Runny nose during teething in children: how to determine what’s on the teeth, how long it takes and how to treat
The appearance of the first incisors in infants is a new stage in their development, which mothers and fathers are looking forward to. However, many parents are unprepared for climbing teeth. Most often they are concerned about snot appearing during teething, as a runny nose makes it difficult for the child to breathe and can be perceived as a sign of a cold. In order to determine the course of treatment, it is first necessary to establish the true cause of nasal congestion.
Content
Reasons for a "runny nose"
Some parents believe that teething snot can appear in babies solely because of a viral disease. However, this assumption is erroneous - in the first year of life, the nose is blocked mainly for physiological reasons.
Anatomically, the oral and nasal cavities are located close to each other and have a common innervation. At the time when the tooth is cut, the blood circulation of the gums and the entire oral cavity increases, which contributes to the flow of blood to the nasal mucosa and stimulates the work of goblet cells, which produce mucus.
Joining an infection also causes a runny nose during teething; this process is caused by a decrease in the body's defenses. At the sixth month after birth, the antibodies that the newborn received in the womb and through breast milk disappear. This period coincides with the age when the first teeth are cut.
A simultaneous decrease in immunity and the appearance of an additional load on the body in the form of the formation of a chewing apparatus increases the risk of infection. As a result, babies can not only block their nose, but also appear lethargic, stable temperature, and sometimes cough.
If the baby’s temperature exceeds 38 ° C and lasts more than 2 days, the baby refuses to eat and cannot breathe freely through her nose, it is necessary to immediately consult a doctor.
Signs of teething
Each baby experiences the process of tooth growth in its own way: someone has strong pain, for others, the process of teething may not cause discomfort. However, in most cases, with active tooth growth, the behavior of the baby noticeably changes:
-
the child becomes moody;
- requires constant attention;
- refuses food;
- restlessly sleeping;
- pulls hard objects and hands into his mouth.
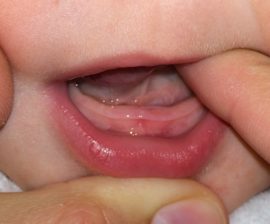
In addition to behavioral symptoms, parents can observe increased salivation, redness and swelling of the gums, cough, rapid bowel movements, hyperthermia, sneezing and runny nose. Symptoms usually last as long as a tooth erupts.
Trying to understand what worries the baby - tooth growth or an attached infection - you should pay attention to the nature of the symptoms. Coughing, fever, and snot arising from tooth growth differ from the symptoms that occur with infection and colds. If the child does not have a temperature, you can contact the dentistry. The dentist will not only determine whether the incisors begin to climb, but will also tell you after what approximate time they should be expected, advise suitable painkillers.
How to determine that a runny nose and snot are a reaction to teeth, not a cold
To determine whether the incisors are cut in the baby, or if his body is fighting infection, it is necessary to pay attention to body temperature. When teething, it should not exceed 37.5 ° C, and according to Dr. Komarovsky, a temperature of 38 ° C is acceptable.
It is also important to determine how much elevated temperature holds. With the growth of dental units, it should not last longer than 2-3 days, infectious diseases are characterized by an increase in temperature from 37 to 40 ° C and its duration of more than 3 days.
The nature of the cough is also different. During the process of teething, the cough is wet and rare, in case of infection - dry and frequent.
It is possible to determine that snot appeared due to tooth growth, both in their appearance and in the duration of the common cold:
| Sign | Teething process | Infection |
|---|---|---|
| Consistency | “Tooth snot” is watery, does not make breathing difficult and does not cause discomfort to infants. | Watery discharge gradually becomes viscous. During the day, they dry out and form crusts that make breathing difficult. |
| Colour | Slime has an exceptionally transparent color. | The initial stage of rhinitis is characterized by the release of transparent snot, which then becomes cloudy and yellow. When bacteria accumulate, the snot turns green. |
| Abundance | "Snot on the teeth" go periodically throughout the day, mildly. | Discharge does not flow from the nose, nasal congestion occurs. Snot need to blow out. |
| Duration | Stuff up the nose can be from 3 to 5 days. | Rhinitis lasts 10-14 days. |
Parents should focus on how long a runny nose during teething, since the symptoms of infectious rhinitis in the initial stages are similar to signs of inflammation of the nasal mucosa for physiological reasons.
How and how to treat a runny nose and snot in a child with teething
A runny nose that occurs in babies with the appearance of teeth often does not require medical treatment. To help babies survive the teething process, it is necessary:
- Periodically clear the nasal cavity of mucus using an aspirator. This should be done as the snot accumulates in the nose.
- Rinse the spout with herbal decoctions or saline.
- Monitor the water balance of the child - the baby should drink a lot of warm water.
- Humidify the air in the room. This can be done either with a humidifier or improvised means (a basin with water, raw linen).
- Ventilate the room at least 4 times a day for 15 minutes.
- Ensure that the baby abides by bed rest.
Such folk remedies help get rid of nasal congestion:
- steam inhalation with medicinal herbs, a solution of salt or soda;
- instillation of diluted aloe juice into the nasal cavity;
- mustard foot baths.
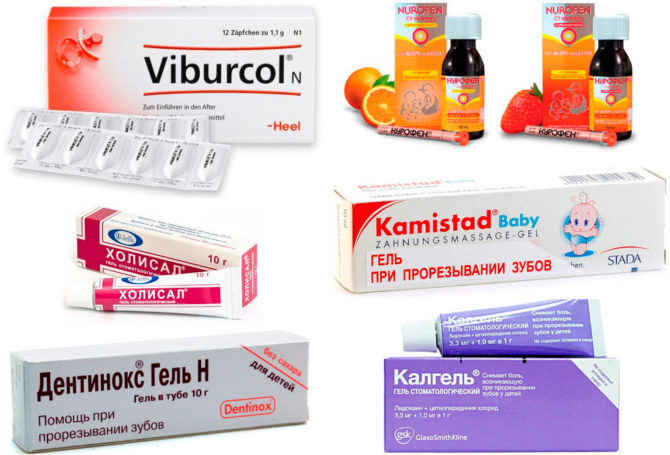
Dr. Komarovsky argues that when cutting teeth and the appearance of snot, it is first necessary to treat swollen gums. To do this, you can use chilled teether, anti-inflammatory gels and antiseptics.
If nasal congestion is strong and makes breathing difficult, and the “tooth snot” is green, nasal drops are acceptable. Many parents try to cure such a runny nose with vasoconstrictors, but their use can turn into an addiction to the body and constant swelling of the nose. Therefore, only a doctor should decide how and with what to treat snot when teething.
Prevention of Infectious Rhinitis
During the first year of life, about 8-10 dental units grow in infants. This trend often leads to a weakening of the immune system and the constant occurrence of infectious rhinitis. Therefore, a cold in a child with teething is better to prevent than to treat it and other symptoms that occur during complications.
To strengthen the immunity of the baby, it is often necessary to walk with him in the fresh air.Dr. Komarovsky believes that a month-old baby and older children should be on the street or on the open balcony throughout the day, excluding the time for eating.
A balanced baby diet also helps prevent rhinitis. If, during teething, the baby is breast-fed, weaning it from the chest is not recommended. Baby on artificial feeding is advised not to transfer to complementary foods until 6 months of age.
Preventive measures such as:
- hardening;
- airing and maintaining cleanliness in the room;
- humidification in the room;
- strict adherence to the daily routine.
Compliance with preventive rules will help not only strengthen the immune system of the crumbs, but also facilitate the process of teething.