What is periodontal disease: causes, stages of development and treatment
Periodontal disease - the causes and treatment of such a pathology are not familiar to many, because it occurs only in 3-10% of people. This the disease affects gum tissue, and has been developing over the years. By name, it can be confused with periodontitis, but this ailment is characterized by the presence of inflammation, which is not present with periodontal disease.
The consequences of the disease are very serious, and everything is complicated by the asymptomatic course in the initial stages - the patient notices the disease when she has already managed to cause significant harm to his teeth.
Content
The essence of pathology
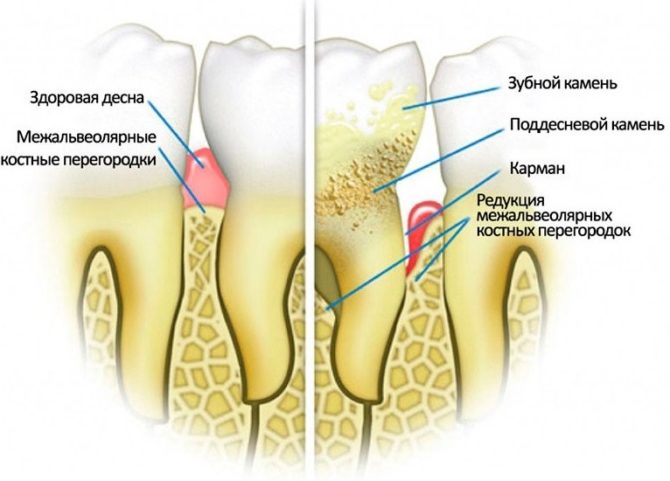
A tooth disease such as periodontal disease begins with dystrophic changes in the tissues of the dentition. Pathological processes arise due to circulatory disorders and vital functions of cells: their nutrition and respiration. As a result, the cells die, and the basic periodontal structures are destroyed.
Dystrophic changes lead to a decrease in the partitions between the teeth, and the tooth roots lose contact with the jaw alveoli as the disease progresses and become exposed - a periodontal pocket is formed. With the progression of the disease, the teeth become loose and fall out. Other complications may occur.
Periodontal disease: causes
It is not always possible to find out exactly what causes periodontal disease. But there is a list of factors that are predisposing for dystrophic changes in the jaw:
- Hereditary predisposition.
- Atherosclerotic changes in blood vessels that impede normal blood supply to tissues.
- Hypertension
- Connective tissue diseases that contribute to dystrophic changes in periodontal pockets, problems with immunity and metabolism.
- Problems with the gastrointestinal tract.
- Vitamin deficiency.
- The negative impact of infections developing in periodontal tissues.
- Non-compliance with the rules of oral hygiene with the subsequent formation of hard tartar near the necks of the teeth.
- Injuries to the oral cavity.
- Exposure to addictions.
- Neurological diseases.
- Incorrect bite, which creates strong pressure on the gums.
- Enamel damage.
- Teeth grinding in a dream.
- Tooth cyst.
Factors that act on the teeth themselves are called local. These include injuries, the presence of pathogenic microflora in the mouth, pathology of the bite. General factors - those deviations in the body systems that affect the development of the disease indirectly.
This is an approximate list of probable reasons, which can be supplemented. To find out what causes periodontal disease is difficult, since several negative effects can provoke pathology at the same time.
Types of disease
Depending on the area of bone tissue damage, the nature of the course of the pathology, its main forms are distinguished:
- Localized periodontal disease is a disease in which only a small area of the dentition is affected.
- Generalized - extensive damage to the teeth of the upper, lower or both jaws at once.
- Acute periodontal disease.
- Chronic periodontal disease.
Symptoms of the disease and degree of development
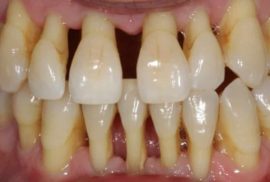
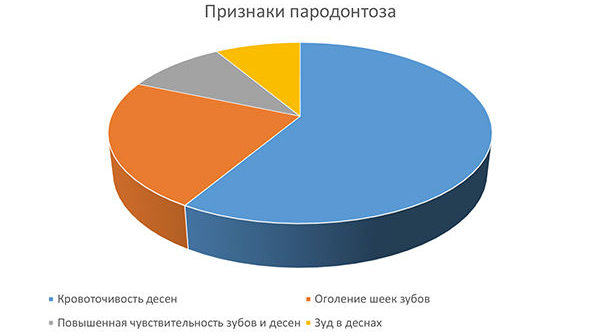
Due to the absence of a perceptible inflammatory process, the signs of periodontal disease appear even with the active destruction of the dentition. The initial stage of periodontal disease is almost asymptomatic, the patient may be disturbed by mild discomfort accompanied by itching of the gums and their bleeding.
The subsequent stages of the progression of the disease accompany the following main symptoms:
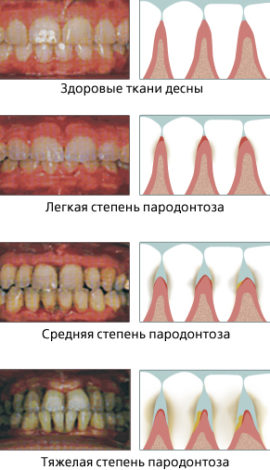 At the first stage, corresponding to a mild degree, the gums redden and slightly swell, tooth instability appears. The first degenerative symptoms are already visible on x-rays.
At the first stage, corresponding to a mild degree, the gums redden and slightly swell, tooth instability appears. The first degenerative symptoms are already visible on x-rays.- In the second stage, corresponding to an average degree, the signs of periodontal disease intensify. The gum takes a bluish tinge, it bleeds more often, noticeable gaps between the teeth and periodontal dredging up to 6 mm deep appear. Tooth mobility increases, purulent-serous discharge appears.
- At the third stage, corresponding to a severe degree of pathology, the tooth loosens in all directions, it can even be displaced by the tongue. The gum is sensitive to hot, cold, sour food, omitted. The recess in which the tooth root is visible is enlarged by more than half a centimeter. Pus continues to stand out, difficulties arise when talking and chewing food.
- In the fourth stage, the cervix is exposed to more than 2/3 of the radix, covered with plaque of dental deposits. Due to pathological changes, the color of the mucous membrane becomes pasty, pus is secreted. The tooth is extremely mobile, in the x-ray it communicates with the apex of the bone.
Diagnosis of the disease
The initial phase of development proceeds either asymptomatically or with signs that do not cause severe discomfort to the patient. This leads to the fact that periodontal disease can only be determined at later stages.
If this disease is suspected, a thorough examination is carried out: checking the sensitivity and mobility of the patient's teeth. After that to establish a complete picture, an x-ray is prescribed, on which internal degenerative changes are visibleoccurring with periodontal disease.
Almost all patients with such manifestations fall into the hands of dentists, but an ordinary doctor does not treat periodontal disease. If this disease is suspected, he will refer the patient to another specialist - a periodontist, who can prescribe additional examinations: periodontal rheography, polarography to diagnose blood supply processes and oxygen supply to the jaw tissues.
Is Periodontal Disease Cured?
Modern methods of dentistry can correct many defects that are formed with such a disease, and improve the condition of the tissues of the jaw. Effective timely treatment stops the degenerative phenomena.
To heal teeth and stop periodontal disease is possible only if the patient goes to the doctors, noticing the first symptoms. In the later stages of the development of the disease, medical care is necessary, but its effectiveness will be lower.
Treatment methods
Modern methods of treatment of periodontal disease include a variety of approaches to normalize the blood supply to the dentition and its restoration:
- Removal of dental deposits is a necessary stage in therapy, since these formations provoke gum inflammation, are a place of accumulation of microorganisms and worsen the appearance of the dentition. Many dentists have special devices for cleaning. They painlessly eliminate deposits, but in advanced cases you have to spend a couple of hours on it.
- Remediation of the oral cavity is an essential component of therapy. It is necessary to cure tooth decay, perform the depulpation of teeth in which the neck and root are very bare, remove the teeth in which the decay began. If these problems are not eliminated, they will remain constant sources of germs and will provoke a further inflammatory purulent process, cause an unpleasant odor, and ruin the appearance.
- Physiotherapeutic treatment - the implementation of procedures aimed at normalizing blood circulation, restoring the nutrition of bone and soft tissue cells. Used electrophoresis with calcium gluconate, darsonvalization to reduce sensitivity. Manipulations are carried out after cleaning the dental plaque.
- Other procedures: restoration of blood circulation of the gums by vacuum, breathing with ionized air, laser treatment.
- Splinting with intensive tooth mobility.
- Drug therapy.
- Surgical intervention.
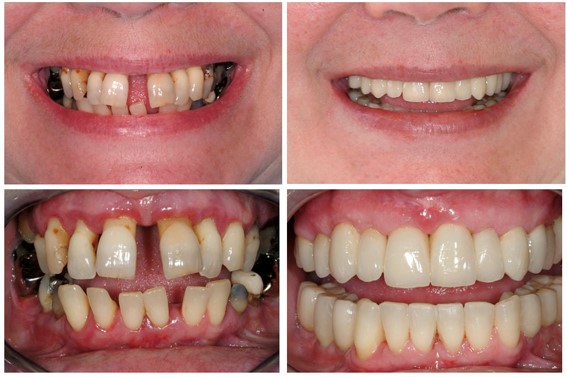
The initial symptoms of periodontal disease, as well as the effectiveness of treatment can be assessed by a photo of the teeth before and after therapy:
Medications
Drug therapy depends on the root cause of periodontal disease. If it is provoked by one of the common factors: systemic disease, changes in blood vessels during atherosclerosis and hypertension, metabolic problems, it is necessary to treat these pathologies.
It should be observed by a doctor and use the medications prescribed by him. Otherwise, in the treatment of dental periodontal disease, only external clinical manifestations will be eliminated, and internal degenerative changes will develop and provoke the destruction of the dentition.
After the doctor can identify the type of periodontal disease: acute or chronic, local or generalized - he will choose the optimal medication:
- Injections into the gums using drugs for blood supply, normalizing the nutrition and respiration of cells, accelerating regeneration. They make it possible to suspend the pathological process.
- Ointments for local exposure to affected areas of the oral cavity.
- Antibiotics. They are necessary for an acute form of pathology or during surgical treatment, prosthetics, and cleaning of dental plaque.
- Immunomodulators that can activate the body's defensive reactions and stop the destruction of tissues.
- General strengthening, vitamin preparations.
- Special toothpastes are agents that help relieve unpleasant symptoms, bleeding and pain, but cannot completely cure periodontal disease.
If complications arise, such as a cyst, fistula, or periodontitis, other medications may be needed.
Home treatment
The patient should use all the medicines prescribed to him: lubricate the gums with ointments, drink pills. If the patient does not understand how dangerous this ailment is, can not be cured, ignores the appointment, periodontal disease will progress and lead to irreversible consequences that are already difficult to treat.
 It is important that the patient knows how to properly care for the oral cavity. When making such a diagnosis, the attending physician should tell you which toothpastes should be used, how to brush your teeth so as not to harm the swollen gums. Brushing your teeth is extremely important for the prevention of this disease. Cleaning should be done at least twice a day, and after eating, you can rinse your mouth with water at room temperature to prevent plaque.
It is important that the patient knows how to properly care for the oral cavity. When making such a diagnosis, the attending physician should tell you which toothpastes should be used, how to brush your teeth so as not to harm the swollen gums. Brushing your teeth is extremely important for the prevention of this disease. Cleaning should be done at least twice a day, and after eating, you can rinse your mouth with water at room temperature to prevent plaque.
Folk remedies by which patients try to treat the disease at home are not able to provide effective help. You can use them as an auxiliary therapy, after consulting with your doctor about this.
Surgical treatment and prosthetics
The advanced stages of the disease are accompanied by the destruction of the interdental septa and the formation of deep periodontal pockets. These changes are no longer able to eliminate drug therapies or procedures. You can use surgical treatment, in which a special implant material is inserted, which provokes the growth of the alveolar process. As a result, the area of contact between the tooth root and the jaw alveolus increases.
Dental disease like periodontal disease, often leads to the loss of part of the dentition due to loosening or the need to remove in advanced cases. To restore its integrity, use various prostheses. In modern dental clinics, ceramic-metal bridges are installed that look natural.
Refusal of prosthetics can have negative consequences: the load on the remaining teeth increases, and they can also fall out after a while.
Having knowledge of periodontal disease, because of what this violation happens, you can avoid its occurrence. If certain clinical signs have already appeared, you should realize that this ailment is dangerous and can not be treated at home with the drugs of your choice. Only in dentistry can they determine the exact diagnosis and prescribe the correct therapy.