Inflammation of the oral mucosa: causes and treatment
Both in children and in adults various diseases associated with non-compliance with hygiene standards and with the general condition of the body can lead to inflammation of the gums and soft tissues lining the oral cavity. Each pathology is characterized by a special clinical picture. The duration of treatment depends on how timely and correctly diagnosed.
Content
Causes of soft tissue inflammation in the oral cavity
Inflammation of the mucous membrane of the gums, lips, tongue, palate and cheeks can trigger the following factors:
- Non-observance of hygiene rules. Both deficiency and excess hygiene can lead to irritation of the mucous membranes of the gums, cheeks, palate and tongue. Incorrect toothbrush selection can lead to the same consequences.
- Failure to comply with the rules of the primary processing of foods before eating.
- Long-term use of medications that lower salivation.
- Gastrointestinal diseases.
- The presence of worms.
- Anemia.
- Infections
- Injuries
- Dehydration due to prolonged diarrhea or vomiting.
- HIV infection.
- Poor dental treatment.
- Hypovitaminosis.
- Smoking.
- Tumors in the mouth.
- Hormonal changes in the body.
- Chemotherapy transferred.
Inflammatory diseases of the oral mucosa: a list with photos
Oral infectious diseases manifest themselves in different ways. The nature of the course of the inflammatory process depends on the pathogen and the localization of the lesion.
Stomatitis
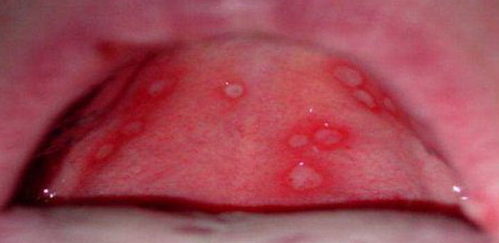
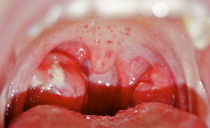
Stomatitis is an inflammation of the soft tissues in the oral cavity, which occurs as a reaction to an infectious agent against the background of a decrease in the efficiency of the immune system. Stomatitis is characterized by an increase in salivation, the appearance of putrid odor from the mouth and the formation of ulcers, erosion, aphthae on the mucous membrane of the lips, cheeks, palate, and tongue. The disease is not contagious.
The classification of stomatitis includes 4 main types of disease, each has a different clinical manifestation:
- Bacterial stomatitis. It occurs due to damage to the soft tissues of the oral cavity by streptococci and some other bacteria. It is accompanied by the appearance on the surface of the inflamed tissues of painful pustules, which, without proper treatment, are converted to ulcers.
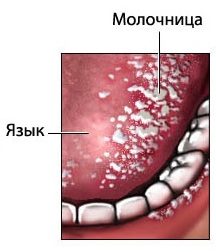
- Fungal stomatitis. It can develop with prolonged use of antibiotics or against a background of impaired immunity. The main symptom of the disease is a loose white coating covering the cheeks, tongue, palate, gums and lips. When removing curdled deposits, reddening spots, wounds and painful ulcers appear.
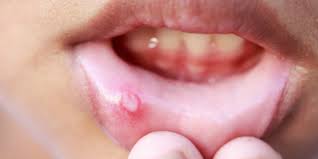
- Viral stomatitis. It is formed when the mucous membrane of the oral cavity is damaged by viral pathogens, most often by the herpes virus. Herpetic stomatitis is characterized by the formation of small vesicles with a clear liquid inside the lesion.
- Chemical stomatitis. It occurs with acid burns of the oral mucosa. It is manifested by the formation of gross erosive and ulcerative lesions that deform soft tissues, which eventually become scarred.
Gingivitis
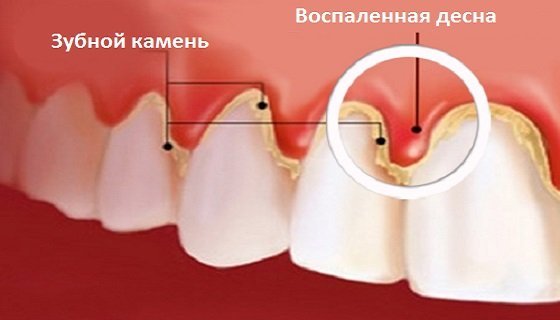
Gingivitis is an inflammation of the gums. The integrity of the gingival connection with this pathology is not violated. But if gingivitis is not cured in a timely manner, it will be converted to periodontitis, accompanied by damage to the alveolar process of the jaw and leading to tooth loss.
The main cause of gingivitis is tartar, the increased formation of which results in a lack of hygiene and the wrong choice of hygiene products and accessories. Therefore, the first step in the treatment of the disease is professional cleaning of tooth enamel, after which conservative treatment is prescribed.
Classification of types of gingivitis:
- Catarrhal (acute). It is characterized by severe redness, irritation and swelling of the gums, the formation of soft and hard deposits on tooth enamel. While brushing your teeth, bleeding gums may occur.
- Chronic. This form of the disease does not cause discomfort, therefore, only a dentist can detect it during the examination.
- Desquamative. Manifested by pronounced redness and lowering of the gums.
- Hyperplastic. It develops as a result of endocrine changes in the body, which affect pregnant women, adolescents and patients with diabetes mellitus. The main symptoms of the disease are swelling, itching, bleeding gums, purulent discharge, putrid breath.
- Simple marginal. Manifested by swelling and hyperemia of the gums, discomfort occurs during brushing and eating.
- Ulcerative. It is determined by severe ulceration of the gums. It is characterized by severe burning and bleeding gums.
- Atrophic. It is a chronic form of gingivitis, which reduces the volume of gingival tissue.
- Acute necrotizing. It develops with bacterial lesions of the gums amid a strong weakening of the immune system. Adults are less susceptible to the disease than children over six years old and adolescents. In addition to painful sensations, reddened swollen gums and necrotic plaque, this form of the disease is characterized by symptoms of general intoxication: nausea, weakness, dizziness.
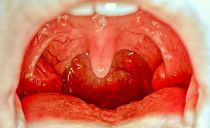
Erosion in the mouth
Erosion is a defective damage to the epithelium of the mucous membrane that forms when the vesicles are opened and the papules are destroyed in the cheeks, gums, tongue and throat. The formation of erosion is accompanied not only by many diseases of the oral cavity, but also by skin, infectious and somatic pathologies.
Diagnosis of erosion of the gums, tongue, cheeks, lips and palate is based on laboratory tests. The classification of erosive and ulcerative pathologies is very complex and requires a doctor's knowledge in many medical fields.
How to treat inflammation in the mouth
Regardless of the reasons why the soft tissues of the gums and oral cavity become inflamed, they are treated comprehensively. First of all, the doctor prescribes drugs to suppress the infection - antiviral or antibacterial. The most effective local antibiotics used for stomatitis are Metrogil and Chlorhexidine in the form of mouthwashes.
If a bacterial infection affects the whole body, or the activity of the pathogenic flora is very high, antibiotics are prescribed for the patient to be taken orally. Treatment with antibacterial tablets should be accompanied by the use of funds for the restoration of microflora: Linex, Bifidum.
If the disease is caused by a virus, antiviral drugs in tablets or ointments are prescribed to the patient. Depending on the type of pathogen, the therapeutic course may include taking Acyclovir, the use of Oxolinic or Bonaphthon ointment.
The second group of medicines used to treat inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity is represented by antiseptics with a pronounced antimicrobial effect. They are necessary in order to prevent the development of secondary infection due to the large number of pathogenic microflora in the oral cavity.Well proven gels Kholisal, Actovegin and Kamistad, as well as lozenges with eucalyptus extract.
Anesthetics are selected depending on the intensity and nature of the pain syndrome and the individual tolerance of the medication. Adult patients are most often prescribed:
- Anestezin for local application.
- Lidochor.
- Lidocaine in the form of a spray.
- Hexoral.
The complex of medicines for the treatment of diseases of the oral mucosa is completed by drugs that promote the healing of wounds and erosion. For this purpose, not only medications are used, but also folk remedies, characterized by a healing effect. To quickly heal the inflamed tissues of the oral cavity, dentists recommend doing every 2-3 hours applications and compresses with oil formulations. The most effective were shown:
- Propolis spray.
- Carotolin oil solution.
- Sea buckthorn oil.
The nuances of treating oral infectious diseases
In addition to prescribing medications, treatment of soft tissue inflammation in the oral cavity requires a list of recommendations.
Diet
The patient must adhere to the rules of clinical nutrition and exclude spicy, pepper and fatty foods from the diet, which cause irritation of the mucous membrane of the mouth and throat. You should completely abandon alcohol and smoking.
Inflammation of the soft tissues in the oral cavity can be a symptom of a weakening of the body's protective functions, therefore it is necessary to include in the diet products that enhance immunity: low-fat cottage cheese, boiled meat, fruits with a low acid content. In addition to the use of foods rich in macro and microelements, the strengthening of immune functions, the rapid regeneration of cells and the speedy healing of erosion and ulcers contributes to the intake of vitamin complexes.
Refusal to eat due to pain is unacceptable, especially in the treatment of young patients. If the mucous membrane of the gums, tongue, palate or cheeks is severely inflamed, and eating causes unbearable discomfort, you need to adjust the menu and include homogenized products with a neutral acid balance.
Mouth rinse
Antibacterial and soda solutions, decoctions of medicinal herbs help to relieve pain and help cleanse and heal wounds. Rinsing your mouth is an integral part of treating inflammation in your mouth. Gargle with a solution recommended by your doctor several times a day.
Timely examination by a dentist
In mild forms of stomatitis, outpatient treatment is prescribed, but every two days the patient should visit the dentist to monitor the condition of the oral cavity and timely correction of the treatment regimen.
Prevention of inflammatory processes in the mouth
To prevent inflammation of the oral mucosa, precautions must be observed:
- Exclude solid foods from the menu that can injure the tongue, cheeks, palate, and periodontium.
- Ensure thorough and regular brushing of the tongue and teeth.
- Every 6 months, come to the dentist for a routine examination.
- Timely treat dental, endocrine, neurological and other diseases.
- Maintain immunity. To do this, you need to eat well, do not overwork and get enough sleep regularly.
- In time to treat gastrointestinal diseases, which can cause the development of stomatitis.
- Do not take medications not approved by your doctor. Some drugs can trigger the development of stomatitis, so you can’t take drugs uncontrollably.
- Wash products thoroughly under running water or heat them.