root system consists of three parts - one root in the center, the rest on the sides.
The second molars of both jaws are characterized by a square shape and more modest sizes. The first molar of the lower jaw has two roots and five tubercles on the crown.
Third molars or wisdom teeth are missing from many. They look the same as the second molars. The main difference lies in their root system - it is curved, with a large number of roots (up to five). The final formation of the roots of the eighth tooth occurs at the age of 24 years.
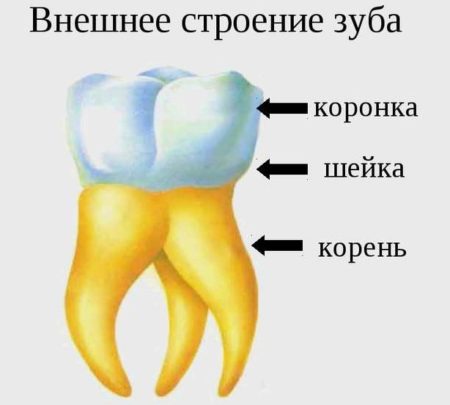
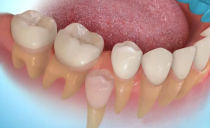
Anatomical structure of teeth with pictures
External anatomical structure of a human tooth:
- A crown is a visible area covered with enamel - the hardest part of a tooth. The surface layer has a protective function and is designed to preserve dentin.
- The root part is a complex of nerve fibers, arteries and veins, providing nutrition and innervation of the tooth. The second root function is retention.
- The neck is the area between the root and the crown, which performs a connecting function. It differs in a narrowed form.
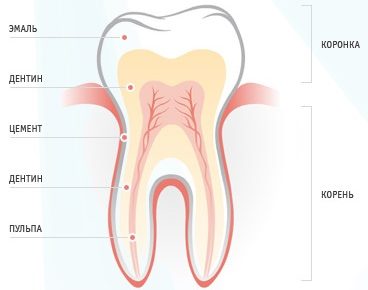
How is a human tooth at the tissue level
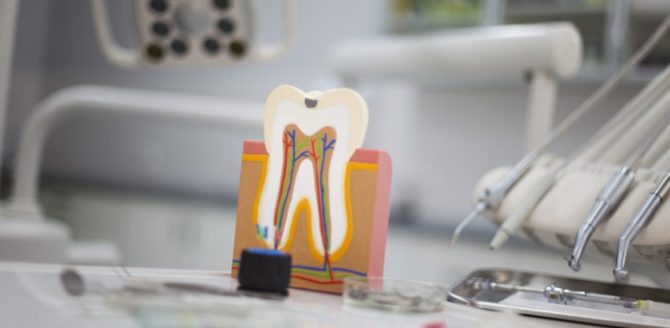
All human teeth have a similar internal structure. The diagram below shows all the dental layers - enamel, dentin, cement, pulp.
Enamel covers the teeth like a case and accounts for 25% of the total mass of all dental tissues. The hardness and strength of this layer of the tooth provides a high content of minerals - 397 kg / mm
The composition of the enamel layer includes:
- minerals - 96%;
- organic matter - 1.2%;
- liquid, water - 2.3%.
The enamel is covered with an outer shell - a cuticle, which covers the chewing surface of the tooth. Most of the tooth is dentin, located just below the enamel. It has less strength, its hardness is 58.9 kg / mm.
Cement - covers the root part and in most respects is similar to bone tissue. Two types of cement are distinguished depending on the type of structure:
- cell-free or primary - consists of collagen fibers;
- cellular or secondary - the composition includes cementoblasts.
The inner tooth cavity is pulp - soft tissue, including:
- numerous nerves;
- blood vessels;
- connective tissue.
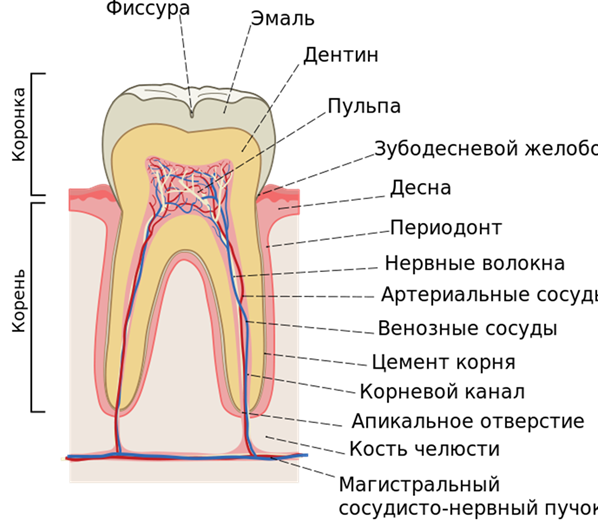
The structure of the tooth in the context
Despite the differences in the purpose and structure of the root system, all teeth have the same internal structure:
- Enamel. A very hard surface layer that protects teeth from environmental influences. It is designed as a structure of glued prisms. Due to the large number of mineral salts in the composition, enamel is the most durable tissue in the human body. Its main task is to preserve the dentin crowns. The presence of pellicules ensured tissue resistance to acid.
- Dentine. It consists of coarse fiber fabric, which is based on collagen fiber. It is similar in structure to a porous bone. Two types of dentin are distinguished: superficial and internal. The first is characterized by a higher density and prevents the infection from entering the tooth cavity.
- Cement. Consists of collagen fibers saturated with limestone salts. Layer thickness - from 50 to 150 microns depending on location. Two types of cement are distinguished - cellular and acellular.
- Cavity. It has an identical crown shape and is located under the dentin. The entire area of the cavity is filled with pulp - a type of tissue responsible for the nutrition of the tooth and performing a connective function. The presence of blood and lymph vessels ensures high sensitivity of the pulp.
The structure of milk and molars - differences
The posterior and anterior temporary and permanent teeth of a person undergo changes in their structure throughout their lives. But, despite the difference in quantity, they have similar functions and appearance. The main difference between milk teeth and molars is the size - children's teeth are smaller than adults.
Other differences include the following:
- In childhood, there are no premolars.
- The roots and crowns of molars are large.
- Milk teeth have a white-blue hue, indigenous - yellow.
- Milk teeth are more prone to caries, since their protective layers - enamel and dentin - contain a small amount of minerals.
- Most of the teeth of babies are pulp, which increases the risk of pain.
- In babies, the tooth roots have a more round shape.
- The first roots are destroyed and absorbed during the change of the milk dentition to a permanent one.
- Children have fewer teeth, due to the small size of the jaw arch.
The first teeth are characterized by a not very long and not too well-developed root system. A similar structure facilitates the process of changing milk teeth to molars.
Throughout life, it is necessary to care for the oral cavity. The negative state of deciduous teeth can affect the health of indigenous. Compliance with simple hygiene rules will ensure the preservation of a beautiful smile for many years.
Dental Care Rules
To maintain a snow-white smile and the health of the dentition, it is necessary to regularly take care of the cleanliness of the oral cavity. How many times a day to brush your teeth and what devices are better to use for this, explain the dentists during preventive examinations. The modern market for dental products offers customers a wide selection of hygiene products and devices, it remains to make the right choice.
Experts recommend brushing your teeth at least twice a day. After each meal, rinse your mouth with a pharmaceutical rinse or plain water.
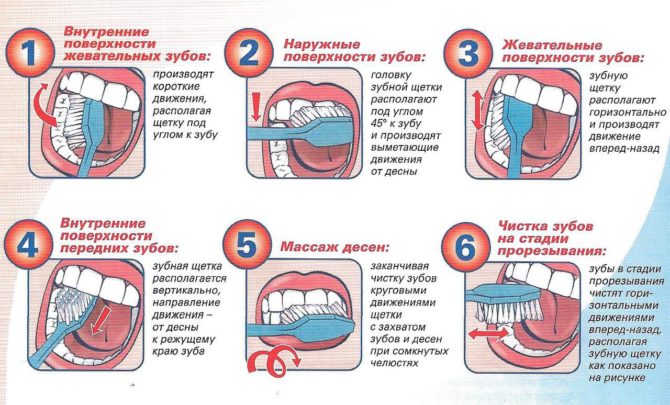
Dentists distinguish three types of brushing:
- Tough. Suitable only for holders of healthy gums. In a circular motion, they treat the surface of the teeth of the lower and upper jaws. They recommend starting the procedure with the upper teeth.
- Universal.The brush holds the floor at an angle of 45 degrees to the work surface. The movements should be smooth, the direction from the gum to the cutting part. They recommend starting the procedure from the outside of the dentition, treating two teeth in each zone.
- Berezhnaya. It requires special care when touching the brush to the gum. The jaw closes and repeat vertical movements from the gums down. The procedure is recommended to begin with the treatment of the external tooth surface.
It is important to choose the right toothbrush. When choosing it, the following parameters should be considered:
- Rigidity. For babies and adults with gum disease, during pregnancy and lactation, with bleeding gums, in the presence of diabetes, it is recommended to use very soft brushes. Brushes with medium hard bristles are suitable for people with a relatively healthy dentition. Hard bristle brushes for smokers and coffee lovers. Brushes with very hard bristles are designed for cleaning bracket systems and prostheses.
- Magnitude. The head of the brush should cover 3-4 teeth.
- Form. The brush with a round head with rounded edges is universal.
Subject to proper storage, a toothbrush is replaced at least once every three months. The brush should be in open space, not in the case. After each cleaning, it must be thoroughly washed.
Additionally, you should choose a toothpaste, mouthwash and dental floss. When choosing these tools and devices are guided by individual characteristics in the anatomy of the dentition and the structure of the teeth.
Proper hygiene of the oral cavity will help to maintain healthy teeth and a snow-white smile.