Stomatitis: symptoms, causes, treatment and prevention
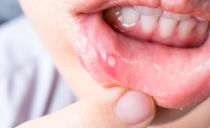
Stomatitis - inflammation of the oral mucosa, which manifests itself in the form of ulcers, erosions that affect the gums, palate, inner side of the lips, cheeks and / or tongue. It is very important to find out in time what stomatitis is and how to treat it so that this disease does not become chronic. To do this, you need to know the main causes and signs of stomatitis, as well as what stomatitis is and the procedure for its treatment.
Content
Causes
The saliva of the oral cavity protects the mucous membrane from various infections, so a healthy person does not know what stomatitis is, his symptoms appear only with weakened immunity. After the ingestion of pathogenic bacteria with food into the mouth, the healthy microflora is disturbed, resulting in specific ulcers.
Specialists identify several factors that can cause the disease:
- Injury. The oral mucosa can be damaged by solid food, a tooth fragment, when biting the skin while chewing, etc. In an ordinary person, such wounds heal on their own in a few days, but if the immune system is weakened, bacteria get into them and an ulcer forms.
- Oral and dental care products containing sodium lauryl sulfate. Many people who were often worried about severe stomatitis noted that after changing their usual toothpastes and cleaners to more gentle means, stomatitis in the mouth ceased to bother. This is due to the property of LSN to cause dehydration of the mucosa, as a result of which the oral cavity becomes more vulnerable to various irritants, including food acids.
- Emotional shock. Severe stress can cause ulceration.
- Malnutrition. An unbalanced diet can cause stomatitis in adults and young children. So, a deficiency of vitamins A, C, group B, as well as iron, zinc, selenium can cause this disease. Carbohydrate-rich foods increase the acidity of saliva, which can also cause inflammation in the mouth.
- Allergy. Allergic stomatitis appears due to an allergic reaction to food products, household chemicals, plant pollen, etc.
If the symptoms of stomatitis are accompanied by signs of allergy, you should first identify the allergen and completely exclude contact with it.
- Hormonal changes. Many women think for the first time what stomatitis is and how it can be treated precisely during pregnancy, and for some, exacerbation always begins on a certain day of the cycle, during menopause. This is due to hormonal fluctuations.
- Genetic predisposition. There are studies that have confirmed that the propensity for this disease is transmitted from parents to children.
- Bad habits. The use of alcohol-containing drinks and smoking leads to poisoning of the mucous membrane with toxins and disruption of the microflora of the oral cavity.
- Recent illness. A viral or infectious disease and the concomitant use of potent antibiotics weakens the immune system, as a result of which the mucosa does not cope with its task of protecting against various bacteria and viruses.
- Bacteria and viruses. Under normal conditions, pathogens do not cause any problems, however, in the presence of other provoking factors, viruses and bacteria can cause diseases of the oral mucosa.
Stomatitis: main signs
Before diagnosing stomatitis and prescribing its correct treatment, the attending physician should consider all the symptoms of the disease. Most often, in patients with stomatitis, the following symptoms are observed:
- First, a little redness appears in the oral cavity, later this place swells, swells, becomes painful, a burning sensation appears.
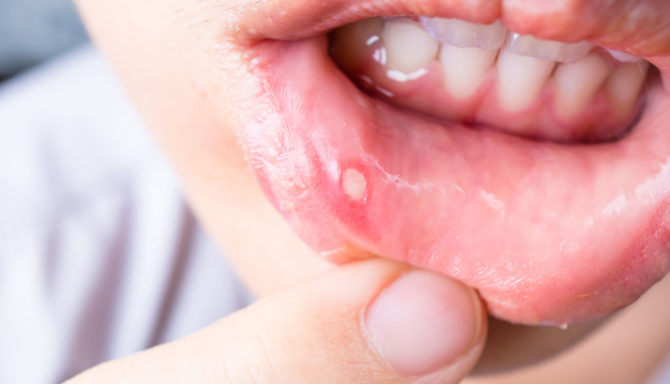
- If the inflammation is provoked by bacteria, soon a round or oval sore with smooth edges and an inflamed red halo in a circle will form at the site of the lesion. In the center of the sore, you can see a thin white film.
- In addition to the main sign - the appearance of a painful ulcer, ulcerative stomatitis is accompanied by increased salivation, bleeding gums, halitosis, and often due to severe pain, the motor activity of the tongue and lips is limited. The course of the disease can occur in acute or chronic form. Acute stomatitis is more difficult, and its treatment is rarely complete without taking antipyretic drugs, since it is often accompanied by an increase in body temperature up to 39 ° C and an increase in lymph nodes. If the cured stomatitis reappears after some time (relapse is observed), it is called chronic.
The duration of the disease with stomatitis is from 4 days to 2 weeks, this causes considerable discomfort to the patient. In order for the disease to pass as quickly and painlessly as possible, adequate treatment is required.
What is stomatitis: classification
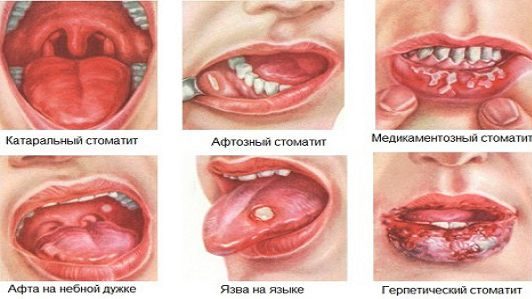
Before determining the type of stomatitis and prescribing its treatment, it is necessary to correctly identify its main signs. Stomatitis is classified according to pathogens:
- Fungal (thrush, candidal stomatitis). Most often occurs after a course of antibiotics: a specific white coating appears in the mouth, after elimination of which erosion can be seen. This type of disease is mainly affected by children, as there is not enough acid in their saliva that fights fungi. With thrush, there is a white coating in the mouth, the patient feels a burning sensation in the larynx and oral cavity).
- Viral (herpes, herpetic stomatitis). It is a consequence of the defeat of the Epstein-Barr virus or herpes simplex. Infection occurs from a virus carrier or a sick person by airborne droplets or by contact. The disease manifests itself quickly: first appears weakness, irritability, loss of appetite, the appearance of fever and swollen lymph nodes. Further, swelling, redness of the mucous membranes intensifies, bubbles appear, which subsequently open, forming surface erosion. Salivation increases, lips dry out and begin to crack.
- Bacterial. It develops as a result of exposure to streptococci and staphylococci, accompanied by the appearance of a purulent rash, which later opens, forming ulcers, erosive formations.
- Ray. Appears due to radiation sickness, chemo- or radiation therapy.
- Chemical. Ulcers form as a result of burns with acid or alkalis.
- Allergic. It occurs against the background of a general allergic reaction, manifests itself in the form of redness and white spots on the mucosa, vesicles, or spot hemorrhages.
Depending on the stage of development of the disease, stomatitis differs in symptoms, and appropriate treatment is prescribed. Three stages of inflammation are distinguished: catarrhal, ulcerative, aphthous stomatitis, this must be taken into account by everyone who is interested in what stomatitis is and how to treat it correctly.
How catarrhal stomatitis proceeds and the procedure for its treatment depends on the pathogen or the cause of the disease. Most often, such a disease manifests itself with a decrease in immunity, candidiasis, problems with the gastrointestinal tract, and worms. The catarrhal form is characterized by the appearance of burning, itching of the mucous membrane, impaired taste sensitivity, dryness and pain during eating.
The appearance of ulcers can be a consequence of a neglected catarrhal stage or stomach ulcer, food or domestic poisoning. In this case, the mucous membrane of the mouth is affected to the full depth, the lymph nodes increase, the temperature may increase. The patient complains of pain, which is greatly enhanced by chewing and even normal conversation, sore throat.
In children, ulcerative stomatitis is more difficult, and with its treatment it is worth paying attention to the prevalence of pathological changes.
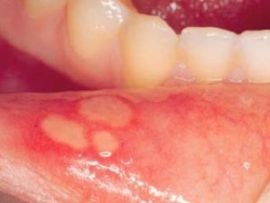
Aphthous stomatitis can be identified by sores (aphthae) up to 5 mm, covered with white or gray bloom, which first have the form of a bubble, but subsequently merge into one vast erosion area. The appearance of aphthae can be triggered by chronic diseases of the internal organs, it also occurs due to a neglected form of a viral, bacterial disease.
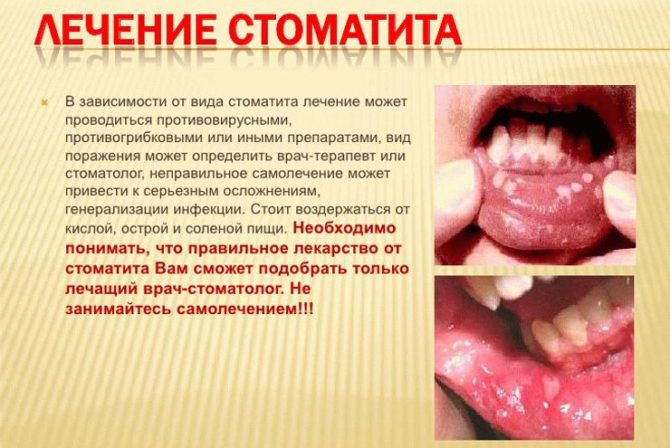
Stomatitis treatment
Many are interested in the question: "Is stomatitis treated?" In fact, stomatitis can be cured, and its treatment is not difficult. However, no doctor can guarantee that with the appearance of provoking factors in the future (decreased immunity, infection with a bacterial infection, etc.), the disease will not reappear.
The treatment includes the following activities:
- local oral disinfection;
- healing of existing wounds;
- removal of unpleasant pain;
- restoration of normal microflora and acidity of the oral mucosa;
- increase in general immunity.
The easiest form of the disease is catarrhal stomatitis and its treatment is carried out by the usual rinsing of the oral cavity using antibacterial and disinfecting drugs.
With ulcerative, it is also necessary to lubricate the wounds in the mouth for their speedy healing with antiseptic and wound healing agents. The doctor may recommend that the patient adhere to a special diet, exclude the intake of spicy, sweet, salty foods, as well as alcohol, you can not smoke. The food should be uniform, so ordinary soup should be replaced with mashed soup.
The most difficult to cure herpetic and candidal stomatitis, caused by viruses, and the treatment of such diseases is always accompanied by the use of antifungal and antiviral ointments. An illness caused by an allergic reaction can be cured by eliminating the source of allergies and taking antihistamines.
Treatment of stomatitis with folk remedies
In the initial stages, treatment can be done at home using the following means:
- Soda. A solution of soda (1 tsp. In a glass of water) must rinse your mouth throughout the day as often as possible.
- Hydrogen peroxide. In half a glass of water add 1 tsp. peroxide and rinse with this compound. Such rinses can be carried out for children only under the supervision of adults so that they do not swallow part of the liquid.
- Carrot juice. Raw carrot juice, when rinsed and consumed inside, effectively heals sores and saturates the body with useful vitamins.
It is advisable to be treated with 1: 1 juice diluted in water.
- Potassium permanganate. It is necessary to dissolve potassium permanganate in water before acquiring a light pink hue and use this composition to rinse every 2 hours.
- Daisies Pour chamomile flowers with pharmacy boiling water in a ratio of 20 g of flowers per 1 glass of liquid, let it brew. Use infusion to rinse.
- Calendula This tool can also be used to treat stomatitis in infants. 1 tbsp. l calendula flowers are poured with a glass of boiling water, insist for at least an hour. The oral cavity is wiped with a cotton swab dipped in the resulting infusion, 3 times a day.
Children's stomatitis
Children's stomatitis and its treatment is not much different from the disease that is observed in an adult.But parents should pay special attention to the hygiene of their child’s oral cavity, as well as to control the quality of their nutrition: offer the baby more seasonal vegetables and fruit, berries rich in vitamins and minerals. Also useful in moderate amounts are nuts, dairy products (fermented baked milk, kefir, yogurt).
Children of different ages are at risk for different types of stomatitis:
- From birth to three years, babies most often suffer from thrush or herpetic stomatitis.
- During teething, against the background of a general weakening of the body, any kind of disease can occur.
- Schoolchildren are more prone to aphthous and allergic stomatitis.
- Regardless of age, children often suffer from bacterial stomatitis (sometimes in severe form), which can occur as a result of burns, mechanical injury to the surface of the mucous membrane of the mouth and when the child does not follow basic hygiene rules (eats unwashed vegetables, fruits, pulls dirty objects in his mouth, etc.).
Probable complications
Timely diagnosis of stomatitis and its surgical treatment will help to avoid such complications:
- bleeding gums;
- tooth loss;
- lesions on the glands, tonsillitis;
- hoarseness, hoarseness of the voice, in the future - chronic laryngitis;
- genital candidiasis or general infection of the body (with fungal stomatitis).
Prevention
Many adults know what stomatitis is and how it is recommended to treat it during an exacerbation, but it is much easier to prevent its occurrence. To prevent a repeat or primary manifestation of stomatitis, it is necessary:
- wash hands frequently (every time after the street and before eating);
- visit the dentist on time for dental treatment and removal of tartar;
- monitor the condition of the gastrointestinal tract;
- adhere to the principles of healthy eating;
- choose the right oral care products (toothpaste, brush, floss, rinse aid).
If you have dentures, you should visit the dentist regularly to adjust them. People who smoke and often drink alcohol should give up their bad habits.
Allergy-prone people need to be especially selective about foods that can trigger an exacerbation. When the first signs of allergies appear, you must immediately start taking antihistamines.
Particular attention should be paid to strengthening the immune system, for this, the doctor can pick up good vitamins and minerals, do not neglect his recommendations on proper nutrition and lifestyle correction.
It is advisable to avoid stressful situations that can lead to weakened immunity and exacerbation of other chronic diseases, and then you won’t have to ask the question “What is stomatitis and how is it better to treat it?”.
Stomatitis is not a terrible disease, but very unpleasant. So that it does not enter a chronic form, it is necessary to diagnose and treat it in time.